| Red fox Temporal range: 0.7 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ Middle Pleistocene – present | |
|---|---|

| |
| in Algonquin Provincial Park, Ontario, Canada | |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
 Secure (NatureServe) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Vulpes |
| Species: | V. vulpes |
| Binomial name | |
| Vulpes vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
| Subspecies | |
| 45 subspecies | |
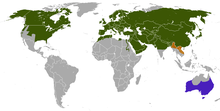
| |
| Distribution of the red fox native introduced presence uncertain | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The red fox (Vulpes vulpes) is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus parts of North Africa. It is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List. Its range has increased alongside human expansion, having been introduced to Australia, where it is considered harmful to native small and medium-sized rodents and marsupials. Due to its impact on native species, it is included on the list of the "world's 100 worst invasive species".
The red fox originated in Eurasia during the Middle Pleistocene at least 400,000 years ago and later colonised North America sometime prior to 130,000 years ago. Among the true foxes, the red fox represents a more progressive form in the direction of carnivory. Apart from its large size, the red fox is distinguished from other fox species by its ability to adapt quickly to new environments. Despite its name, the species often produces individuals with other colourings, including leucistic and melanistic individuals. Forty-five subspecies are currently recognised, which are divided into two categories: the large northern foxes and the small, basal southern grey desert foxes of Asia and North Africa.
Red foxes are usually found in pairs or small groups consisting of families, such as a mated pair and their young, or a male with several females having kinship ties. The young of the mated pair remain with their parents to assist in caring for new kits. The species primarily feeds on small rodents, though it may also target rabbits, squirrels, game birds, reptiles, invertebrates and young ungulates. Fruit and vegetable matter is also eaten sometimes. Although the red fox tends to kill smaller predators, including other fox species, it is vulnerable to attack from larger predators, such as wolves, coyotes, golden jackals, large predatory birds such as golden eagles and Eurasian eagle owls, and medium- and large-sized felids.
The species has a long history of association with humans, having been extensively hunted as a pest and furbearer for many centuries, as well as being represented in human folklore and mythology. Because of its widespread distribution and large population, the red fox is one of the most important furbearing animals harvested for the fur trade. Too small to pose a threat to humans, it has extensively benefited from the presence of human habitation, and has successfully colonised many suburban and urban areas. Domestication of the red fox is also underway in Russia, and has resulted in the domesticated silver fox.
Terminology

Males are called tods or dogs, females are called vixens, and young are known as cubs or kits. Although the Arctic fox has a small native population in northern Scandinavia, and while the corsac fox's range extends into European Russia, the red fox is the only fox native to Western Europe, and so is simply called "the fox" in colloquial British English.
Etymology
The word "fox" comes from Old English, which derived from Proto-Germanic *fuhsaz. Compare with West Frisian foks, Dutch vos, and German Fuchs. This, in turn, derives from Proto-Indo-European *puḱ- 'thick-haired; tail'. Compare to the Hindi pū̃ch 'tail', Tocharian B päkā 'tail; chowrie', and Lithuanian pūkas 'fur / fluff'. The bushy tail also forms the basis for the fox's Welsh name, llwynog, literally 'bushy', from llwyn 'bush'. Likewise, Portuguese: raposa from rabo 'tail', Lithuanian uodẽgis from uodegà 'tail', and Ojibwe waagosh from waa, which refers to the up and down "bounce" or flickering of an animal or its tail.
The scientific term vulpes derives from the Latin word for fox, and gives the adjectives vulpine and vulpecular.
Evolution

The red fox is considered to be a more specialised form of Vulpes than the Afghan, corsac and Bengal fox species, in regards to their overall size and adaptation to carnivory; the skull displays far fewer neotenous traits than in other foxes, and its facial area is more developed. It is, however, not as adapted for a purely carnivorous diet as the Tibetan fox.
The sister lineage to the red fox is the Rüppell's fox, but the two species are surprisingly closely related through mitochondrial DNA markers, with Rüppell's fox nested inside the lineages of red foxes. Such a nesting of one species within another is called paraphyly. Several hypotheses have been suggested to explain this, including (1) recent divergence of Rüppell's fox from a red fox lineage, (2) incomplete lineage sorting, or introgression of mtDNA between the two species. Based on fossil record evidence, the last scenario seems most likely, which is further supported by the clear ecological and morphological differences between the two species.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Origins
The species is Eurasian in origin, and may have evolved from either Vulpes alopecoides or the related Chinese V. chikushanensis, both of which lived during the Middle Villafranchian of the Pleistocene Epoch. The earliest fossil specimens of V. vulpes were uncovered in Baranya County, Hungary, dating from 3.4 to 1.8 million years ago. The ancestral red fox was likely more diminutive compared to today's extant foxes, as the earliest red fox fossils have shown a smaller build than living specimens. The earliest fossil remains of the modern species date back to the mid-Pleistocene, found in association with middens and refuse left by early human settlements. This has led to the theory that the red fox was hunted by primitive humans (as both a source of food and pelts); the possibility also exists of red foxes scavenging from middens or butchered animal carcasses.
Colonisation of North America
Red foxes colonised the North American continent in two waves: before and during the Illinoian glaciation, and during the Wisconsinan glaciation. Gene mapping demonstrates that red foxes in North America have been isolated from their Old World counterparts for over 400,000 years, thus raising the possibility that speciation has occurred, and that the previous binomial name of Vulpes fulva may be valid. In the far north, red fox fossils have been found in Sangamonian Stage deposits near the Fairbanks District, Alaska, and Medicine Hat, Alberta. Fossils dating from the Wisconsinan are present in 25 sites across Arkansas, California, Colorado, Idaho, Missouri, New Mexico, Ohio, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and Wyoming. Although they ranged far south during the Wisconsinan, the onset of warm conditions shrank their range toward the north, and they have only recently reclaimed their former North American ranges because of human-induced environmental changes. Genetic testing indicates that two distinct red fox refugia exist in North America, which have been separated since the Wisconsinan. The northern (or boreal) refugium occurs in Alaska and western Canada, and consists of the larger subspecies V. v. alascensis, V. v. abietorum, V. v. regalis, and V. v. rubricosa. The southern (or montane) refugium occurs in the subalpine parklands and alpine meadows of the west, from the Rocky Mountains to the Cascades and the Sierra Nevada ranges, consisting of the smaller subspecies V. v. cascadensis, V. v. macroura, V. v. necator, and V. v. patwin. The latter clade has been separated from all other red fox populations since at least the last glacial maximum, and may possess unique ecological or physiological adaptations.
Although European foxes (V. v. crucigera) were introduced to portions of the United States in the 1900s, recent genetic investigation indicates an absence of European fox mitochondrial haplotypes in any North American populations. Additionally, introduced eastern North American red foxes have colonised most of inland California, from Southern California to the San Joaquin Valley, Monterey and north-coastal San Francisco Bay Area (including urban San Francisco and adjacent cities). In spite of the red fox's adaptability to city life, they are still found in somewhat greater numbers in the northern portions of California (north of the Bay Area) than in the south, as the wilderness is more alpine and isolated. The eastern red foxes appear to have mixed with the Sacramento Valley red fox (V. v. patwin) only in a narrow hybrid zone. In addition, no evidence is seen of interbreeding of eastern American red foxes in California with the montane Sierra Nevada red fox (V. v. necator) or other populations in the Intermountain West (between the Rocky Mountains to the east and the Cascade and Sierra Nevada Mountains to the west).
Subspecies


