
Anna Johnson Dupree (November 27, 1891 - February 19, 1977) was a Houston businesswoman and philanthropist.
In 1952, she and her husband opened the Eliza Johnson Home for Aged Negros. In addition, they donated money to the Houston College of Negroes.
Biography
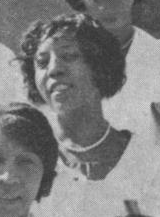

Dupree was born in Carthage and grew up in a family where they picked cotton to make a living. She was the "great-grandchild of a slaveholder and the grandchild of former slaves," and stories she heard about life in slavery had a deep effect on her. Dupree grew up poor, living in a two-room house with her five siblings, her parents, and her grandmother. Dupree's mother "never permitted her to complain" of their poverty and "reminded her there were other children 'worse off' than she."
As a young woman in 1904, she moved to Galveston where she earned a living as a domestic worker. She was noticed for her sewing skills by a Mrs. Zula Kyle, who hired Dupree to work for her in Houston in 1911. Dupree would return home to Galveston often to visit her family.
She met her husband, Clarence Dupree, who was from Louisiana, in Galveston. Anna Dupree would call Clarence a "very unusual person." They were married in 1914, and moved to Houston in 1916. The Duprees saved money by "living simply" and they began to invest what they could into real estate. During World War I, Clarence was sent overseas to fight and during the conflict, he saved his money, returning to the United States with $1,000.
During World War I, Anna Dupree continued to work and save money. She worked as a beautician and manicurist, and later, worked on her own, making beauty "house calls" which were so successful, white beauticians in Houston banded together to stop her. Dupree was stopped from making house calls, but she vowed to create her own shop. Dupree built her own beauty salon which also had a Turkish bath, a sweatbox and massage parlor in 1936.
Together, the couple invested in other businesses and opened the Eldorado Ballroom in the Third Ward. The Eldorado was built in 1939 and was one of the first black clubs and entertainment venues in Houston. Previously, they had also opened the Pastime Theater in 1929. Other businesses that they opened included a pharmacy, men's apparel store, paint store and a nightclub.
Dupree "startled not only the community, but the whole United States with a gift of $20,000 (equivalent to $283,000 in 2018) for the construction of a building for underprivileged Negro children" in March 1944. This was considered one of the largest gifts ever given by a Southern black person at the time. The place was named the Anna Dupree Cottage of the Negro Child Center and was located in the Fifth Ward.
In 1952, the Duprees opened the Eliza Johnson Home for Aged Negros. The home was named in memory of Dupree's mother. Anna Dupree donated property in Highland Heights for the Eliza Johnson Home. Dupree would make fruit cobblers and fruit and boiled dumplings for the "old timers."
Dupree and her husband gave money to the Houston College of Negroes (Now Texas Southern University) and the United Negro College Fund. The couple gave $11,000 in 1946 to the Houston College of Negroes so that the college could construct its first permanent building. They also raised money for Camp Robinhood, the first black Girl Scout camp, and sponsored the first Little League baseball team for blacks in Houston.
When her husband died in 1959, Dupree's health declined and eventually she moved into the Eliza Johnson Home. She died there on February 19, 1977, and her body was donated to medical research.
References
- ^ "Anna Dupree Collection MSS.0110". Texas Archival Resources Online. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ^ Steptoe, Tyina (2015). Houston Bound: Culture and Color in a Jim Crow City. University of California Press. p. 170. ISBN 9780520958531.
- ^ Jones, Nancy Baker (12 June 2010). "Dupree, Anna Johnson". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ^ Jones, Yvette (November 1976). "Seeds of Compassion". The Texas Historian. 37: 16–21. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- Pruitt, Bernadette (2013). The Other Great Migration: The Movement of Rural African Americans to Houston, 1900-1941. Texas A&M University Press. p. 277. ISBN 9781603449489.
- ^ Winegarten, Ruthe; Humphrey, Janet G.; Werden, Frieda (1996). Black Texas Women: A Sourcebook. University of Texas Press. pp. 173–174. ISBN 9780292791008.