| Bornaviridae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Negarnaviricota |
| Class: | Monjiviricetes |
| Order: | Mononegavirales |
| Family: | Bornaviridae |
| Genera | |
Bornaviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fatal neurologic disease of mammals restricted to central Europe; and proventricular dilatation disease (PDD) in birds. Bornaviruses may cause encephalitis in mammals like horses or sheep. The family includes 11 species assigned to three genera.
History
Borna disease was first identified in 1926 and its genome was isolated in 1990. The ICTV proposed the creation in 1996 of the family Bornaviridae along with the genus Bornavirus (today Orthobornavirus). The viral family is named after the city of Borna in Saxony, Germany, which is where many animals were lost to the sporadic encephalopathy caused by the viral disease.
Structure

Orthobornavirions are enveloped, with spherical geometries and helical capsids. The diameter is around 70 to 130 nm. Genomes are made of negative-sense single-stranded RNA. They are linear, monopartite and around 8.9 kbp in length. The genome codes for nine proteins.
Proteins of orthobornaviruses that have been characterized:
| Protein | Function |
|---|---|
| N | Helical nucleoside protein |
| G | Envelope glycoprotein |
| L | Viral polymerase |
| P | Phosphoprotein involved in replication |
| M | Matrix protein |
| X | Has not been fully characterized—perhaps nuclear transport |
Life cycle
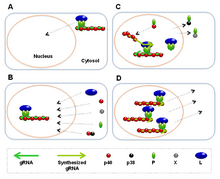
In the Mononegavirales order, Bornaviridae is one of only two families with viruses that replicate in the nucleus. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral GP glycoproteins to host receptors, which mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Replication follows the negative stranded RNA virus replication model. Negative stranded RNA virus transcription, using polymerase stuttering, with some alternative splicing mechanism, is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by nuclear pore export. This virus usually has a highly variable incubation period of around a few weeks to several months. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, and humans serve as the natural hosts. Transmission routes are fomites, contact, urine, feces, and saliva.
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthobornavirus | Horses; sheep; cattle; rodents; birds; humans | Neurons; astrocytes; oligodendrocytes; ependymal cells | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Budding | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | Fomites; contact: saliva; contact: urine; contact: feces |
Pathogenicity
Between 2011 and 2013, three German breeders of variegated squirrels (Sciurus variegatoides) had encephalitis with similar clinical signs and died 2 to 4 months after onset of the clinical symptoms. Genomic analysis found a previously unknown orthobornavirus in a contact squirrel and in brain tissue from the three men, the researchers reported, and it is the "likely causative agent" in their deaths. Prior to this, bornaviruses were not thought to be responsible for human diseases. More VSBV-1 infected squirrels from the subfamilies Sciurinae and Callosciurinae were also confirmed to be present not only in Germany but in the Netherlands. Zero VSBV-1 positive squirrels showed clinical signs of infection. Since behavioral disease has been studied in BoDV-1 infected animals like rhesus monkeys, tree shrews, and rats, BoDV-1 has also been hypothesized to be associated with humans psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and affective psychoses. In several studies with large sample sizes, there has been an association with increased presence of BoDV-1 antibodies in hospitalized psychiatric patients and a higher seroprevalence rate among the psychiatric patients when compared to the control groups.
