| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Α-Hexachlorocyclohexane" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2021) |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
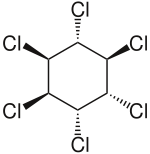
| Preferred IUPAC name (1R,2R,3S,4S,5S,6S)-1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexachlorocyclohexane | |
| Other names
α-HCH α-Benzenehexachloride α-BHC alpha-hexacloran(e) alpha-Lindane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.702 |
| EC Number |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2761, 2811, 3082 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
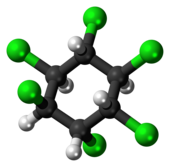
| Chemical formula | C6H6Cl6 |
| Molar mass | 290.83 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
α-Hexachlorocyclohexane (α-HCH) is an organochloride which is one of the isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). It is a byproduct of the production of the insecticide lindane (γ-HCH) and it is typically still contained in commercial grade lindane used as insecticide. Lindane, however, has not been produced or used in the United States for more than 20 years. At ambient temperatures it is a stable, white, powdery solid substance. As of 2009, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants classified (α-HCH) and (β-HCH) as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), due to the chemical's ability to persistence in the environment, bioaccumulative, biomagnifying, and long-range transport capacity.
See also
References
- ^ Toxicological Profile for Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Delta-Hexachlorocyclohexane, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, August 2005
External links
- α-hexachlorocyclohexane United States Environmental Protection Agency IRIS fact sheet
- Cyclohexane, 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachloro-, (1α,2β,3α,4β,5α,6β)- – NIST