| This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (September 2023) |

This article covers the water based Canadian canoe routes used by early explorers of Canada with special emphasis on the fur trade.
Introduction
European exploration of the Canadian interior was principally by river. The land has many navigable rivers with short portages between them. There are no serious barriers to water-borne travel east of the Rockies. The fur trade, principally in beaver, drove and financed exploration and initial settlement. Traders obtained furs from the natives and exported them to Europe.
Canada and Siberia
Both Canada and Siberia are largely covered by Boreal Forest. Both were opened up by water-borne fur traders. In both countries the problem was to find streams that flowed in approximately the right direction and to find short portages to move from one river basin to the next. Both regions are flat. One can move from the Saint Lawrence to the Rockies or from the Urals almost to the Pacific with only a few short portages. In both countries furs were obtained by natives and exported by Europeans. In Siberia a band of armed Cossacks would enter a native village and demand yasak or tribute. In Canada furs were exchanged for European merchandise.
Russian expansion into Siberia began with the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582. Fifty seven years later they reached the Pacific. European settlement of Canada began in 1583 (St. John's), 1605 (Port Royal, Nova Scotia), and 1608 (Quebec City). Canada-based Europeans reached the Arctic Ocean in 1789 and the Pacific in 1793, both expeditions led by Alexander Mackenzie. For Siberian exploration see Siberian River Routes and its linked articles.
Gateways to the continent

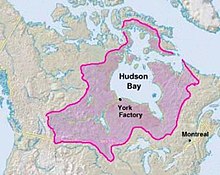
An explorer naturally wishes to travel as far as possible by water. Hudson Bay gets one more than a third of the way across the continent, but it leads to unproductive country and is blocked by ice for most of the year. The Mississippi River is a natural entry point, but it only began to be used in 1718 with the foundation of New Orleans. Early sea ships could follow the Hudson River as far as Albany, but this leads north to the Saint Lawrence and westward travel was blocked by the Iroquois league. The Chesapeake and Delaware Bays lead a short way inland and the other east coast rivers are too short or shallow to be of much use. This leaves the St. Lawrence River.
Two ages of trade and exploration
French Era: In the 16th century, cod fishermen began trading for furs, especially at Tadoussac on the St. Lawrence River. With the foundation of Quebec in 1608, Coureurs des bois spread out through the many rivers and lakes to trade with the Indians, while Indians would carry canoe-loads of fur down to Montreal. Nearby tribes became middlemen, drawing furs from further inland. Montreal was the main base where furs were stored before transshipment to Europe. By the end of the period, trade and exploration had spread to all the Great Lakes and was extending down the Mississippi. Meanwhile, the British maintained posts on Hudson Bay, ignored the interior and waited for Indians to bring furs to them.
British Era: The second era began when trade reached the pays d'en haut west of Lake Superior. In these cold lands beaver had longer and thicker fur. After the British conquered Canada in 1759, management of the Montreal trade was taken over by English-speakers while the real work continued to be done by French-Canadians. The Montreal-based North West Company was formed in 1779 largely because distances had become so great as to require a highly organized transport system (The Athabasca country was 3000 miles from Montreal and a canoe might go 1000 miles in a month). The independent coureur des bois was replaced by hired voyageurs. Since the west country was too far for a round trip in one season, each spring, when the ice broke up, boats would set out from Montreal while winterers would start east. They exchanged their goods at Grand Portage on Lake Superior and returned before the rivers froze five months later. To save the cost of hauling food from Montreal, Metis around Winnipeg began the large-scale production of pemmican. The Hudson Bay trade was diverted southwest to the edge of the prairie where pemmican was picked up to feed the voyageurs on their journey northwest to the Athabasca country. Competition from the Nor'Westers forced the Hudson's Bay Company to build posts in the interior. The two companies competed for a while and, in 1821, merged. Management was taken over by the capital-rich HBC, but trading methods were those of the Montreal-based Nor'Westers. Much trade shifted to York Factory and later some went south to Minnesota. After 1810 the western posts were linked to the British bases on the Oregon coast. By mid-century the HBC ruled an inland empire that stretched from Hudson Bay to the Pacific. The Carlton Trail became a land route across the prairies. HBC land claims were transferred to Canada by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. From 1874 the North-West Mounted Police began to extend formal government into the area. The fur trade routes grew obsolete from the 1880s with the coming of railways and steamships.
