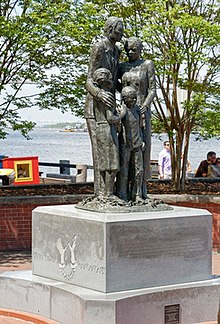 The monument in 2015 The monument in 2015 | |
| 32°04′54″N 81°05′27″W / 32.081711°N 81.090884°W / 32.081711; -81.090884 | |
| Location | River Street, Savannah, Georgia, United States |
|---|---|
| Designer | Dorothy Spradley |
| Material | Bronze Granite (pedestal) |
| Height | 11 feet (3.4 m) |
| Dedicated date | July 27, 2002 |
| Dedicated to | African Americans |
The African-American Monument is a public monument in Savannah, Georgia, United States, dedicated in 2002. Located near River Street along the city's waterfront with the Savannah River, the monument commemorates African Americans in the city and highlights the "invisible story of the Trans Atlantic slave trade". The monument consists of four statues depicting an African American family atop a granite pedestal.
History
Efforts towards erecting the monument was spearheaded by Abigail Jordan, an African American activist from the city who spent several decades trying to get the monument created. According to a 2001 article in the Los Angeles Times, "none of the more than 40 plaques, pillars and statues" in the city paid tribute to African Americans. In 1998, the city's Historic Site and Monument Commission approved the monument and passed the proposal on to the city council to vote on it.
In January 2001, the city council approved the monument, but deferred action on a decision regarding a quote by Maya Angelou that would appear on the base of the monument. The proposed quote would have read, in part, "We lay back to belly in the holds of the slave ships in each others’ excrement and urine together, sometimes died together, and our lifeless bodies thrown overboard together." At the time, the quote was considered controversial in part due to the monument's proposed location along the Savannah River promenade, which was one of the biggest tourist attractions in the city. Jordan claimed that she had fought back against the insistences of some city council members who proposed placing the monument at a church rather than the promenade. David Jones, an African American city council member at the time, had the following to say about the quote: “Maya Angelou’s description was a little far out. I myself wouldn’t want to be reminded of that every time I look at it. History . . . can hurt.” Savannah Mayor Floyd Adams Jr. was also opposed to the quote. In January 2002, Angelou submitted to the city council the following addition to the quote: "Today, we are standing up together, with faith and even some joy." This amended version of the inscription was unanimously agreed upon by the city council in May of that year.
In total, the cost of the monument was $350,000, with $30,000 provided by the city to prepare the site and the rest of the money raised through donations. The monument was sculpted by Dorothy Radford Spradley (born 1946). The monument was dedicated on July 27, 2002. In July 2019, a plaque was added to the base of the monument describing the efforts of Abigail Jordan to erect the monument.
Design
The monument, which stands approximately 11 feet (3.4 m) tall, consists of a bronze depiction of an African American family. These four statues, dressed in modern attire, stand atop a granite pedestal. At the statues' feet are broken chains.
See also
References
- ^ Dwyer, Owen J.; Alderman, Derek H. (2008). Civil Rights Memorials and the Geography of Memory. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 978-1-930066-83-0 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Savannah Divided Over Monument". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. February 10, 2001. Archived from the original on November 27, 2020. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ "Angelou amends statue inscription". The Washington Times. May 17, 2002. Archived from the original on February 18, 2021. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ Dvorak, Petula (August 28, 2017). "America's missing slave memorials: It's time to truly acknowledge our bloody past". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on December 20, 2018. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ Darby, Betty (July 21, 2019). "River Street monument addition honors Savannah's Abigail Jordan". Savannah Morning News. GateHouse Media. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ "Addition added to African-American monument on River Street". WTOC-TV. July 26, 2019. Archived from the original on July 26, 2019. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
External links
| Public art in Savannah, Georgia | |
|---|---|
| Works | |
- 2002 establishments in Georgia (U.S. state)
- 2002 sculptures
- African-American monuments and memorials
- Bronze sculptures in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Granite sculptures in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Landmarks in Savannah, Georgia
- Monuments and memorials in Savannah, Georgia
- Outdoor sculptures in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Sculptures of African Americans