| Rucervus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Barasingha stag | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Tribe: | Cervini |
| Genus: | Rucervus Hodgson, 1838 |
| Type species | |
| Cervus duvaucelii (Cuvier, 1823) | |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Rucervus is a genus of deer from India, Nepal, Indochina, and the Chinese island of Hainan. The only extant representatives, the barasingha or swamp deer (R. duvaucelii) and Eld's deer (R. eldii), are threatened by habitat loss and hunting; another species, Schomburgk’s deer (R. schomburgki), went extinct in 1938. Deer species found within the genus Rucervus are characterized by a specific antler structure, where the basal ramification is often supplemented with an additional small prong, and the middle tine is never present. The crown tines are inserted on the posterior side of the beam and may be bifurcated or fused into a small palmation.
Species
Recent species
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barasingha, swamp deer | Rucervus duvaucelii (Cuvier, 1823) Three subspecies
|
Northern and central India and southwestern Nepal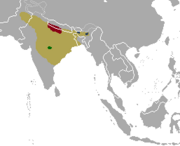
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
VU
|
| Eld's deer, brow-antlered deer, thamin | Rucervus eldii (McClelland, 1842) Three subspecies
|
South Asia and Southeast Asia
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EN
|
| Schomburgk’s deer | Rucervus schomburgki (Blyth, 1863) |
Thailand | Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EX
|
Fossil species
- †Rucervus ardei (Croizet & Jobert, 1828) (Pliocene, France)
- †Rucervus colberti (Azzaroli, 1954) (Tertiary, Sivalik Hills)
- †Rucervus gigans Croitor, 2018 (Early Pleistocene, Greece)
- †Rucervus giulii (Kahlke, 1997) (Early Pleistocene, Germany)
- †Rucervus radulescui Croitor, 2018 (Early Pleistocene, Romania)
- †Rucervus simplicidens (Lydekker, 1876) (Tertiary, Sivalik Hills)
- †Rucervus verestchagini (David, 1992) (Early Pleistocene, Moldova)
According to the old tradition of zoological taxonomy, swamp deer originally were regarded as members of the genus Cervus. Rucervus was originally proposed by Hodgson as a subgenus of the genus Cervus. The original definition of Rucervus was mostly based on antler shape believed to be intermediate between that of 'elaphus' and 'hippelaphus'. Hodgson reported that upper canines are present only in males of barasingha, but the additional craniological material shows that upper canines are present in both sexes. Eld's deer was regarded as another species of the genus Rucervus, however, the recent genetic evidences suggest that Eld's deer is most closely related to Père David's deer and should be placed in its own genus, Panolia. However, it has recently been place back into Rucervus by the American Society of Mammalogists despite Eld's deer is not closely related to barasingha in genetics and antler structure.
The generic name derives from its resemblance to both Rusa and Cervus.
Rucervus is an ancient cervid lineage that--together with the genus Axis--represents the oldest evolutionary radiation of the subfamily Cervinae (plesiometacarpal deer).
Paleontological record
The fossil species of Rucervus of Europe were included in the genus Arvernoceros Heintz, 1971 (the type species: Cervus ardei Croizet & Jobert, 1828) or in the genus Eucladoceros, as in the case of R. giulii. Today, Arvernoceros is regarded as a subgenus of Rucervus. The European fossil forms of Rucervus are distinguished from the South Asian species by more compact crown part of the antler and by the frequent development of a small distal palmation as for instance in R. ardei and R. radulescui. South Asian fossil forms of Rucervus are represented by large-sized R. simplicidens and R. colberti. The late Early Pleistocene of Greece has yielded the remains of a giant species R. gigans that rivaled in size Irish elk Megaloceros giganteus, The giant Rucervus from Greece is distinguished by unusually for such a large animal long limbs and apparently is closely related to R. simplicidens and R. colberti from the Sivaliks. The Southwest-Europe endemic Mid to early Late Pleistocene genus Haploidoceros is regarded as closely allied.
References
- Ellis, Richard (2004). No Turning Back: The Life and Death of Animal Species. New York: Harper Perennial. pp. 311–312. ISBN 0-06-055804-0.
- ^ Hodgson, B.H. 1838. Proceedings of Learned Societies. Linnaean Society, Feb. 20, 1838. Ann. Nat. Hist., 1, 152-154.
- ^ Croitor, Roman (2018-09-11). "A Description of Two New Species of the Genus Rucervus (Cervidae, Mammalia) from the Early Pleistocene of Southeast Europe, with Comments on Hominin and South Asian Ruminants Dispersals". Quaternary. 1 (2): 17. doi:10.3390/quat1020017.
- ^ Pitraa, Fickela, Meijaard, Groves (2004). Evolution and phylogeny of old world deer. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 33: 880–895.
- Gilbert, C.; Ropiquet, A.; Hassanin, A. (2006). "Mitochondrial and nuclear phylogenies of Cervidae (Mammalia, Ruminantia): Systematics, morphology, and biogeography". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 40 (1): 101–17. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.02.017. PMID 16584894.
- Groves (2006). The genus Cervus in eastern Eurasia. European Journal of Wildlife Research 52: 14–22
- Groves, C. and Grubb, P. 2011. Ungulate Taxonomy. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, USA.
- "Rucervus eldii". ASM Mammal Diversity Database. 1.5. American Society of Mammalogists. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- Samejima, Y.; Matsuoka, H. (2020). "A new viewpoint on antlers reveals the evolutionary history of deer (Cervidae, Mammalia)". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 8910. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-64555-7. PMC 7265483. PMID 32488122.
- The Encyclopaedic Dictionary: A New & Original Work of Reference to All the Words in the English Language, with a Full Account of Their Origin, Meaning, Pronunciation, & Use. (1887:201). United Kingdom: Cassell, Petter, Galpin & Company.
- Croitor, Roman; Sanz, Montserrat; Daura, Joan (2020-03-15). "The endemic deer Haploidoceros mediterraneus (Bonifay) (Cervidae, Mammalia) from the Late Pleistocene of Cova del Rinoceront (Iberian Peninsula): origin, ecomorphology, and paleobiology". Historical Biology. 32 (3): 409–427. doi:10.1080/08912963.2018.1499018. ISSN 0891-2963. S2CID 92318533.
External links
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Rucervus | |




