| Black-striped wallaby | |
|---|---|

| |
| Artist’s rendition | |

| |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Infraclass: | Marsupialia |
| Order: | Diprotodontia |
| Family: | Macropodidae |
| Genus: | Notamacropus |
| Species: | N. dorsalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Notamacropus dorsalis (J. E. Gray, 1837) | |
| |
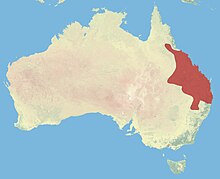
| Black-striped wallaby range | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The black-striped wallaby (Notamacropus dorsalis), also known as the scrub wallaby or eastern brush wallaby, is a medium-sized wallaby found in Australia, from Townsville in Queensland to Narrabri in New South Wales. In New South Wales, it is only found west of the Great Dividing Range. It is decreasing in these areas, but is not classified as threatened as a species yet. The New South Wales population, however, is classified as endangered.
The black-striped wallaby resembles the mainland Australian subspecies of the red-necked wallaby, differing in the black line down its back, a white stripe over the hip and more red colouration (extending down the arms and further down the abdomen). It is a shy, predominantly nocturnal grazer and is not well-known, owing to its preference for thick scrub, where it may easily be hidden. Monocotyledonous plants (leaves and seedheads) seem to constitute preferred food.
References
- Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 64. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Winter, J.; Burnett, S.; Menkhorst, P. (2016). "Notamacropus dorsalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40562A21953658. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T40562A21953658.en.
- ^ Menkhorst, Peter (2001). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Australia. Oxford University Press. p. 120. ISBN 9780195508703.
- "NSW Department of Environment and Conservation Threatened Species".
- Jarman, P.J.; Phillips, C.M.; Rabbidge, J.J. (1991). "Diets of Black-Striped Wallabies in New South Wales". Wildlife Research. 18 (4): 403–411. doi:10.1071/WR9910403. Retrieved 3 November 2024.
External links
- NSW Department of Environment and Conservation
- National Parks and Wildlife Threatened Species Information
- Department of Environment and Energy Species Profile
- "Notamacropus dorsalis (Gray, 1837) – Black-Striped Wallaby". Atlas of Living Australia.
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Notamacropus dorsalis | |
| Macropus dorsalis | |
| Halmaturus dorsalis | |
This article about a diprotodont is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |