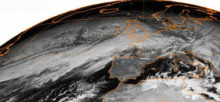
The Boxing Day Storm (also called the Great Boxing Day Storm of 1998 or Hurricane Stephen) was an Atlantic windstorm that made landfall in northwest Ireland. It peaked on Boxing Day, 26 December, which is celebrated as St. Stephen's Day in Ireland.
Storm
The storm lasted from 3:00 on 24 December to 15:00 on 29 December 1998, peaking on 26 December. The Met Office reported that mean speeds over land reached nearly 60 miles per hour (97 km/h) over a period of twelve hours, with gusts exceeding 90 miles per hour (140 km/h) and being recorded at over 100 miles per hour (160 km/h) were recorded at some locations.
The storm followed a period of higher than average rainfall, with 400 mm to 800 mm falling in the west of the country and 200 mm to 300 mm in the east, in the four-month period from September to December. This softened the soil, making trees more vulnerable to wind. The Met Office estimated that a storm on the magnitude of the one in December 1998 occurs around once every four years somewhere in Britain, and once every twenty at any given point, with the wind coming in a belt around 200 kilometres (120 mi) wide.
Damage
Large parts of northern England and Scotland lost access to electricity. 50,000 households were without electricity for more than 24 hours, with some supplies not restored until the New Year. Six electricity companies in Great Britain declared a systems emergency as a result of the damage.
The reactors at Hunterston B nuclear power station were shut down when power was lost, possibly due to arcing at pylons caused by salt spray from the sea. When the grid connection was restored, the generators that had powered the station during the blackout were shut down and left on "manual start", so when the power failed again the station was powered by batteries for a short time of around 30 minutes, until the diesel generators were started manually. During this period the reactors were left without forced cooling, in a similar fashion to the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, but the event at Hunterston was rated as INES 2.
References
- "Hurricane force winds over north and northwest" (PDF). Met Éireann. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- "Stephen". University of Reading. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ^ "Supply interruptions following the Boxing Day storms 1998" (PDF). Ofgem. May 1999. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ^ "Nuclear power station loss of electricity grid during severe storm (1998)" (PDF). safetyinengineering.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- "UK Nuclear alert at Scottish plant". BBC News. 30 December 1998. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
External links
BBC Weather forecasts for Christmas 1998 and the Boxing Day storm.
| Weather events in Ireland | ||
|---|---|---|
| Climate of Ireland | ||
| Coldwaves |  | |
| Floods |
| |
| Heat waves | ||
| Windstorms | ||
| Storm Surges | ||
| Tornadoes | ||
| Thunderstorms |
| |
| Windstorm seasons | ||