The 3rd edition of Mammal Species of the World listed 45 subspecies as valid. In 2010, a distinct 46th subspecies, the Sacramento Valley red fox (V. v. patwin), which inhabits the grasslands of the Sacramento Valley, was identified through mitochondrial haplotype studies. Castello (2018) recognized 30 subspecies of the Old World red fox and nine subspecies of the North American red fox as valid.
Substantial gene pool mixing between different subspecies is known; British red foxes have crossbred extensively with red foxes imported from Germany, France, Belgium, Sardinia and possibly Siberia and Scandinavia. However, genetic studies suggest very little differences between red foxes sampled across Europe. Lack of genetic diversity is consistent with the red fox being a highly agile species, with one red fox covering 320 km (200 mi) in under a year's time.
Red fox subspecies in Eurasia and North Africa are divided into two categories:
- Northern foxes are large and brightly coloured.
- Southern grey desert foxes include the Asian subspecies V. v. griffithi, V. v. pusilla, and V. v. flavescens. These foxes display transitional features between the northern foxes and other, smaller fox species; their skulls possess more primitive, neotenous traits than the northern foxes and they are much smaller; the maximum sizes attained by southern grey desert foxes are invariably less than the average sizes of northern foxes. Their limbs are also longer and their ears larger.
Red foxes living in Middle Asia show physical traits intermediate to the northern foxes and southern grey desert foxes.
| Subspecies | Trinomial authority | Trinomial authority (year) | Description | Range | Synonyms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scandinavian red fox V. v. vulpes (nominate subspecies) |
Linnaeus | 1758 | A large subspecies measuring 70–90 cm in length and weighing 5–10 kg; the maximum length of the skull for males is 163.2 mm. The fur is bright red with a strongly developed whitish and yellow ripple on the lower back. | Scandinavia and the northern and middle (forest) districts of the European part of the former Soviet Union, southwards to the forest-steppe and eastwards approximately to the Urals and probably Central and Western Europe | alopex (Linnaeus, 1758) communis (Burnett, 1829) |
| British Columbia red fox V. v. abietorum |
Merriam | 1900 | Generally similar to V. v. alascensis, but with a lighter, longer and more slender skull | Southern Yukon, the North-West Territories, northern Alberta, the interior of British Columbia and in the adjoining coastal southeast Alaska (US). | sitkaensis (Brass, 1911) |
| Northern Alaskan fox V. v. alascensis |
Merriam | 1900 | A large, long-tailed, small-eared form with golden-fulvous fur | The Andreafsky Wilderness, Alaska, U.S. | |
| Eastern Transcaucasian fox V. v. alpherakyi |
Satunin | 1906 | A small subspecies weighing 4 kg; its maximum skull length is 132–39 mm in males and 121–26 mm in females. The fur is rusty grey or rusty brown, with a brighter rusty stripe along the spine. The coat is short, coarse and sparse. | Geok Tepe, Aralsk, Kazakhstan | |
| Anatolian fox V. v. anatolica |
Thomas | 1920 | İzmir, the Aegean Region, Turkey | ||
| Arabian red fox V. v. arabica |
Thomas | 1920 | Dhofar and the Hajar Mountains, Oman | ||
| Atlas fox V. v. atlantica |
Wagner | 1841 | The Atlas Mountains, Mila Province, Algeria | algeriensis (Loche, 1858) | |
| Labrador fox V. v. bangsi |
Merriam | 1900 | Similar to V. v. fulva, but with smaller ears and less pronounced black markings on the ears and legs. | L'Anse au Loup, the Strait of Belle Isle, Labrador, Canada | |
| Barbary fox V. v. barbara |
Shaw | 1800 | The Barbary Coast, northwestern Africa | acaab (Cabrera, 1916) | |
| Anadyr fox V. v. beringiana |
Middendorff | 1875 | A large subspecies; it is the most brightly coloured of the Old World red foxes, the fur being saturated bright-reddish and almost lacking the bright ripple along the back and flanks. The coat is fluffy and soft. | The shores of the Bering Strait, northeastern Siberia | anadyrensis (J. A. Allen, 1903) beringensis (Merriam, 1902) |
| Cascade red fox V. v. cascadensis |
Merriam | 1900 | A short-tailed, small-toothed subspecies with yellow rather than fulvous fur; it is the subspecies most likely to produce "cross" colour morphs. | The Cascade Mountains, Skamania County, Washington, U.S. | |
| North Caucasian fox V. v. caucasica |
Dinnik | 1914 | A large subspecies; its coat is variable in colour, ranging from reddish to red-grey and nearly grey. The fur is short and coarse. This subspecies could be a hybrid caused by mixing the populations of V. v. stepensis and V. v. karagan. | Near Vladikavkaz, the Caucasus, Russia | |
| European fox V. v. crucigera |
Bechstein | 1789 | A medium-sized subspecies; its yellowish-fulvous or reddish-brown pelt lacks the whitish shading on the upper back. The tail is not grey, as in most other red fox subspecies. It is primarily distinguished from V. v. vulpes by its slightly smaller size, distinctly smaller teeth and widely spaced premolars. Red foxes present in Great Britain (and therefore Australia) are usually ascribed to this subspecies, though many populations there display a great degree of tooth compaction not present in continental European red fox populations. | All of Europe except Scandinavia, the Iberian Peninsula and some islands of the Mediterranean Sea; introduced to Australia and North America | alba (Borkhausen, 1797) cinera (Bechstein, 1801) |
| Trans-Baikal fox V. v. daurica |
Ognev | 1931 | A large subspecies; the colour along its spine is light, dull yellowish-reddish with a strongly developed white ripple and greyish longitudinal stripes on the anterior side of the limbs. The coat is coarse but fluffy. | Kharangoi, 45 km west of Troizkosavsk, Siberia | ussuriensis (Dybowski, 1922) |
| Newfoundland fox V. v. deletrix |
Bangs | 1898 | A very pale-coloured form; its light, straw-yellow fur deepens to golden yellow or buff-fulvous in some places. The tail lacks the usual black basal spot. The hind feet and claws are very large. | St. George's Bay, Newfoundland, Canada | |
| Ussuri fox V. v. dolichocrania |
Ognev | 1926 | Sidemi, southern Ussuri, southeastern Siberia | ognevi (Yudin, 1986) | |
| V. v. dorsalis | J. E. Gray | 1838 | |||
| Turkmenian fox V. v. flavescens |
J. E. Gray | 1838 | A small subspecies with an infantile-looking skull and an overall grey-coloured coat; its body length is 49–57.5 cm and it weighs 2.2–3.2 kg. | Northern Iran | cinerascens (Birula, 1913) splendens (Thomas, 1902) |
| American red fox V. v. fulva |
Desmarest | 1820 | This is a smaller subspecies than V. v. vulpes, with a smaller, sharper face, a shorter tail, a lighter pelt more profusely mixed with whitish and darker limbs. | Eastern Canada and the eastern U.S. | pennsylvanicus (Rhoads, 1894) |
| Afghan red fox V. v. griffithi |
Blyth | 1854 | Slightly smaller than V. v. montana; it has a more extensively hoary and silvered pelt. | Kandahar, Afghanistan | flavescens (Hutton, 1845) |
| Kodiak fox V. v. harrimani |
Merriam | 1900 | This large subspecies has an enormous tail and coarse, wolf-like fur on the tail and lower back. The hairs on the neck and shoulders are greatly elongated and form a ruff. | Kodiak Island, Alaska, U.S. | |
| South Chinese fox V. v. hoole |
R. Swinhoe | 1870 | Near Amoy, Fukien, southern China | aurantioluteus (Matschie, 1907) lineiventer (R. Swinhoe, 1871) | |
| Sardinian fox V. v. ichnusae |
Miller | 1907 | A small subspecies with proportionately small ears. | Sarrabus, Sardinia, Italy; may have been introduced to the English Midlands | |
| Cyprus fox V. v. indutus |
Miller | 1907 | Cape Pyla, Cyprus | ||
| Yakutsk fox V. v. jakutensis |
Ognev | 1923 | This subspecies is large, but smaller than V. v. beringiana. The back, neck and shoulders are brownish-rusty, while the flanks are bright ocherous reddish-yellow. | The taiga south of Yakutsk, eastern Siberia | sibiricus (Dybowski, 1922) |
| Japanese fox V. v. japonica |
Ognev | 1923 | Japan, except for Hokkaido | ||
| Karaganka fox V. v. karagan |
Erxleben | 1777 | A smaller subspecies than V. v. vulpes; its fur is short, coarse and of a light sandy-yellow or yellowish-grey colour. | The Kirghiz Steppes, Khirgizia, Russia | ferganensis (Ognev, 1926) melanotus (Pallas, 1811) |
| Kenai Peninsula fox V. v. kenaiensis |
Merriam | 1900 | One of the largest North American subspecies; it has softer fur than V. v. harrimani. | The Kenai Peninsula, Alaska, U.S. | |
| Transcaucasian montane fox V. v. kurdistanica |
Satunin | 1906 | A form intermediate in size between V. v. alpheryaki and V. v. caucasica; its fur is pale yellow or light grey, sometimes brownish-reddish and is fluffier and denser than that of the other two Caucasian red fox subspecies. | Northeastern Turkey | alticola (Ognev, 1926) |
| Wasatch Mountains fox V. v. macroura |
Baird | 1852 | This fox is similar to V. v. fulvus, but with a much longer tail, larger hind feet and more extensive blackening of the limbs. | Named for the Wasatch Mountains near the Great Salt Lake, Utah, found in the Rocky Mountains from Colorado and Utah, western Wyoming and Montana through Idaho north to southern Alberta | |
| Hill fox V. v. montana |
Pearson | 1836 | This subspecies is distinguished from V. v. vulpes by its smaller size, proportionately smaller skull and teeth and coarser fur. The hairs on the sole of the feet are copiously mixed with softer, woolly hairs. | The Himalayas and northern Indian subcontinent | alopex (Blanford, 1888) himalaicus (Ogilby, 1837) |
| Sierra Nevada red fox or High Sierra fox V. v. necator |
Merriam | 1900 | Externally similar to V. v. fulvus; it has a short tail, but cranially it is more like V. v. macroura | The High Sierra, California | |
| Nile fox V. v. niloticus |
E. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire | 1803 | A small subspecies; it measures 76.7–105.3 cm in body length, 30.2–40.1 cm in tail length and weighs 1.8–3.8 kg. It is ruddy to grey-brown above and darker on the back of the neck. The flanks are greyer and tinged with buff. It is larger than V. v. arabica and V. v. palaestina. | Egypt and Sudan | aegyptiacus (Sonnini, 1816) anubis (Hemprich and Ehrenberg, 1833) |
| Turkestan fox V. v. ochroxantha |
Ognev | 1926 | Aksai, Semirechye, eastern Russian Turkestan, Kirgizia | ||
| Palestinian fox V. v. palaestina |
Thomas | 1920 | Ramleh, near Jaffa, Israel | ||
| Korean fox V. v. peculiosa |
Kishida | 1924 | Northeastern China, Southeastern Russia, and Korea | kiyomassai (Kishida and Mori, 1929) | |
| White-footed fox V. v. pusilla |
Blyth | 1854 | Slightly smaller than V. v. griffithii; it closely resembles the Bengal fox (V. bengalensis) in size, but is distinguished by its longer tail and hind feet. | The Salt Range, Punjab, Pakistan | leucopus (Blyth, 1854) persicus (Blanford, 1875) |
| Northern plains fox V. v. regalis |
Merriam | 1900 | The largest North American red fox subspecies; it has very large and broad ears and a very long tail. It is a golden-yellow colour with pure black feet. | The Elk River, Sherburne County, Minnesota, US | |
| Nova Scotia fox V. v. rubricosa |
Bangs | 1898 | A large-sized subspecies with a large, broad tail and larger teeth and rostrum than V. v. fulvus; it is the deepest-coloured subspecies. | Digby County, Nova Scotia, Canada | bangsi (Merriam, 1900) deletrix (Bangs, 1898) |
| Ezo red fox V. v. schrencki |
Kishida | 1924 | Sakhalin, Russia and Hokkaido, Japan | ||
| Iberian fox V. v. silacea |
Miller | 1907 | Though equal in size to V. v. vulpes, it has smaller teeth and more widely spaced premolars. The fur is dull buff without any yellowish or reddish tints. The hindquarters are frosted with white and the tail is clear grey in colour. | The Iberian Peninsula | |
| Kurile Islands fox V. v. splendidissima |
Kishida | 1924 | The northern and central Kurile Islands, Russia | ||
| Steppe red fox V. v. stepensis |
Brauner | 1914 | This subspecies is slightly smaller and more lightly coloured than V. v. crucigera, with shorter, coarser fur. Specimens from the Crimean Mountains have brighter, fluffier and denser fur. | The steppes near Kherson, Ukraine | krymeamontana (Brauner, 1914) crymensis (Brauner, 1914) |
| Tobolsk fox V. v. tobolica |
Ognev | 1926 | This large subspecies has yellowish-rusty or dirty-reddish fur with a well-developed cross and often a black area on the belly. The coat is long and fluffy. | Obdorsk, Tobolsk, Russia | |
| North Chinese fox V. v. tschiliensis |
Matschie | 1907 | Slightly larger than V. v. hoole, but unlike other Chinese red foxes, it closely approaches V. v. vulpes in size. | Beijing and Hebei province, China | huli (Sowerby, 1923) |
Description
Build

The red fox has an elongated body and relatively short limbs. The tail, which is longer than half the body length (70 percent of head and body length), is fluffy and reaches the ground when in a standing position. Their pupils are oval and vertically oriented. Nictitating membranes are present, but move only when the eyes are closed. The forepaws have five digits, while the hind feet have only four and lack dewclaws. They are very agile, being capable of jumping over 2 m (6 ft 7 in) high fences, and swim well. Vixens normally have four pairs of teats, though vixens with seven, nine, or ten teats are not uncommon. The testes of males are smaller than those of Arctic foxes.
Their skulls are fairly narrow and elongated, with small braincases. Their canine teeth are relatively long. Sexual dimorphism of the skull is more pronounced than in corsac foxes, with female red foxes tending to have smaller skulls than males, with wider nasal regions and hard palates, as well as having larger canines. Their skulls are distinguished from those of dogs by their narrower muzzles, less crowded premolars, more slender canine teeth, and concave rather than convex profiles.
Dimensions
Red foxes are the largest species of the genus Vulpes. However, relative to dimensions, red foxes are much lighter than similarly sized dogs of the genus Canis. Their limb bones, for example, weigh 30 percent less per unit area of bone than expected for similarly sized dogs. They display significant individual, sexual, age and geographical variation in size. On average, adults measure 35–50 cm (14–20 in) high at the shoulder and 45–90 cm (18–35 in) in body length with tails measuring 30–55.5 cm (11.8–21.9 in). The ears measure 7.7–12.5 cm (3.0–4.9 in) and the hind feet 12–18.5 cm (4.7–7.3 in). Weights range from 2.2–14 kg (4.9–30.9 lb), with vixens typically weighing 15–20% less than males. Adult red foxes have skulls measuring 129–167 mm (5.1–6.6 in), while those of vixens measure 128–159 mm (5.0–6.3 in). The forefoot print measures 60 mm (2.4 in) in length and 45 mm (1.8 in) in width, while the hind foot print measures 55 mm (2.2 in) long and 38 mm (1.5 in) wide. They trot at a speed of 6–13 km/h (3.7–8.1 mph), and have a maximum running speed of 50 km/h (31 mph). They have a stride of 25–35 cm (9.8–13.8 in) when walking at a normal pace. North American red foxes are generally lightly built, with comparatively long bodies for their mass and have a high degree of sexual dimorphism. British red foxes are heavily built, but short, while continental European red foxes are closer to the general average among red fox populations. The largest red fox on record in Great Britain was a 1.4 m (4 ft 7 in) long male, that weighed 17.2 kg (38 lb), killed in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, in early 2012.
Fur

The winter fur is dense, soft, silky and relatively long. For the northern foxes, the fur is very long, dense and fluffy, but it is shorter, sparser and coarser in southern forms. Among northern foxes, the North American varieties generally have the silkiest guard hairs, while most Eurasian red foxes have coarser fur. The fur in "thermal windows" areas such as the head and the lower legs is kept dense and short all year round, while fur in other areas changes with the seasons. The foxes actively control the peripheral vasodilation and peripheral vasoconstriction in these areas to regulate heat loss. There are three main colour morphs; red, silver/black and cross (see Mutations). In the typical red morph, their coats are generally bright reddish-rusty with yellowish tints. A stripe of weak, diffuse patterns of many brown-reddish-chestnut hairs occurs along the spine. Two additional stripes pass down the shoulder blades, which, together with the spinal stripe, form a cross. The lower back is often a mottled silvery colour. The flanks are lighter coloured than the back, while the chin, lower lips, throat and front of the chest are white. The remaining lower surface of the body is dark, brown or reddish. During lactation, the belly fur of vixens may turn brick red. The upper parts of the limbs are rusty reddish, while the paws are black. The frontal part of the face and upper neck is bright brownish-rusty red, while the upper lips are white. The backs of the ears are black or brownish-reddish, while the inner surface is whitish. The top of the tail is brownish-reddish, but lighter in colour than the back and flanks. The underside of the tail is pale grey with a straw-coloured tint. A black spot, the location of the supracaudal gland, is usually present at the base of the tail. The tip of the tail is white.
Colour morphs

Atypical colouration in the red fox usually represents stages toward full melanism, and mostly occurs in cold regions.
| Colour morph | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Red | 
|
The typical colouration (see fur above) |
| Smokey | The rump and spine is brown or grey with light yellowish bands on the guard hairs. The cross on the shoulders is brown, rusty brown or reddish-brown. The limbs are brown. | |
| Cross | 
|
The fur has a darker colouration than the colour morph listed directly above. The rump and lower back are dark brown or dark grey, with varying degrees of silver on the guard hairs. The cross on the shoulders is black or brown, sometimes with light silvery fur. The head and feet are brown. |
| Blackish-brown | The melanistic colour morph of the Eurasian red foxes. Has blackish-brown or black skin with a light brownish tint. The skin area usually has a variable admixture of silver. Reddish hairs are either completely absent or in small quantities. | |
| Silver | 
|
The melanistic colour morph of the North American red foxes, but introduced to the Old World by the fur trade. Characterised by pure black colour with skin that usually has a variable admixture of silver (covering 25–100% of the skin area) |
| Platinum | 
|
Distinguished from the silver colour morph by its pale, almost silvery-white fur with a bluish cast |
| Amber | 
|
|
| Samson | 
|
Distinguished by its woolly pelt, which lacks guard hairs |
Senses
Red foxes have binocular vision, but their sight reacts mainly to movement. Their auditory perception is acute, being able to hear black grouse changing roosts at 600 paces, the flight of crows at 0.25–0.5 km (0.16–0.31 mi) and the squeaking of mice at about 100 m (330 ft). They are capable of locating sounds to within one degree at 700–3,000 Hz, though less accurately at higher frequencies. Their sense of smell is good, but weaker than that of specialised dogs.
Scent glands
Red foxes have a pair of anal sacs lined by sebaceous glands, both of which open through a single duct. The size and volume of the anal sacs increases with age, ranging in size from 5–40mm in length, 1–3mm in diameter, and with a capacity of 1–5 mL. The anal sacs act as fermentation chambers in which aerobic and anaerobic bacteria convert sebum into odorous compounds, including aliphatic acids. The oval-shaped caudal gland is 25 mm (0.98 in) long and 13 mm (0.51 in) wide, and reportedly smells of violets. The presence of foot glands is equivocal. The interdigital cavities are deep, with a reddish tinge and smell strongly. Sebaceous glands are present on the angle of the jaw and mandible.
Distribution and habitat

The red fox is a wide-ranging species. Its range covers nearly 70,000,000 km (27,000,000 sq mi) including as far north as the Arctic Circle. It occurs all across Europe, in Africa north of the Sahara Desert, throughout Asia apart from extreme Southeast Asia, and across North America apart from most of the southwestern United States and Mexico. It is absent in Greenland, Iceland, the Arctic islands, the most northern parts of central Siberia, and in extreme deserts. It is not present in New Zealand and is classed as a "prohibited new organism" under the Hazardous Substances and New Organisms Act 1996, which does not allow import.
Australia
Main article: Feral foxes in AustraliaIn Australia, estimates in 2012 indicated that there were more than 7.2 million red foxes, with a range extending throughout most of the continental mainland. They became established in Australia through successive introductions in the 1830s and 1840s, by settlers in the British colonies of Van Diemen's Land (as early as 1833) and the Port Phillip District of New South Wales (as early as 1845), who wanted to foster the traditional English sport of fox hunting. A permanent red fox population did not establish itself on the island of Tasmania, and it is widely held that foxes were out-competed by the Tasmanian devil. On the mainland, however, the species was successful as an apex predator. The fox is generally less common in areas where the dingo is more prevalent, but it has, primarily through its burrowing behaviour, achieved niche differentiation with both the feral dog and the feral cat. Consequently, the fox has become one of the continent's most destructive invasive species.
The red fox has been implicated in the extinction or decline of several native Australian species, particularly those of the family Potoroidae, including the desert rat-kangaroo. The spread of red foxes across the southern part of the continent has coincided with the spread of rabbits in Australia, and corresponds with declines in the distribution of several medium-sized ground-dwelling mammals, including brush-tailed bettongs, burrowing bettongs, rufous bettongs, bilbies, numbats, bridled nail-tail wallabies and quokkas. Most of those species are now limited to areas (such as islands) where red foxes are absent or rare. Local fox eradication programs exist, although elimination has proven difficult due to the fox's denning behaviour and nocturnal hunting, so the focus is on management, including the introduction of state bounties. According to the Tasmanian government, red foxes were accidentally introduced to the previously fox-free island of Tasmania in 1999 or 2000, posing a significant threat to native wildlife, including the eastern bettong, and an eradication program was initiated, conducted by the Tasmanian Department of Primary Industries and Water.
Sardinia, Italy
The origin of the ichnusae subspecies in Sardinia, Italy is uncertain, as it is absent from Pleistocene deposits in their current homeland. It is possible it originated during the Neolithic following its introduction to the island by humans. It is likely then that Sardinian fox populations stem from repeated introductions of animals from different localities in the Mediterranean. This latter theory may explain the subspecies' phenotypic diversity.
Behaviour
Social and territorial behaviour
 Red fox pressed against the trunk of a pine tree in Ilmatsalu, Estonia
Red fox pressed against the trunk of a pine tree in Ilmatsalu, Estonia Red foxes grooming each other
Red foxes grooming each other A pair of European red foxes (V. v. crucigera) at the British Wildlife Centre, Surrey, England
A pair of European red foxes (V. v. crucigera) at the British Wildlife Centre, Surrey, England

Red foxes either establish stable home ranges within particular areas or are itinerant with no fixed abode. They use their urine to mark their territories. A male fox raises one hind leg and his urine is sprayed forward in front of him, whereas a female fox squats down so that the urine is sprayed in the ground between the hind legs. Urine is also used to mark empty cache sites, used to store found food, as reminders not to waste time investigating them. Males generally have higher urine marking rates during late summer and autumn, but the rest of the year the rates between male and female are similar. The use of up to 12 different urination postures allows them to precisely control the position of the scent mark. Red foxes live in family groups sharing a joint territory. In favourable habitats and/or areas with low hunting pressure, subordinate foxes may be present in a range. Subordinate foxes may number one or two, sometimes up to eight in one territory. These subordinates could be formerly dominant animals, but are mostly young from the previous year, who act as helpers in rearing the breeding vixen's kits. Alternatively, their presence has been explained as being in response to temporary surpluses of food unrelated to assisting reproductive success. Non-breeding vixens will guard, play, groom, provision and retrieve kits, an example of kin selection. Red foxes may leave their families once they reach adulthood if the chances of winning a territory of their own are high. If not, they will stay with their parents, at the cost of postponing their own reproduction.
Reproduction and development
Further information: Mating behavior of melanistic red foxes

 Red fox kits
Red fox kits

Red foxes reproduce once a year in spring. Two months prior to oestrus (typically December), the reproductive organs of vixens change shape and size. By the time they enter their oestrus period, their uterine horns double in size, and their ovaries grow 1.5–2 times larger. Sperm formation in males begins in August–September, with the testicles attaining their greatest weight in December–February. The vixen's oestrus period lasts three weeks, during which the dog-foxes mate with the vixens for several days, often in burrows. The male's bulbus glandis enlarges during copulation, forming a copulatory tie which may last for more than an hour. The gestation period lasts 49–58 days. Though foxes are largely monogamous, DNA evidence from one population indicated large levels of polygyny, incest and mixed paternity litters. Subordinate vixens may become pregnant, but usually fail to whelp, or have their kits killed postpartum by either the dominant female or other subordinates.
The average litter size consists of four to six kits, though litters of up to 13 kits have occurred. Large litters are typical in areas where fox mortality is high. Kits are born blind, deaf and toothless, with dark brown fluffy fur. At birth, they weigh 56–110 g (2.0–3.9 oz) and measure 14.5 cm (5.7 in) in body length and 7.5 cm (3.0 in) in tail length. At birth, they are short-legged, large-headed and have broad chests. Mothers remain with the kits for 2–3 weeks, as they are unable to thermoregulate. During this period, the fathers or barren vixens feed the mothers. Vixens are very protective of their kits, and have been known to even fight off terriers in their defence. If the mother dies before the kits are independent, the father takes over as their provider. The kits' eyes open after 13–15 days, during which time their ear canals open and their upper teeth erupt, with the lower teeth emerging 3–4 days later. Their eyes are initially blue, but change to amber at 4–5 weeks. Coat colour begins to change at three weeks of age, when the black eye streak appears. By one month, red and white patches are apparent on their faces. During this time, their ears erect and their muzzles elongate. Kits begin to leave their dens and experiment with solid food brought by their parents at the age of 3–4 weeks. The lactation period lasts 6–7 weeks. Their woolly coats begin to be coated by shiny guard hairs after 8 weeks. By the age of 3–4 months, the kits are long-legged, narrow-chested and sinewy. They reach adult proportions at the age of 6–7 months. Some vixens may reach sexual maturity at the age of 9–10 months, thus bearing their first litters at one year of age. In captivity, their longevity can be as long as 15 years, though in the wild they typically do not survive past 5 years of age.
Denning behaviour

Outside the breeding season, most red foxes favour living in the open, in densely vegetated areas, though they may enter burrows to escape bad weather. Their burrows are often dug on hill or mountain slopes, ravines, bluffs, steep banks of water bodies, ditches, depressions, gutters, in rock clefts and neglected human environments. Red foxes prefer to dig their burrows on well drained soils. Dens built among tree roots can last for decades, while those dug on the steppes last only several years. They may permanently abandon their dens during mange outbreaks, possibly as a defence mechanism against the spread of disease. In the Eurasian desert regions, foxes may use the burrows of wolves, porcupines and other large mammals, as well as those dug by gerbil colonies. Compared to burrows constructed by Arctic foxes, badgers, marmots and corsac foxes, red fox dens are not overly complex. Red fox burrows are divided into a den and temporary burrows, which consist only of a small passage or cave for concealment. The main entrance of the burrow leads downwards (40–45°) and broadens into a den, from which numerous side tunnels branch. Burrow depth ranges from 0.5–2.5 m (1 ft 8 in – 8 ft 2 in), rarely extending to ground water. The main passage can reach 17 m (56 ft) in length, standing an average of 5–7 m (16–23 ft). In spring, red foxes clear their dens of excess soil through rapid movements, first with the forepaws then with kicking motions with their hind legs, throwing the discarded soil over 2 m (6 ft 7 in) from the burrow. When kits are born, the discarded debris is trampled, thus forming a spot where the kits can play and receive food. They may share their dens with woodchucks or badgers. Unlike badgers, which fastidiously clean their earths and defecate in latrines, red foxes habitually leave pieces of prey around their dens. The average sleep time of a captive red fox is 9.8 hours per day.
Communication
Body language

Red fox body language consists of movements of the ears, tail and postures, with their body markings emphasising certain gestures. Postures can be divided into aggressive/dominant and fearful/submissive categories. Some postures may blend the two together. Inquisitive foxes will rotate and flick their ears whilst sniffing. Playful individuals will perk their ears and rise on their hind legs. Male foxes courting females, or after successfully evicting intruders, will turn their ears outwardly, and raise their tails in a horizontal position, with the tips raised upward. When afraid, red foxes grin in submission, arching their backs, curving their bodies, crouching their legs and lashing their tails back and forth with their ears pointing backwards and pressed against their skulls. When merely expressing submission to a dominant animal, the posture is similar, but without arching the back or curving the body. Submissive foxes will approach dominant animals in a low posture, so that their muzzles reach up in greeting. When two evenly matched foxes confront each other over food, they approach each other sideways and push against each other's flanks, betraying a mixture of fear and aggression through lashing tails and arched backs without crouching and pulling their ears back without flattening them against their skulls. When launching an assertive attack, red foxes approach directly rather than sideways, with their tails aloft and their ears rotated sideways. During such fights, red foxes will stand on each other's upper bodies with their forelegs, using open mouthed threats. Such fights typically only occur among juveniles or adults of the same sex.
Vocalisations


Problems playing this file? See media help.
Red foxes have a wide vocal range, and produce different sounds spanning five octaves, which grade into each other. Recent analyses identify 12 different sounds produced by adults and 8 by kits. The majority of sounds can be divided into "contact" and "interaction" calls. The former vary according to the distance between individuals, while the latter vary according to the level of aggression.
- Contact calls: The most commonly heard contact call is a three to five syllable barking "wow wow wow" sound, which is often made by two foxes approaching one another. This call is most frequently heard from December to February (when they can be confused with the territorial calls of tawny owls). The "wow wow wow" call varies according to individual; captive foxes have been recorded to answer pre-recorded calls of their pen-mates, but not those of strangers. Kits begin emitting the "wow wow wow" call at the age of 19 days, when craving attention. When red foxes draw close together, they emit trisyllabic greeting warbles similar to the clucking of chickens. Adults greet their kits with gruff huffing noises.
- Interaction calls: When greeting one another, red foxes emit high pitched whines, particularly submissive animals. A submissive fox approached by a dominant animal will emit a ululating siren-like shriek. During aggressive encounters with conspecifics, they emit a throaty rattling sound, similar to a ratchet, called "gekkering". Gekkering occurs mostly during the courting season from rival males or vixens rejecting advances.
Another call that does not fit into the two categories is a long, drawn-out, monosyllabic "waaaaah" sound. As it is commonly heard during the breeding season, it is thought to be emitted by vixens summoning males. When danger is detected, foxes emit a monosyllabic bark. At close quarters, it is a muffled cough, while at long distances it is sharper. Kits make warbling whimpers when nursing, these calls being especially loud when they are dissatisfied.
Ecology
Diet, hunting and feeding behaviour

Red foxes are omnivores with a highly varied diet. Research conducted in the former Soviet Union showed red foxes consuming over 300 animal species and a few dozen species of plants. They primarily feed on small rodents like voles, mice, ground squirrels, hamsters, gerbils, woodchucks, pocket gophers and deer mice. Secondary prey species include birds (with Passeriformes, Galliformes and waterfowl predominating), leporids, porcupines, raccoons, opossums, reptiles, insects, other invertebrates, flotsam (marine mammals, fish and echinoderms) and carrion. On very rare occasions, foxes may attack young or small ungulates. They typically target mammals up to about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) in weight, and they require 500 g (18 oz) of food daily. Red foxes readily eat plant material and in some areas fruit can amount to 100% of their diet in autumn. Commonly consumed fruits include blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, cherries, persimmons, mulberries, apples, plums, grapes and acorns. Other plant material includes grasses, sedges and tubers.
Red foxes are implicated in the predation of game and song birds, hares, rabbits, muskrats and young ungulates, particularly in preserves, reserves and hunting farms where ground-nesting birds are protected and raised, as well as in poultry farms.
While the popular consensus is that olfaction is very important for hunting, two studies that experimentally investigated the role of olfactory, auditory and visual cues found that visual cues are the most important ones for hunting in red foxes and coyotes.
Red foxes prefer to hunt in the early morning hours before sunrise and late evening. Although they typically forage alone, they may aggregate in resource-rich environments. When hunting mouse-like prey, they first pinpoint their prey's location by sound, then leap, sailing high above their quarry, steering in mid-air with their tails, before landing on target up to 5 m (16 ft) away. They typically only feed on carrion in the late evening hours and at night. They are extremely possessive of their food and will defend their catches from even dominant animals. Red foxes may occasionally commit acts of surplus killing; during one breeding season, four red foxes were recorded to have killed around 200 black-headed gulls each, with peaks during dark, windy hours when flying conditions were unfavourable. Losses to poultry and penned game birds can be substantial because of this. Red foxes seem to dislike the taste of moles, but will nonetheless catch them alive and present them to their kits as playthings.
A 2008–2010 study of 84 red foxes in the Czech Republic and Germany found that successful hunting in long vegetation or under snow appeared to involve an alignment of the red fox with the Earth's magnetic field.
Enemies and competitors

Red foxes typically dominate other fox species. Arctic foxes generally escape competition from red foxes by living farther north, where food is too scarce to support the larger-bodied red species. Although the red species' northern limit is linked to the availability of food, the Arctic species' southern range is limited by the presence of the former. Red and Arctic foxes were both introduced to almost every island from the Aleutian Islands to the Alexander Archipelago during the 1830s–1930s by fur companies. The red foxes invariably displaced the Arctic foxes, with one male red fox having been reported to have killed off all resident Arctic foxes on a small island in 1866. Where they are sympatric, Arctic foxes may also escape competition by feeding on lemmings and flotsam rather than voles, as favoured by red foxes. Both species will kill each other's kits, given the opportunity. Red foxes are serious competitors of corsac foxes, as they hunt the same prey all year. The red species is also stronger, is better adapted to hunting in snow deeper than 10 cm (3.9 in) and is more effective in hunting and catching medium-sized to large rodents. Corsac foxes seem to only outcompete red foxes in semi-desert and steppe areas. In Israel, Blanford's foxes escape competition with red foxes by restricting themselves to rocky cliffs and actively avoiding the open plains inhabited by red foxes. Red foxes dominate kit and swift foxes. Kit foxes usually avoid competition with their larger cousins by living in more arid environments, though red foxes have been increasing in ranges formerly occupied by kit foxes due to human-induced environmental changes. Red foxes will kill both species and compete with them for food and den sites. Grey foxes are exceptional, as they dominate red foxes wherever their ranges meet. Historically, interactions between the two species were rare, as grey foxes favoured heavily wooded or semiarid habitats as opposed to the open and mesic ones preferred by red foxes. However, interactions have become more frequent due to deforestation, allowing red foxes to colonise grey fox-inhabited areas.

Wolves may kill and eat red foxes in disputes over carcasses. In areas in North America where red fox and coyote populations are sympatric, red fox ranges tend to be located outside coyote territories. The principal cause of this separation is believed to be active avoidance of coyotes by the red foxes. Interactions between the two species vary in nature, ranging from active antagonism to indifference. The majority of aggressive encounters are initiated by coyotes, and there are few reports of red foxes acting aggressively toward coyotes except when attacked or when their kits were approached. Foxes and coyotes have sometimes been seen feeding together. In Israel, red foxes share their habitat with golden jackals. Where their ranges meet, the two canids compete due to near-identical diets. Red foxes ignore golden jackal scents or tracks in their territories and avoid close physical proximity with golden jackals themselves. In areas where golden jackals become very abundant, the population of red foxes decreases significantly, apparently because of competitive exclusion. However, there is one record of multiple red foxes interacting peacefully with a golden jackal in southwestern Germany.

Red foxes dominate raccoon dogs, sometimes killing their kits or biting adults to death. Cases are known of red foxes killing raccoon dogs after entering their dens. Both species compete for mouse-like prey. This competition reaches a peak during early spring when food is scarce. In Tatarstan, red fox predation accounted for 11.1% of deaths among 54 raccoon dogs and amounted to 14.3% of 186 raccoon dog deaths in northwestern Russia.
Red foxes may kill small mustelids like weasels, stone martens, pine martens (martes martes), stoats, Siberian weasels, polecats and young sables. Eurasian badgers may live alongside red foxes in isolated sections of large burrows. It is possible that the two species tolerate each other out of mutualism; red foxes provide Eurasian badgers with food scraps, while Eurasian badgers maintain the shared burrow's cleanliness. However, cases are known of Eurasian badgers driving vixens from their dens and destroying their litters without eating them. Wolverines may kill red foxes, often while the latter is sleeping or near carrion. Red foxes, in turn, may kill young wolverines.
Red foxes may compete with striped hyenas on large carcasses. Red foxes may give way to striped hyenas on unopened carcasses, as the latter's stronger jaws can easily tear open flesh that is too tough for red foxes. Red foxes may harass striped hyenas, using their smaller size and greater speed to avoid the hyena's attacks. Sometimes, red foxes seem to deliberately torment striped hyenas even when there is no food at stake. Some red foxes may mistime their attacks and are killed. Red fox remains are often found in striped hyena dens and striped hyenas may steal red foxes from traps.
In Eurasia, red foxes may be preyed upon by leopards, caracals and Eurasian lynxes. The Eurasian lynxes chase red foxes into deep snow, where their long legs and larger paws give them an advantage over red foxes, especially when the depth of the snow exceeds one meter. In the Velikoluksky District in Russia, red foxes are absent or are seen only occasionally where Eurasian lynxes establish permanent territories. Researchers consider Eurasian lynxes to represent considerably less danger to red foxes than wolves do. North American felid predators of red foxes include cougars, Canada lynxes and bobcats.
Red foxes compete with various birds of prey such as common buzzards (Buteo buteo) and northern goshawks (Accipiter gentilis) and even steal their kills. In turn, golden eagles (Aquila chrysaetos) regularly takes young red foxes and prey on adults if needed. Other large eagles such as wedge-tailed eagles (Aquila audax), eastern imperial eagles (Aquila heliaca), white-tailed eagles (Haliaeetus albicilla), and steller's sea eagles (Haliaeetus pelagicus) have also been known to kill red foxes less frequently. Additionally, large owls such as Eurasian eagle-owls (Bubo bubo) and snowy owls (Bubo scandiacus) will prey on young foxes, and adults on exceptional occasions.
Diseases and parasites

Red foxes are the most important rabies vector in Europe. In London, arthritis is common in foxes, being particularly frequent in the spine. Foxes may be infected with leptospirosis and tularemia, though they are not overly susceptible to the latter. They may also fall ill from listeriosis and spirochetosis, as well as acting as vectors in spreading erysipelas, brucellosis and tick-borne encephalitis. A mysterious fatal disease near Lake Sartlan in the Novosibirsk Oblast was noted among local red foxes, but the cause was undetermined. The possibility was considered that it was caused by an acute form of encephalomyelitis, which was first observed in captive-bred silver foxes. Individual cases of foxes infected with Yersinia pestis are known.
Red foxes are not readily prone to infestation with fleas. Species like Spilopsyllus cuniculi are probably only caught from the fox's prey species, while others like Archaeopsylla erinacei are caught whilst traveling. Fleas that feed on red foxes include Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides canis and Paraceras melis. Ticks such as Ixodes ricinus and I. hexagonus are not uncommon in red foxes, and are typically found on nursing vixens and kits still in their earths. The louse Trichodectes vulpis specifically targets red foxes, but is found infrequently. The mite Sarcoptes scabiei is the most important cause of mange in red foxes. It causes extensive hair loss, starting from the base of the tail and hindfeet, then the rump before moving on to the rest of the body. In the final stages of the condition, red foxes can lose most of their fur, 50% of their body weight and may gnaw at infected extremities. In the epizootic phase of the disease, it usually takes red foxes four months to die after infection. Other endoparasites include Demodex folliculorum, Notoderes, Otodectes cynotis (which is frequently found in the ear canal), Linguatula serrata (which infects the nasal passages) and ringworms.
Up to 60 helminth species are known to infect captive-bred foxes in fur farms, while 20 are known in the wild. Several coccidian species of the genera Isospora and Eimeria are also known to infect them. The most common nematode species found in red fox guts are Toxocara canis and Uncinaria stenocephala, Capillaria aerophila and Crenosoma vulpis; the latter two infect their lungs and trachea. Capillaria plica infects the red fox's bladder. Trichinella spiralis rarely affects them. The most common tapeworm species in red foxes are Taenia spiralis and T. pisiformis. Others include Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis. Eleven trematode species infect red foxes, including Metorchis conjunctus. A red fox from was found to be a host of intestinal parasitic acanthocephalan worms, Pachysentis canicola in Bushehr Province, Iran, Pachysentis procumbens and Pachysentis ehrenbergi in both in Egypt.
Relationships with humans
In folklore, religion and mythology
Further information: Foxes in culture
Red foxes feature prominently in the folklore and mythology of human cultures with which they are sympatric. In Greek mythology, the Teumessian fox, or Cadmean vixen, was a gigantic fox that was destined never to be caught. The fox was one of the children of Echidna.
In Celtic mythology, the red fox is a symbolic animal. In the Cotswolds, witches were thought to take the shape of foxes to steal butter from their neighbours. In later European folklore, the figure of Reynard the Fox symbolises trickery and deceit. He originally appeared (then under the name of "Reinardus") as a secondary character in the 1150 poem "Ysengrimus". He reappeared in 1175 in Pierre Saint Cloud's Le Roman de Renart, and made his debut in England in Geoffrey Chaucer's The Nun's Priest's Tale. Many of Reynard's adventures may stem from actual observations on fox behaviour; he is an enemy of the wolf and has a fondness for blackberries and grapes.
Chinese folk tales tell of fox-spirits called huli jing that may have up to nine tails, or kumiho as they are known in Korea. In Japanese mythology, the kitsune are fox-like spirits possessing magical abilities that increase with their age and wisdom. Foremost among these is the ability to assume human form. While some folktales speak of kitsune employing this ability to trick others, other stories portray them as faithful guardians, friends, lovers, and wives. In Arab folklore, the fox is considered a cowardly, weak, deceitful, and cunning animal, said to feign death by filling its abdomen with air to appear bloated, then lies on its side, awaiting the approach of unwitting prey. The animal's cunning was noted by the authors of the Bible who applied the word "fox" to false prophets (Ezekiel 13:4) and the hypocrisy of Herod Antipas (Luke 13:32).
The cunning Fox is commonly found in Native American mythology, where it is portrayed as an almost constant companion to Coyote. Fox, however, is a deceitful companion that often steals Coyote's food. In the Achomawi creation myth, Fox and Coyote are the co-creators of the world, that leave just before the arrival of humans. The Yurok tribe believed that Fox, in anger, captured the Sun, and tied him to a hill, causing him to burn a great hole in the ground. An Inuit story tells of how Fox, portrayed as a beautiful woman, tricks a hunter into marrying her, only to resume her true form and leave after he offends her. A Menominee story tells of how Fox is an untrustworthy friend to Wolf.
Hunting
Further information: Fox hunting
The earliest historical records of fox hunting come from the 4th century BC; Alexander the Great is known to have hunted foxes and a seal dated from 350 BC depicts a Persian horseman in the process of spearing a fox. Xenophon, who viewed hunting as part of a cultured man's education, advocated the killing of foxes as pests, as they distracted hounds from hares. The Romans were hunting foxes by AD 80. During the Dark Ages in Europe, foxes were considered secondary quarries, but gradually grew in importance. Cnut the Great re-classed foxes as Beasts of the Chase, a lower category of quarry than Beasts of Venery. Foxes were gradually hunted less as vermin and more as Beasts of the Chase, to the point that by the late 1200s, Edward I had a royal pack of foxhounds and a specialised fox huntsman. In this period, foxes were increasingly hunted above ground with hounds, rather than underground with terriers. Edward, Second Duke of York assisted the climb of foxes as more prestigious quarries in his The Master of Game. By the Renaissance, fox hunting became a traditional sport of the nobility. After the English Civil War caused a drop in deer populations, fox hunting grew in popularity. By the mid-1600s, Great Britain was divided into fox hunting territories, with the first fox hunting clubs being formed (the first was the Charlton Hunt Club in 1737). The popularity of fox hunting in Great Britain reached a peak during the 1700s. Although already native to North America, red foxes from England were imported for sporting purposes to Virginia and Maryland in 1730 by prosperous tobacco planters. These American fox hunters considered the red fox more sporting than the grey fox.
The grays furnished more fun, the reds more excitement. The grays did not run so far, but usually kept near home, going in a circuit of six or eight miles. 'An old red, generally so called irrespective of age, as a tribute to his prowess, might lead the dogs all day, and end by losing them as evening fell, after taking them a dead stretch for thirty miles. The capture of a gray was what men boasted of; a chase after 'an old red' was what they 'yarned' about.
Red foxes are still widely persecuted as pests, with human-caused deaths among the highest causes of mortality in the species. Annual red fox kills are: UK 21,500–25,000 (2000); Germany 600,000 (2000–2001); Austria 58,000 (2000–2001); Sweden 58,000 (1999–2000); Finland 56,000 (2000–2001); Denmark 50,000 (1976–1977); Switzerland 34,832 (2001); Norway 17,000 (2000–2001); Saskatchewan (Canada) 2,000 (2000–2001); Nova Scotia (Canada) 491 (2000–2001); Minnesota (US) 4,000–8,000 (average annual trapping harvest 2002–2009); New Mexico (US) 69 (1999–2000).
Fur use


Red foxes are among the most important fur-bearing animals harvested by the fur trade. Their pelts are used for trimmings, scarfs, muffs, jackets and coats. They are principally used as trimming for both cloth coats and fur garments, including evening wraps. The pelts of silver foxes are popular as capes, while cross foxes are mostly used for scarves and rarely for trimming. The number of sold fox scarves exceeds the total number of scarves made from other fur-bearers. However, this amount is overshadowed by the total number of red fox pelts used for trimming purposes. The silver colour morphs are the most valued by furriers, followed by the cross colour morphs and the red colour morphs, respectively. In the early 1900s, over 1,000 American red fox skins were imported to Great Britain annually, while 500,000 were exported annually from Germany and Russia. The total worldwide trade of wild red foxes in 1985–86 was 1,543,995 pelts. Red foxes amounted to 45% of U.S. wild-caught pelts worth $50 million. Pelt prices are increasing, with 2012 North American wholesale auction prices averaging $39 and 2013 prices averaging $65.78.
North American red foxes, particularly those of northern Alaska, are the most valued for their fur, as they have guard hairs of a silky texture which, after dressing, allow the wearer unrestricted mobility. Red foxes living in southern Alaska's coastal areas and the Aleutian Islands are an exception, as they have extremely coarse pelts that rarely exceed one-third of the price of their northern Alaskan cousins. Most European peltries have coarse-textured fur compared to North American varieties. The only exceptions are the Nordic and Far Eastern Russian peltries, but they are still inferior to North American peltries in terms of silkiness.
Livestock and pet predation