Taxonomy

| Genus | Species | Virus (Abbreviation) |
| Carbovirus | Queensland carbovirus | jungle carpet python virus (JCPV) |
| Southwest carbovirus | southwest carpet python virus (SWCPV) | |
| Cultervirus | Sharpbelly cultervirus | |
| Orthobornavirus | Elapid 1 orthobornavirus | Loveridge's garter snake virus 1 (LGSV-1) |
| Mammalian 1 orthobornavirus | Borna disease virus 1 (BoDV-1) | |
| Borna disease virus 2 (BoDV-2) | ||
| Mammalian 2 orthobornavirus | variegated squirrel bornavirus 1 (VSBV-1) | |
| Passeriform 1 orthobornavirus | canary bornavirus 1 (CnBV-1) | |
| canary bornavirus 2 (CnBV-2) | ||
| canary bornavirus 3 (CnBV-3)) | ||
| Passeriform 2 orthobornavirus | estrildid finch bornavirus 1 (EsBV-1) | |
| Psittaciform 1 orthobornavirus | parrot bornavirus 1 (PaBV-1) | |
| parrot bornavirus 2 (PaBV-2) | ||
| parrot bornavirus 3 (PaBV-3) | ||
| parrot bornavirus 4 (PaBV-4) | ||
| parrot bornavirus 7 (PaBV-7) | ||
| Psittaciform 2 orthobornavirus | parrot bornavirus 5 (PaBV-5) | |
| Waterbird 1 orthobornavirus | aquatic bird bornavirus 1 (ABBV-1) | |
| aquatic bird bornavirus 2 (ABBV-2) |
References
- ^ Richt, Jurgen; Pfeuffer, I.; Christ, M.; Frese, K.; Bechter, K.; Herzog, S. (1997). "Borna Disease Virus Infection in Animals and Humans". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 3 (3): 343–352. doi:10.3201/eid0303.970311. PMC 2627631. PMID 9284379.
- ^ "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- Amarasinghe, Gaya K.; Bào, Yīmíng; Basler, Christopher F.; Bavari, Sina; Beer, Martin; Bejerman, Nicolás; Blasdell, Kim R.; Bochnowski, Alisa; Briese, Thomas (7 April 2017). "Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: update 2017". Archives of Virology. 162 (8): 2493–2504. doi:10.1007/s00705-017-3311-7. ISSN 1432-8798. PMC 5831667. PMID 28389807.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 February 2018. Retrieved 2 February 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Carbone, KM (2001). "Borna". Clin Microbiol Rev. 14 (3): 513–27. doi:10.1128/CMR.14.3.513-527.2001. PMC 88987. PMID 11432811.
- Richt, JA; Rott, R (2001). "Borna disease virus: a mystery as an emerging zoonotic pathogen". Vet J. 161 (1): 24–40. doi:10.1053/tvjl.2000.0533. PMID 11145828.
- Veterinary Microbiology and microbial disease, 2nd edition, P J Quinn et al. Wiley-Blackwell
- Hoffmann, Bernd; Tappe, Dennis; Höper, Dirk; Herden, Christiane; Boldt, Annemarie; Mawrin, Christian; Niederstraßer, Olaf; Müller, Tobias; Jenckel, Maria; van der Grinten, Elisabeth; Lutter, Christian; Abendroth, Björn; Teifke, Jens P.; Cadar, Daniel; Schmidt-Chanasit, Jonas; Ulrich, Rainer G.; Beer, Martin (9 July 2015). "A Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus Associated with Fatal Human Encephalitis". New England Journal of Medicine. 373 (2): 154–162. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415627. PMID 26154788.
- "Is There a Killer Squirrel Virus?". 9 July 2015.
- Schlottau, K; Jenckel, M; van den Brand, J; Fast, C; Herden, C; Höper, D; Homeier-Bachmann, T; Thielebein, J; Mensing, N; Diender, B; Hoffmann, D; Ulrich, RG; Mettenleiter, TC; Koopmans, M; Tappe, D; Schmidt-Chanasit, J; Reusken, CB; Beer, M; Hoffmann, B (2017). "Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1 in Squirrels, Germany and the Netherlands". Emerg Infect Dis. 23 (3): 477–481. doi:10.3201/eid2303.161061. PMC 5382762. PMID 28221112.
- Milad Azami, Farid Azizi Jalilian, Ali Khorshidi, Younes Mohammadi, Zeinab Tardeh, The association between Borna Disease Virus and schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Asian Journal of Psychiatry, Volume 34, 2018,Pages 67-73, ISSN 1876-2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2017.11.026.
- Amarasinghe, Gaya K.; Aréchiga Ceballos, Nidia G.; Banyard, Ashley C.; Basler, Christopher F.; Bavari, Sina; Bennett, Andrew J.; Blasdell, Kim R.; Briese, Thomas; Bukreyev, Alexander (11 April 2018). "Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: update 2018". Archives of Virology. 163 (8): 2283–2294. doi:10.1007/s00705-018-3814-x. ISSN 1432-8798. PMC 6076851. PMID 29637429.
External links
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Bornaviridae | |