This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
AutoCAST is a software program for casting methods design, simulation and optimization developed by Indian Institute of Technology Bombay.
Software
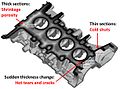
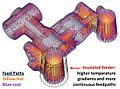
AutoCAST uses geometric reasoning for automating the design of casting methods elements – cores, mold cavity layout, feeders, feed aids and gating channels. Fast and intelligent simulation technology is employed to visualize mold filling and casting solidification in near-real time. Foundry engineers can quickly import a 3D model of cast part, create methods elements, simulate the casting, predict internal defects (like shrinkage porosity and sand inclusion), and modify the methods design to improve quality and yield. Product designers can improve the casting design for manufacturability by minor modifications, such as fillets at junctions. This enables better compatibility between part requirements and process capability, leading to zero defects.
Applications
The latest version AutoCAST-X1 incorporates many innovations, including part thickness analysis, multi-cavity mould layout, multi-neck feeder design, vector element method for solidification simulation, automatic optimisation of feeders and gating system, tooling cost estimation and methods report generation. The database includes all major metal families and casting processes; which can be customised to accommodate new alloys and mould materials.
History
The software has a 20-year history of technology development at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, supported by several Ph.D. and Masters-level researchers. It is maintained and supported by 3D Foundry Tech, a company incubated at the institute. The software is used in industry (especially, SME foundries) for quality and yield improvement, and in academic institutes for simulation labs.