| Bronchopneumonia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bronchial pneumonia, bronchogenic pneumonia |
 | |
| Typical distribution of lobar pneumonia (left in image) and bronchopneumonia (right in image) | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology, infectious disease |
Bronchopneumonia is a subtype of pneumonia. It is the acute inflammation of the bronchi, accompanied by inflamed patches in the nearby lobules of the lungs.
It is often contrasted with lobar pneumonia; but, in clinical practice, the types are difficult to apply, as the patterns usually overlap. Bronchopneumonia (lobular) often leads to lobar pneumonia as the infection progresses. The same organism may cause one type of pneumonia in one patient, and another in a different patient.
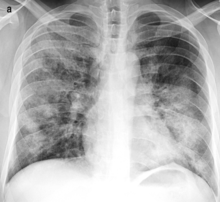
Causes
It is more commonly a hospital-acquired pneumonia than a community-acquired pneumonia, in contrast to lobar pneumonia.
Bronchopneumonia is less likely than lobar pneumonia to be associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Rather, the bronchopneumonia pattern has been associated mainly with the following: Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, E. coli and Pseudomonas.
Pathology
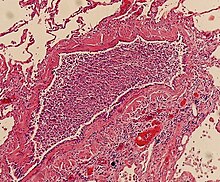
Bronchopneumonia may sometimes be diagnosed after death, during autopsy.
On gross pathology there are typically multiple foci of consolidation present in the basal lobes of the human lung, often bilateral. These lesions are 2–4 cm in diameter, grey-yellow, dry, often centered on a bronchiole, poorly delimited, and with the tendency to confluence, especially in children.
Light microscopy typically shows neutrophils in bronchi, bronchioles and adjacent alveolar spaces.
Treatment
Further information: PneumoniaCompared to pneumonia in general, the association between the bronchopneumonia pattern and hospital-acquired pneumonia warrants greater consideration of multiple drug resistance in the choice of antibiotics.
References
- "bronchopneumonia". YourDictionary. Retrieved 2020-01-08. citing: Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fifth Edition, Copyright 2014
- ^ Elliot Weisenberg, M.D. "Lung - nontumor, Infections, Pneumonia - general". PathologyOutlines. Topic Completed: 1 August 2011
- Franquet, Tomás; Chung, Johnathan H. (2019). "Imaging of Pulmonary Infection". Diseases of the Chest, Breast, Heart and Vessels 2019-2022. IDKD Springer Series. Part of the IDKD Springer Series Book Series (IDKD). pp. 65–77. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-11149-6_7. ISBN 978-3-030-11148-9. ISSN 2523-7829. PMC 7123565. PMID 32096948.
-"This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)" - Reynolds, J H; Mcdonald, G; Alton, H; Gordon, S B (2010). "Pneumonia in the immunocompetent patient". The British Journal of Radiology. 83 (996): 998–1009. doi:10.1259/bjr/31200593. ISSN 0007-1285. PMC 3473604. PMID 21088086.
- "Lobar Pneumonia". Loyola University Chicago, Health Sciences Campus. Retrieved 2008-11-16.
- "Pulmonary Pathology". Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
| Diseases of the respiratory system | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper RT (including URTIs, common cold) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower RT/ lung disease (including LRTIs) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pleural cavity/ mediastinum |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other/general | |||||||||||||||||||||||