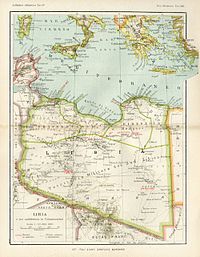
The Aouzou Strip (/ˈaʊzuː/; Arabic: قطاع أوزو, romanized: Qiṭāʿ Awzū, French: Bande d'Aozou) is a strip of land in northern Chad that lies along the border with Libya, extending south to a depth of about 100 kilometers into Chad's Borkou, Ennedi Ouest, Ennedi Est, and Tibesti regions for an area of 114,000 km. It is named after the small town and oasis of Aouzou. The strip played a significant role in the Chadian–Libyan War when it was claimed by Libya.
Inclusion in Italian Libya

The Aouzou strip was defined for the first time in the discussions between France and Italy after World War I, in relation to an award to Italy for the victory in that war. At the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, the Kingdom of Italy did not receive any of the German colonies, but instead was given the Oltre Giuba from the United Kingdom, and France agreed to give some Saharan territories to Italian Libya.
After many discussions during the 1920s, in 1935 the Franco-Italian Agreement was signed between Benito Mussolini and Pierre Laval, which included a provision under which Italy would receive the Aouzou strip, which was to be added to Libya. France's other motivations in concluding this agreement with Italy were to settle the status of the Italian Tunisian community in its protectorate of the country, to remove irredentist Italian claims to Nice, and to prevent Italy from growing closer to Nazi Germany by keeping it closely aligned with France and the United Kingdom (the Stresa Front).
This policy failed two years later when Italy drifted into the German orbit by concluding the Pact of Steel with Nazi Germany, leading to the "instruments of ratification" of the Mussolini-Laval Treaty never being exchanged with France. Despite this, the new border was conventionally assumed to be the southern boundary of Libya until 1955.
History

Claimed to be rich in uranium deposits, the area was the cause of dispute of Chad with Libya, which led to a war between the two countries. In 1973, Libya engaged in military operations in the Aouzou Strip to gain access to minerals and to use it as a base of influence in Chadian politics. This ultimately resulted in the Chadian–Libyan conflict. Libya then claimed an area it called the Borderlands which included the Aouzou Strip.
Libya argued that the territory, as part of the Borderlands, was inhabited by indigenous people who owed vassalage to the Senoussi Order and subsequently to the Ottoman Empire, and that this title had been inherited by Libya. It also supported its claim with an unratified 1935 treaty between France and Italy (the Mussolini-Laval Treaty), the colonial powers of Chad and Libya, respectively, that confirmed the possession of the strip by Italy.
The frontier claimed by the Chadian government was based on a 1955 treaty between France and Libya, which, in turn, referred back to an 1899 agreement between Great Britain and France about "spheres of influence." Despite other differences, this was one position on which all Chadian political parties and factions were able to agree.
Libya occupied the Aouzou Strip during the first half of 1973. During the so-called Toyota War in 1987, the final stage of the Chadian–Libyan conflict, Chadian forces were able to force the Libyans to temporarily retreat from part of the Strip. A cease-fire between Chad and Libya held from 1987 to 1988, followed by unsuccessful negotiations over the next several years.
In 1990, the territorial dispute was referred for adjudication to the International Court of Justice (ICJ). Finally, a February 1994 ICJ decision found (by a majority of 16 to 1) in favour of Chad's sovereignty over the Borderlands and the Aouzou Strip, and ended the Libyan claim.
The United Nations Security Council established the United Nations Aouzou Strip Observer Group in Resolution 915 (May 1994) to monitor the withdrawal of Libyan troops, and terminated it in Resolution 926 (June 1994), when the withdrawal was completed.
See also
References
- ^ Hodder, Lloyd, McLachlan (1998). Land-locked states of Africa and Asia, Volume 2, p. 32. Frank Cass, London, Great Britain.
- Libya Issue Brief, Congressional Research Service (US State Department). April 10, 2002.
- ^ "Case Concerning the Territorial Dispute (Libyan Arab Jamahiriya/Chad)". International Law Reports. 100: 53. January 1995. doi:10.1017/CBO9781316152294.001. ISSN 0309-0671.
- Robert W. McKoeon (1991). "The Aouzou Strip: Adjudication of Competing Territorial Claims in Africa by the International Court of Justice". Case Western Reserve Journal of International Law, Vol. 23, Issue 1. pp. 147–170. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
External links
- Territorial Dispute (Libyan Arab Jamahiriya/Chad) – The case documents on ICJ website
- Frank Jacobs: Borderlines: The World's Largest Sandbox, The New York Times / The Opinion Pages on November 7, 2011
| Countries and territories of North Africa | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |||||||||||||||||
| Partially recognized state | |||||||||||||||||
| Territories |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Entirely claimed by both Morocco and the SADR. Spanish exclaves claimed by Morocco. Portuguese archipelago claimed by Spain. Disputed between Egypt and the Sudan. Unclaimed territory located between Egypt and the Sudan. Disputed between South Sudan and the Sudan. Part of Chad, formerly claimed by Libya. Disputed between Morocco and Spain | |||||||||||||||||