| Blunt splenic trauma | |
|---|---|
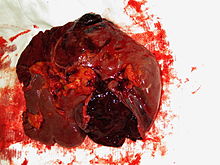 | |
| Spleen ruptured by trauma | |
| Specialty | Hematology |
| Symptoms | Hemorrhage, shock, abdominal pain, distention |
| Causes | Major impact to the spleen (such as in traumatic accidents) |
| Diagnostic method | CT, ultrasound, exploratory laparotomy |
| Treatment | Embolism, splenectomy |
Blunt splenic trauma occurs when a significant impact to the spleen from some outside source (i.e. automobile accident) damages or ruptures the spleen. Treatment varies depending on severity, but often consists of embolism or splenectomy.
Signs and symptoms
The primary symptom, hemorrhage, presents differently depending on the degree of injury, with the symptoms of major hemorrhage, shock, abdominal pain, and distention being clinically obvious. Minor hemorrhage often presents as upper left quadrant pain. Patients with unexplained left upper quadrant pain, particularly if there is evidence of hypovolemia or shock, are generally inquired regarding any recent trauma.
The primary concern in any splenic trauma is internal hemorrhage, though the exact amount of hemorrhage may be small or large, depending on the nature and degree of injury. Small or minor injuries often heal spontaneously, especially in children. Larger injuries hemorrhage extensively, often causing hemorrhagic shock. A splenic hematoma sometimes ruptures, usually in the first few days, although rupture can occur from hours to even months after injury.
Cause
Blunt splenic trauma most often occurs in automobile accident victims, in which it is a leading cause of internal bleeding. However, any type of major impact directed to the spleen may cause splenic trauma. This can happen in bicycling accidents, when the handlebar is forced into the left subcostal margin, and into the spleen. The degree of injury ranges from subcapsular hematoma, to splenic rupture.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is confirmed with CT, or bedside ultrasound for less stable patients. Exploratory laparotomy is rarely used, though it may be of benefit in patients with particularly severe hemorrhage to assess for any retroperitoneal hematomas. An exploratory laparotomy is an opportunity to assess the four quadrants of the abdomen and to look at the bowel for any perforations, vascular injuries, or abnormalities. A set of CT scan grading criteria was created to identify the need for intervention (surgery or embolization) in patients with splenic injury. The criteria were established using 20 CT scans from a database of hemodynamically stable patients with blunt splenic injury. These criteria were then validated in 56 consecutive patients retrospectively and appear to reliably predict the need for invasive management in patients with blunt injury to the spleen (sensitivity of 100%, specificity 88%, overall accuracy was 93%).
The study suggested that the following three CT findings correlate with the need for intervention:
- Devascularization or laceration involving 50% or more of the splenic parenchyma
- Contrast blush greater than one centimeter in diameter (from active extravasation of IV contrast or pseudoaneurysm formation)
- A large hemoperitoneum.
Interactive tools have been developed that facilitate grading of splenic injury based on imaging findings.
Treatment
Treatment has traditionally been splenectomy. Splenectomy involves ligation of three splenic attachments (splenorenal ligament, splenocolic ligament and splenophrenic ligament) to mobilize the spleen. The splenorenal ligament is located laterally, the splenocolic ligament inferiorly and the splenophrenic ligament superiorly. followed by suture ligation of the splenic blood supply. After the spleen has been removed, the abdomen is irrigated with normal saline to confirm hemostasis. After confirmation abdominal organs are put into anatomical position, followed by closure of the abdomen. However, splenectomy is avoided if possible, particularly in children, to avoid the resulting permanent susceptibility to bacterial infections. Most small, and some moderate-sized lacerations in stable patients (particularly children) are managed with hospital observation and sometimes transfusion rather than surgery. Embolization, blocking off of the hemorrhaging vessels, is a newer and less invasive treatment. When surgery is needed, the spleen can be surgically repaired in a few cases, but splenectomy is still the primary surgical treatment, and has the highest success rate of all treatments.
References
- ^ Beers, Mark; Porter, Robert; Jones, Thomas (2006). "11". The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy (18th ed.). New Jersey: Merck Research Laboratories. ISBN 0-911910-18-2.
- , Suah A, Williams B. Exploratory Laparotomy and Splenectomy for Ruptured Spleen Following Blunt Force Trauma. J Med Ins. 2020;2020(299.9) doi:https://jomi.com/article/299.9
- ^ Thompson BE, Thompson BT, Munera F, et al. (2006). "Novel computed tomography scan scoring system predicts the need for intervention after splenic injury". The Journal of Trauma. 60 (5): 1083–6. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000218251.67141.ef. PMID 16688074. S2CID 35829758.
- , Suah A, Williams B. Exploratory Laparotomy and Splenectomy for Ruptured Spleen Following Blunt Force Trauma. J Med Ins. 2020;2020(299.9) doi:https://jomi.com/article/299.9
| Nonmusculoskeletal injuries of abdomen and pelvis | |
|---|---|
| Abdomen / GI | |
| Pelvic | |