St. Lawrence River basin


Seagoing ships can reach Quebec City and smaller ones can reach Montreal. One might think that the route would continue up the St. Lawrence, but this was not the case. Possible reasons are the Lachine Rapids and other rapids above Montreal, Niagara Falls, Iroquois hostility, the poorer quality of southern furs and the lack of large birch trees to make canoes. The route west from Montreal has been called the 'first Trans-Canada Highway'. It ran from near Montreal, up the Ottawa River, west up the Mattawa River to Trout Lake and over the 7 mile La Vase portage at what is now North Bay on Lake Nipissing and down the French River to Georgian Bay of Lake Huron. This route was first used by Étienne Brûlé in 1610 and later by Champlain. When the Iroquois made the Ottawa dangerous it was possible for small canoes to continue up the Ottawa above the Mattawa and from its sources across to the Saint-Maurice River and down to the St. Lawrence at Trois-Rivières.
Routes ran from the French River south to the Jesuit Huron missions at the southern end of Georgian Bay (1626–1640), west through the Strait of Mackinac to Lake Michigan, or west north of Manitoulin Island and up the St Marys River (26 feet difference in elevation) to Lake Superior. On Lake Superior voyageurs would normally hug the northern shore because of the danger of frequent squalls that could overturn their boats.
The route up the St. Lawrence to Lake Ontario, Niagara Falls, Lake Erie, Detroit River, Lake St. Clair, St. Clair River and lower Lake Huron developed later (Adrien Jolliet in 1669 was probably the first) and was never the main westward route. North of the St. Lawrence were many complex lakes and rivers that were sometimes used to go as far as James Bay. The Toronto Carrying-Place Trail was a major portage route in the St. Lawrence basin, linking Lake Ontario with Lake Simcoe and the northern Great Lakes.
Nelson River basin

The Canada–United States border meets Lake Superior near Grand Portage, Minnesota. From here to Lake of the Woods the voyageurs' route went northwest across the 9 mile (14 km) long Grand Portage to avoid the falls and canyon of the Pigeon River, thence along the present international border west up the 50 miles (80 km) long Pigeon River and Arrow River to South Lake, and then across the 400 metres (1,300 ft) Height of Land Portage to North Lake whose waters drain into Hudson Bay. From North Lake the route goes through Gunflint Lake, thence down the Pine and Granite Rivers to Saganaga lake and through a chain of lakes, including Knife and Basswood Lakes, to Lac La Croix, where the route from Fort William comes in. It continues down the Loon River to Lake Namakan and north over either of two portages to Rainy Lake (a depot was established here to shorten the voyage of the Athabasca brigade) and down the Rainy River to Lake of the Woods 210 miles (340 km) west-northwest of Grand Portage. Leaving the US border, northwest down the Winnipeg River with 26 portages to Lake Winnipeg, a poor lake for small craft. This area was opened up by La Vérendrye in 1731–1737. Following the current downstream leads to the Nelson River and Hudson Bay, which is not very useful. (The Nelson River is difficult and the parallel Hayes River was preferred. The Hayes route became more important after 1821 when much trade shifted from Montreal to York Factory)
In 1803 it was found that Grand Portage was on the US side of the border and the Lake Superior base was moved 45 miles (72 km) northeast to Fort William, Ontario, from which an old trail led inland to the north and west to Lac La Croix in the watershed of the Rainy River. For the two routes from Lake Superior see Grand Portage National Monument and Kaministiquia River.
A minor route ran from Duluth, Minnesota west and north up the St. Louis River and Embarrass River over another Height of Land Portage and north down the Pike River (Minnesota) and Vermilion River (Minnesota) to Rainy Lake on the Grand Portage route. During the negotiations for the Webster-Ashburton Treaty Britain tried to make this as the Canada–US border.
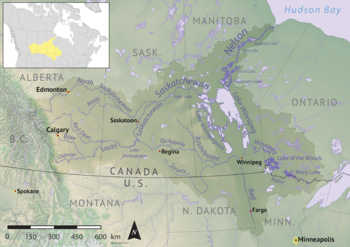
The Nelson River drains Lake Winnipeg northeast into Hudson Bay.
The Red River comes in from the south.
The Saskatchewan River enters Lake Winnipeg at Grand Rapids, Manitoba. Around these rapids to Cedar Lake. (Cedar Lake is one of the chain of lakes that look like a single lake west of Lake Winnipeg.) Although it was not much used, a route ran from Cedar Lake south over the 4 miles (6.4 km) Mossy portage to Lake Winnipegosis and then the mile-and-a-half Meadow Portage to Lake Manitoba and then at least 5 miles (8.0 km) of Portage la Prairie to the Assiniboine River. Another route reached Lake Manitoba from Lake Winnipeg via the Dauphin River. Up the Saskatchewan, past Cumberland House and up the North Saskatchewan River almost to the Rocky Mountains at Fort Edmonton and Rocky Mountain House, Alberta. The North Saskatchewan is approximately the southern limit of forested beaver country. There are no portages between Cumberland and Edmonton, but there are sand bars and 125 miles (201 km) stretch of strong current east of Prince Albert, Saskatchewan where canoes were dragged upstream on ropes. Above Prince Albert is the La Montée prairie country where voyageurs were fed by buffalo hunters. Both York boats and north canoes were used. Trade was helped by the fact that the Cree Language was spoken along the whole route. South of the river there was enough grass for horses and one could travel from Edmonton to Red River on horseback. Horses were used for speed and canoes for freight. There are, of course, no canoe routes over the Rockies.
The Assiniboine River which meets the Red River just south of Lake Winnipeg provided another route west. The Red River of the North, which flows north into the southern tip of Lake Winnipeg gained some importance after 1812 with the establishment of the Red River Colony and when the Metis began supplying buffalo Pemmican to feed the voyageurs. These are prairie rivers and not good beaver country. Much transport was by horse and Red River cart, and American traders were able to subvert the British monopoly over the fur trade by siphoning off much of the trade to entrepôts on the Mississippi River to the south by way of the Red River Trails.
Mackenzie River basin
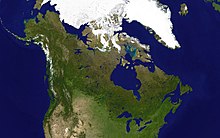

The axis from Lake Superior to the Mackenzie River runs along the southwest side of the forested beaver country between the prairie to the southwest and the Barren Grounds to the northeast. Here beaver fur is longer and thicker than further southeast. The southern part of the axis was near the source of pemmican. From the depot at Cumberland House, Saskatchewan on the lower Saskatchewan River, this route runs north up the Sturgeon-Weir River, across Frog Portage to the east-flowing Churchill River which is mostly a chain of lakes, west up the Churchill past the depot on Lac Île-à-la-Crosse, through Peter Pond Lake to Lac La Loche and over the 12 mile Methye Portage to the Clearwater River whose waters reach the Arctic. The Methye Portage, which was first reached by Peter Pond in 1778 ranks with Grand Portage as the most difficult of the major portages.
The route continues west down the Clearwater River to the Athabasca River at Fort McMurray and north down the Athabasca to the Peace-Athabasca Delta and the depot at Fort Chipewyan, Alberta, at the west end of Lake Athabasca. This was about as far as canoes could reach and return in one season and was the gathering place for furs from the rich Athabasca region and further west. One could continue into poorer country north down the Slave River to the Great Slave Lake and thence northwest down the Mackenzie River to the Arctic Ocean.
Pacific coast


After the voyages of Captain Cook European ships entered the Pacific in large numbers. A Maritime fur trade with China developed from the Columbia District (known as Oregon Country in the US). The inland canoe routes were linked to the Pacific coast in 1811 when David Thompson reached the mouth of the Columbia River. A fur trade developed in the interior. Here, horses were used more often than canoes, furs were trapped by non-Indians and the pelts exported by ship. Here Canadians competed, rather successfully, with the American Fur Company. In 1846 the Columbia District was divided between the two nations at the 49th parallel.
The interior of British Columbia around the upper Fraser River was called New Caledonia. Goods were carried from Fort Chipewyan up the Peace River (1,500 foot elevation gain and only one significant portage at Hudson Hope, British Columbia) to Fort McLeod and carried over the mountains. It normally took two years for heavy goods to cross the continent, goods being stored at Fort Chipewyan over the winter. Later there was a horse trail from the Fraser River south to Fort Okanogan on the Columbia River.
The route to the Columbia River ran from Fort Chipewyan southwest up the Athabasca River to Fort Assiniboine and after 1825, west from Fort Edmonton on the North Saskatchewan over an 80-mile horse track to Fort Assiniboine. From there it went up the Athabasca to Jasper House and thence over Athabasca Pass to Boat Encampment on the Columbia. The route was used for messages and light freight but was not practical for heavy freight.
The far northwest was supplied by an unusual route which was found in 1851 by Robert Campbell who travelled in the opposite direction from the one described here. From the Mackenzie River delta it went south up the Peel River to the depot at Fort McPherson, Northwest Territories, thence back down the Peel and west up the Rat River (by poling or dragging, not paddling) or by a parallel trail and over a half-mile portage to the Little Bell River. The route from Bell River (Yukon) went past a post called Lapierre's House and down the Porcupine River to Fort Yukon, Alaska about 300 miles west of Fort McPherson. From there it went at least 400 miles south-southeast up the Yukon River and Pelly River, then the Findlayson and Campbell Rivers and a portage to Frances Lake, down the Frances River to the Liard River and east to Fort Simpson on the Mackenzie about 275 miles east of Frances Lake. There was some transport on the Liard, but the Liard river canyon made this difficult.
Mississippi basin
In 1682 La Salle reached the mouth of the Mississippi from the Great Lakes. From about 1715 the French sought to link the St. Lawrence and Mississippi basins and bottle up the English on the east coast. From the southeast side of Lake Michigan, east up the St. Joseph River to near the present site of South Bend, Indiana and across a short portage to the Kankakee River, west down to Kankakee, which joins the Des Plaines River to become the Illinois River which runs first west and then southwest to the Mississippi. Another route was the Chicago River and across the Chicago Portage to the Des Plaines River and south to the Illinois. Alternatively, from the northwest side of Lake Michigan, at the head of Green Bay, up the Fox River, past serious rapids to Lake Winnebago, up the Fox and over a short portage to the Wisconsin River and southwest to the Mississippi. Another route ran from the western extremity of Lake Superior up the Saint Louis River and the East Savanna River, across the Savanna Portage, and down south and west flowing streams to the Mississippi River and the fur country of what is now the U.S. state of Minnesota.
By the time of the British conquest there were French trading posts from New Orleans up the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers to the Great Lakes.
Lake-Champlain-Hudson River

This was the main axis of British-French and British-US military conflict late in the period. From Quebec upriver about a third of the way to Montreal, up the Richelieu River to Lake Champlain, portage west parallel to the La Chute River (230 feet drop in 3+1⁄2 miles) to Lake George, overland to the Hudson River and downstream to New York.
Upper Ohio River basin
Although the French had long been in the Ohio country (La Salle in 1669, Fort des Miamis from 1715), this area only became important after about 1743 when the French tried to block Anglo-American expansion into the Ohio country. From Lake Erie, at Fort Presque Isle (1753), south up an army-built wagon road to Fort Le Boeuf at the head of the Rivière aux Boeufs (LeBoeuf Creek), down LeBoeuf Creek to French Creek to Fort Machault at its junction with the Allegheny River and down the Allegany to Fort Duquesne (1754) at modern-day Pittsburgh. The British response to this move was the beginning of the French and Indian War.
Hudson Bay

The Hudson's Bay Company began establishing posts on the Bay in 1668. Unlike the French-Canadians, the English were usually content to sit on the coast and let the Indians bring furs to them. 'Asleep by the frozen sea' is how Joseph Robson described it. Movement inland began about 1750 after the French entered the western country and tried to divert the Hudson Bay fur trade to Montreal. The most important route ran from York Factory up the Hayes River (not the Nelson River) to Norway House at the north end of Lake Winnipeg. Most posts were on the southwest side of the bay. Inland were many complex routes, most being too small for heavy freight canoes. Main routes from east to west were:
- On James Bay
- North of the Eastmain were Barren Grounds with few beaver.
- Eastmain River from James Bay east.
- Rupert River with Rupert House: Rupert Bay at the southeast corner of James Bay, east up the Rupert to Lake Mistassini, over to Lake Saint-Jean and down the Saguenay River to the St. Lawrence at Tadoussac.
- Nottaway River: Rupert Bay southeast to Lake Matagami.
- Moose River with Moose Factory on the south end of James Bay: 1) south: Moose River, Abitibi River, Lake Abitibi, portage to the upper Ottawa River near Lake Timiskaming. This was the best route from James Bay to the Ottawa and was used by the Hudson Bay expedition (1686); 2) southwest: Moose River, Missinaibi River, portage to the Michipicoten River to Lake Superior at Wawa, Ontario. This route was used to supply Lake Superior from Hudson Bay.
- Albany River with Fort Albany, Ontario on the west side of James Bay with Henley House (1743) 160 miles upstream: 1) southwest: up the Albany, up the Ogoki River, cross to Lake Nipigon and south to Lake Superior; 2) West: Albany River to Lake St. Joseph, portage to a river going south to Lac Seul and down the English River (Ontario) to the Winnipeg River.
- Severn River (northern Ontario) with Fort Severn on the 'shoulder' west of James Bay. The Severn flows northeast from the general area of Lake St. Joseph
- Hayes River with York Factory, Manitoba: York Factory was the Hudson's Bay Company base of operations. Up most of the Hayes, across the Echimamish River to the upper Nelson River and upstream to Norway House, Manitoba at the north end of Lake Winnipeg. (Close by is the mouth of the Saskatchewan River, used to egress parts of the Prairies].
- Nelson River with Port Nelson just north of the mouth of the Hayes. Although the Nelson drains Lake Winnipeg, this route was avoided in preference to the Hayes.
- Churchill River (Hudson Bay) with Fort Churchill: This route was used mainly by Chipewyans to bring furs down from the rich Athabasca country. The route ran from the east end of Lake Athabasca up the Fond du Lac River (Saskatchewan) to Wollaston Lake and south through Reindeer Lake to the Churchill. This route was used by George Simpson in 1824 but was rarely used by Europeans because the large lakes retain their ice long into the season.
- Inland between the Churchill and Hayes Rivers: Smaller Indian canoes used the Upper and Middle Tracts between the Hayes and Nelson. These routes grew obsolete after 1774 when Cumberland House, Saskatchewan was founded, which allowed transport by heavy freight canoes and York boats.
- Middle Tract: One branch left the Hayes about 100 miles from the Bay and went up the Fox River (Manitoba) and Bigstone River to Utik (Deer) Lake and somehow over to Cross Lake, Manitoba on the Nelson. The other left the Hayes at Oxford Lake and went up the Carrot River and crossed to Walker Lake which connects to Cross Lake about 50 miles west of Oxford Lake. From the west end of Cross Lake, up the Minago River and over a low divide to Moose Lake and along the Summerberry River to the Saskatchewan River.
- Upper Tract: began on the Nelson River at Split Lake, Manitoba, somehow avoiding about 150 difficult miles of the lower Nelson, and went about 200 miles west-southwest up the Grass River, over the Cranberry Portage to the Goose River and down the Goose and Sturgeon-Weir River to Cumberland Lake on the Saskatchewan River about 50 miles west of the start of the Middle Tract.
- Another route connected the Nelson and Churchill. It ran from Split Lake west up the Burntwood River and a portage via the Kississing River to the Churchill and up to Frog Portage.
- North of the Churchill is Barren Grounds.
See also
Siberian River Routes: development of riverine routes in the interior of Siberia.
References
- Butterfield (1898).
- Lass (1980), pp. 37–39, 44.
- Lass (1980), pp. 37–39, 49
- Vogel et al. (1992), pp. E-12, E-13.
- Gilman (1979), pp. 7-8, 14
- Axelson, passim
- Luukkonen, passim
Sources and further reading
- Axelson, Gustave (January–February 2008), "In the Vanishing Footsteps of Voyageurs", Minnesota Conservation Volunteer, 71 (416): 50–63
- Butterfield, Consul Willshire (1898). History of Brulé's discoveries and explorations, 1610-1626
- Eccles, William J (1969). The Canadian Frontier 1534-1760 Reprinted 1974 University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque ISBN 0-8263-0705-1, ISBN 0-8263-0706-X
- Gilman, Rhoda R.; Carolyn Gilman; Deborah M. Stultz (1979). The Red River Trails: Oxcart Routes Between St. Paul and the Selkirk Settlement, 1820–1870. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press. ISBN 0-87351-133-6.
- Lass, William E. (1980). Minnesota's Boundary with Canada. St. Paul, Minnesota: Minnesota Historical Society. ISBN 0-87351-153-0.
- Luukkonen, Larry (2007). Between the Waters: Tracing the Northwest Trail from Lake Superior to the Mississippi. Duluth: Dovetailed Press. ISBN 978-0-9765890-4-4.
- Morse, Eric W (1979). Fur Trade Routes of Canada. Minoqua, WI: NorthWord Press. ISBN 1-55971-045-4.
- Newman, Peter Charles (1989). Empire of the Bay. Madison Press Books.
- Vogel, Robert C.; David G. Stanley (1992). "Portage Trails in Minnesota, 1630s-1870s" (pdf). Multiple Property Documentation Form. US Dept. of the Interior, Nat'l Park Service. Retrieved 6 November 2013.