| Hydergarh Basoda Stateबसोदा रियासत | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State | |||||||
| 1753–1947 | |||||||
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||
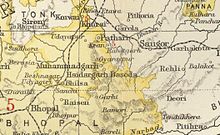 Basoda State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
| • 1901 Census of India | 104 km (40 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
| • 1901 Census of India | 4,897 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
| • Established | 1753 | ||||||
| • Accession to the Indian Union | 1947 | ||||||
| |||||||
Basoda State was a former princely state in Central India, part of the Bhopal Agency during the British Raj in India, with its capital at Haidergarh. It was also known as Nawab-Basoda or Haidargarh-Basoda in order to distinguish it from a place with the same name in Gwalior State.
The state was established in 1753 by Nawab Muhammad Ahsanullah Khan, son of Nawab Muhammad Diler Khan, who founded the Kurwai State. In 1822 Basoda became a British protectorate. In 1947, Nawab Masood Ali Khan, signed the accession to the Indian Union. After the death of Nawab Masood Ali Khan in 1976, the titular ruler of the Royal House of Basoda has been Nawab Kiswhar Ali Khan.
See also
- List of Pashtun empires and dynasties
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
- Political integration of India
- Pathans of Madhya Pradesh
References
- ^ Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 7, p. 105.
- "Basoda (Princely State)". Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- Imperial Gazetteer of India, Central India, vol. 12. 1908. pp. 282–283.
- Alavi, Shams Ur Rehman (15 February 2023). "Haidargarh Basoda: The princely state that survived for two centuries in Central India". NewsBits. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
23°51′N 77°56′E / 23.85°N 77.93°E / 23.85; 77.93
| Former princely states in Central India | |
|---|---|
| Salute states | |
| Non-salute states |
|
| Jagir estates | |
| Extinguished (e)states | |
| Related topics | |