| β-Bungarotoxin | |
|---|---|
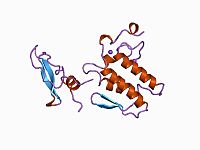 Schematic diagram of the three-dimensional structure of β2-bungarotoxin (PDB: 1bun) Schematic diagram of the three-dimensional structure of β2-bungarotoxin (PDB: 1bun) | |
| Identifiers | |
| Organism | Bungarus multicinctus |
| Symbol | N/A |
| CAS number | 12778-32-4 β1:65862-89-7 β2:82446-04-6 |
β-Bungarotoxin is a form of bungarotoxin that is fairly common in Krait (Bungarus multicinctus) venoms. It is the prototypic class of snake β-neurotoxins. There are at least five isoforms, coded β1 to β5, assembled from different combinations of A and Bchains.
The toxin is a heterodimer of two chains. The A chain confers phospholipase A2 (PLP A2) activity, and the B chain, like dendrotoxins, have a Kunitz domain. There are many isoforms of these chains: examples of A chains include A1 (P00617), A3 (P00619), and A4 (P17934), and examples of B chains include B2 (P00989) and B3 (Q75S50). The B chain plays a functional role in inducing apoptosis.
The target of this neurotoxin is at the presynaptic terminal, where it blocks release of acetylcholine. It seems to do so by blocking the phosphorylation of MARCKS. It is thought that the dendrotoxin-like B chain acts first by inhibition of ion channels, causing cessation of twitches followed by a prolonged facilitatory phase. The A chain (bearing phospholipase activity) then induces a blocking phase by destruction of phospholipids.
Binding sites
Neurobiological research from the late 1980s has found that beta-bungarotoxin selectively binds to (125)I-DTX-I receptor.
See also
References
- Kondo, K; Toda, H; Narita, K; Lee, CY (May 1982). "Amino acid sequences of three beta-bungarotoxins (beta 3-, beta 4-, and beta 5- bungarotoxins) from Bungarus multicinctus venom. Amino acid substitutions in the A chains". Journal of Biochemistry. 91 (5): 1531–48. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133844. PMID 7096305.
- Cheng YC, Wang JJ, Chang LS (February 2008). "B chain is a functional subunit of beta-bungarotoxin for inducing apoptotic death of human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells". Toxicon. 51 (2): 304–15. Bibcode:2008Txcn...51..304C. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.10.006. PMID 18037462.
- Ueno, E; Rosenberg, P (1996). "Mechanism of action of beta-bungarotoxin, a presynaptically acting phospholipase A2 neurotoxin: its effect on protein phosphorylation in rat brain synaptosomes". Toxicon. 34 (11–12): 1219–27. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(96)00113-4. PMID 9027977.
- Rowan, EG (January 2001). "What does beta-bungarotoxin do at the neuromuscular junction?". Toxicon. 39 (1): 107–18. Bibcode:2001Txcn...39..107R. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(00)00159-8. PMID 10936627.
| Acetylcholine metabolism and transport modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||
| Release (modulators) |
| ||||||
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |