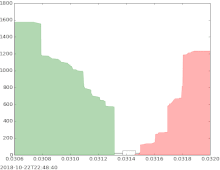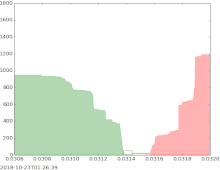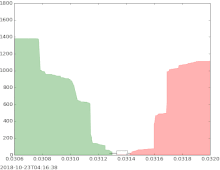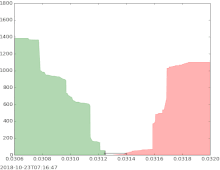
The bid–ask spread (also bid–offer or bid/ask and buy/sell in the case of a market maker) is the difference between the prices quoted (either by a single market maker or in a limit order book) for an immediate sale (ask) and an immediate purchase (bid) for stocks, futures contracts, options, or currency pairs in some auction scenario. The size of the bid–ask spread in a security is one measure of the liquidity of the market and of the size of the transaction cost. If the spread is 0 then it is a frictionless asset.
Liquidity
The trader initiating the transaction is said to demand liquidity, and the other party (counterparty) to the transaction supplies liquidity. Liquidity demanders place market orders and liquidity suppliers place limit orders. For a round trip (a purchase and sale together) the liquidity demander pays the spread and the liquidity supplier earns the spread. All limit orders outstanding at a given time (i.e. limit orders that have not been executed) are together called the Limit Order Book. In some markets such as NASDAQ, dealers supply liquidity. However, on most exchanges, such as the Australian Securities Exchange, there are no designated liquidity suppliers, and liquidity is supplied by other traders. On these exchanges, and even on NASDAQ, institutions and individuals can supply liquidity by placing limit orders.
The bid–ask spread is an accepted measure of liquidity costs in exchange traded securities and commodities. On any standardized exchange, two elements comprise almost all of the transaction cost—brokerage fees and bid–ask spreads. Under competitive conditions, the bid–ask spread measures the cost of making transactions without delay. The difference in price paid by an urgent buyer and received by an urgent seller is the liquidity cost. Since brokerage commissions do not vary with the time taken to complete a transaction, differences in bid–ask spread indicate differences in the liquidity cost.
Types of spreads
Quoted spread
The simplest type of bid-ask spread is the quoted spread. This spread is taken directly from quotes, that is, posted prices. Using quotes, this spread is the difference between the lowest asking price (the lowest price at which someone will sell) and the highest bid price (the highest price at which someone will buy). This spread is often expressed as a percent of the midpoint, that is, the average between the lowest ask and highest bid: .
Effective spread
Quoted spreads often over-state the spreads finally paid by traders, due to "price improvement", that is, a dealer offering a better price than the quotes, also known as "trading inside the spread". Effective spreads account for this issue by using trade prices, and are typically defined as: . The effective spread is more difficult to measure than the quoted spread, since one needs to match trades with quotes and account for reporting delays (at least pre-electronic trading). Moreover, this definition embeds the assumption that trades above the midpoint are buys and trades below the midpoint are sales.
Realized spread
Quoted and effective spreads represent costs incurred by traders. This cost includes both a cost of asymmetric information, that is, a loss to traders that are more informed, as well as a cost of immediacy, that is, a cost for having a trade being executed by an intermediary. The realized spread isolates the cost of immediacy, also known as the "real cost". This spread is defined as: where the subscript k represents the kth trade. The intuition for why this spread measures the cost of immediacy is that, after each trade, the dealer adjusts quotes to reflect the information in the trade (and inventory effects).
Inner price moves are moves of the bid-ask price where the spread has been deducted.
Example: Currency spread
If the current bid price for the EUR/USD currency pair is 1.5760 and the current offer price is 1.5763, this means that currently you can sell the EUR/USD at 1.5760 and buy at 1.5763. The difference between those prices (3 pips) is the spread.
If the USD/JPY currency pair is currently trading at 101.89/101.92, that is another way of saying that the bid for the USD/JPY is 101.89 and the offer is 101.92. This means that currently, holders of USD can sell US$1 for 101.89 JPY and investors who wish to buy dollars can do so at a cost of 101.92 JPY per US$1.
Example: Metals
Gold and silver are known for having the tightest bid-ask spreads, making them useful as money, while other metals may have wider bid-ask spreads due to lower trading volumes, less liquidity, or large fluctuations in supply and demand. For example, rare metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium have lower trading volumes compared to gold or silver, which can result in larger bid-ask spreads.
See also
- Bid–ask matrix
- Demand and offer
- Market maker
- Mid price
- Price elasticity of demand
- Spot price
- Underwriting spread
References
- "Spreads – definition". Riskglossary.com. Archived from the original on 2012-08-15. Retrieved 2019-04-24.
- Demsetz, H. 1968. "The Cost of Transacting." Quarterly Journal of Economics 82: 33–53 doi:10.2307/1882244 JSTOR 1882244
- Lee, Charles M. C. (July 1993). "Market Integration and Price Execution for NYSE-Listed Securities". The Journal of Finance. 48 (3): 1009–1038. doi:10.2307/2329024. ISSN 0022-1082. JSTOR 2329024.
- Lee, Charles M. C.; Ready, Mark J. (June 1991). "Inferring Trade Direction from Intraday Data". The Journal of Finance. 46 (2): 733. doi:10.2307/2328845. ISSN 0022-1082. JSTOR 2328845.
- Huang, Roger D.; Stoll, Hans R. (July 1996). "Dealer versus auction markets: A paired comparison of execution costs on NASDAQ and the NYSE". Journal of Financial Economics. 41 (3): 313–357. doi:10.1016/0304-405x(95)00867-e. ISSN 0304-405X.
Further reading
- Bartram, Söhnke M.; Fehle, Frank R.; Shrider, David (May 2008). "Does Adverse Selection Affect Bid-Ask Spreads for Options?". Journal of Futures Markets. 28 (5): 417–437. doi:10.1002/fut.20316. S2CID 154229351. SSRN 1089222.
 .
.
 . The effective spread is more difficult to measure than the quoted spread, since one needs to match trades with quotes and account for reporting delays (at least pre-electronic trading). Moreover, this definition embeds the assumption that trades above the midpoint are buys and trades below the midpoint are sales.
. The effective spread is more difficult to measure than the quoted spread, since one needs to match trades with quotes and account for reporting delays (at least pre-electronic trading). Moreover, this definition embeds the assumption that trades above the midpoint are buys and trades below the midpoint are sales.
 where the subscript k represents the kth trade. The intuition for why this spread measures the cost of immediacy is that, after each trade, the dealer adjusts quotes to reflect the information in the trade (and inventory effects).
where the subscript k represents the kth trade. The intuition for why this spread measures the cost of immediacy is that, after each trade, the dealer adjusts quotes to reflect the information in the trade (and inventory effects).