Red foxes may on occasion prey on lambs. Usually, lambs targeted by red foxes tend to be physically weakened specimens, but not always. Lambs belonging to small breeds, such as the Scottish Blackface, are more vulnerable than larger breeds, such as the Merino. Twins may be more vulnerable to red foxes than singlets, as ewes cannot effectively defend both simultaneously. Crossbreeding small, upland ewes with larger, lowland rams can cause difficult and prolonged labour for ewes due to the heaviness of the resulting offspring, thus making the lambs more at risk to red fox predation. Lambs born from gimmers (ewes breeding for the first time) are more often killed by red foxes than those of experienced mothers, who stick closer to their young.
Red foxes may prey on domestic rabbits and guinea pigs if they are kept in open runs or are allowed to range freely in gardens. This problem is usually averted by housing them in robust hutches and runs. Urban red foxes frequently encounter cats and may feed alongside them. In physical confrontations, the cats usually have the upper hand. Authenticated cases of red foxes killing cats usually involve kittens. Although most red foxes do not prey on cats, some may do so and may treat them more as competitors rather than food.
Taming and domestication
Further information: Domesticated silver fox
In their unmodified wild state, red foxes are generally unsuitable as pets. Many supposedly abandoned kits are adopted by well-meaning people during the spring period, though it is unlikely that vixens would abandon their young. Actual orphans are rare and the ones that are adopted are likely kits that simply strayed from their den sites. Kits require almost constant supervision; when still suckling, they require milk at four-hour intervals day and night. Once weaned, they may become destructive to leather objects, furniture and electric cables. Though generally friendly toward people when young, captive red foxes become fearful of humans, save for their handlers, once they reach 10 weeks of age. They maintain their wild counterparts' strong instinct of concealment and may pose a threat to domestic birds, even when well-fed. Although suspicious of strangers, they can form bonds with cats and dogs, even ones bred for fox hunting. Tame red foxes were once used to draw ducks close to hunting blinds.
White to black individual red foxes have been selected and raised on fur farms as "silver foxes". In the second half of the 20th century, a lineage of domesticated silver foxes was developed by Russian geneticist Dmitry Belyayev who, over a 40-year period, bred several generations selecting only those individuals that showed the least fear of humans. Eventually, Belyayev's team selected only those that showed the most positive response to humans, thus resulting in a population of silver foxes whose behaviour and appearance was significantly changed. After about 10 generations of controlled breeding, these foxes no longer showed any fear of humans and often wagged their tails and licked their human caretakers to show affection. These behavioural changes were accompanied by physical alterations, which included piebald coats, floppy ears in kits and curled tails, similar to the traits that distinguish domestic dogs from grey wolves.
Urban red foxes


Distribution
Red foxes have been exceedingly successful in colonising built-up environments, especially lower-density suburbs, although many have also been sighted in dense urban areas far from the countryside. Throughout the 20th century, they have established themselves in many Australian, European, Japanese and North American cities. The species first colonised British cities during the 1930s, entering Bristol and London during the 1940s, and later established themselves in Cambridge and Norwich. In Ireland, they are now common in suburban Dublin. In Australia, red foxes were recorded in Melbourne as early as the 1930s, while in Zurich, Switzerland, they only started appearing in the 1980s. Urban red foxes are most common in residential suburbs consisting of privately owned, low-density housing. They are rare in areas where industry, commerce or council-rented houses predominate. In these latter areas, the distribution is of a lower average density because they rely less on human resources; the home range of these foxes average from 80–90 ha (0.80–0.90 km; 200–220 acres), whereas those in more residential areas average from 25–40 ha (0.25–0.40 km; 62–99 acres).
In 2006, it was estimated that there were 10,000 red foxes in London. City-dwelling red foxes may have the potential to consistently grow larger than their rural counterparts as a result of abundant scraps and a relative lack of predators. In cities, red foxes may scavenge food from litter bins and bin bags, although much of their diet is similar to rural red foxes.
Behaviour
Urban red foxes are most active at dusk and dawn, doing most of their hunting and scavenging at these times. It is uncommon to spot them during the day, but they can be caught sunbathing on roofs of houses or sheds. Urban red foxes will often make their homes in hidden and undisturbed spots in urban areas as well as on the edges of a city, visiting at night for sustenance. They sleep at night in dens.
While urban red foxes will scavenge successfully in the city (and the red foxes tend to eat anything that humans eat) some urban residents will deliberately leave food out for the animals, finding them endearing. Doing this regularly can attract urban red foxes to one's home; they can become accustomed to human presence, warming up to their providers by allowing themselves to be approached and in some cases even played with, particularly young kits.
Urban red fox control
Urban red foxes can cause problems for local residents. They have been known to steal chickens, disrupt rubbish bins and damage gardens. Most complaints about urban red foxes made to local authorities occur during the breeding season in late January/early February or from late April to August when the new kits are developing.
In the U.K., hunting red foxes in urban areas is banned and shooting them in an urban environment is not suitable. One alternative to hunting urban red foxes has been to trap them, which appears to be a more viable method. However, killing red foxes has little effect on the population in an urban area; those that are killed are very soon replaced, either by new kits during the breeding season or by other red foxes moving into the territory of those that were killed. A more effective method of urban red fox control is to deter them from the specific areas they inhabit. Deterrents such as creosote, diesel oil, or ammonia can be used. Cleaning up and blocking access to den locations can also discourage an urban red fox's return.
Relationship between urban and rural red foxes

In January 2014 it was reported that "Fleet", a relatively tame urban red fox tracked as part of a wider study by the University of Brighton in partnership with the BBC TV series Winterwatch, had unexpectedly traveled 195 miles in 21 days from his neighbourhood in Hove at the western edge of East Sussex across rural countryside as far as the town of Rye, near the eastern edge of the county. He was still continuing his journey when the GPS collar stopped transmitting due to suspected water damage. Along with setting a record for the longest journey undertaken by a tracked red fox in the United Kingdom, his travels have highlighted the fluidity of movement between rural and urban red fox populations.
References
- ^ Hoffmann, M. & Sillero-Zubiri, C. (2021) . "Vulpes vulpes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T23062A193903628. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T23062A193903628.en. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- "Vulpes vulpes". NatureServe Explorer. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- Linnaeus, Carl (1758). "Canis Vulpes". Caroli Linnæi Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. Tomus I (decima, reformata ed.). Holmiae: Laurentius Salvius. p. 40.
- "100 of the World's Worst Invasive Alien Species". Global Invasive Species Database. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- Bartolini Lucenti, Saverio; Madurell-Malapeira, Joan (May 2020). "Unraveling the fossil record of foxes: An updated review on the Plio-Pleistocene Vulpes spp. from Europe". Quaternary Science Reviews. 236: 106296. Bibcode:2020QSRv..23606296B. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106296.
- Kutschera, Verena E; Lecomte, Nicolas; Janke, Axel; Selva, Nuria; Sokolov, Alexander A; Haun, Timm; Steyer, Katharina; Nowak, Carsten; Hailer, Frank (2013). "A range-wide synthesis and timeline for phylogeographic events in the red fox (Vulpes vulpes)". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 13 (1): 114. Bibcode:2013BMCEE..13..114K. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-114. ISSN 1471-2148. PMC 3689046. PMID 23738594.
- ^ Heptner, V. G.; Naumov, N. P. (1998). Mammals of the Soviet Union. Leiden: Brill. pp. 115, 341–365, 453–502, 513–562. ISBN 978-1886106819.
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 532–628. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Harris, S. & Yalden, D. (2008). Mammals of the British Isles: Handbook (Fourth ed.). Southampton: Mammal Society. pp. 408–422. ISBN 978-0906282656.
- ^ Feldhamer, G.; Thompson, B. & Chapman, J. (2003). Wild Mammals of North America: Biology, Management, and Conservation: Biology, Management and Economics (Second ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 516–530. ISBN 9780801874161.
- "Red Fox Predators". Wildlife Online. Archived from the original on 10 June 2022. Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- Fedriani, J. M.; Palomares, F. & Delibes, M. (1999). "Niche relations among three sympatric Mediterranean carnivores". Oecologia. 121 (1): 138–148. Bibcode:1999Oecol.121..138F. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.587.7215. doi:10.1007/s004420050915. JSTOR 4222449. PMID 28307883. S2CID 39202154.
- ^ Bachrach, M. (1953). Fur: A Practical Treatise (Third ed.). New York: Prentice-Hall.
- "10 Fascinating Facts About Foxes (With Photos)". PETA UK. 26 April 2012. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- "Vulpine". dictionary.com. Archived from the original on 12 June 2016. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
- ^ Basuony, Ali E; Saleh, Mostafa; Sarhan, Moustafa; Younes, Mahmoud; Abdel-Hamid, Fouad; Rodriguez Fernandes, Carlos; Vercammen, Paul; Aboshaala, Faraj; Bounaceur, Farid; Chadwick, Elizabeth A; Hailer, Frank (2023). "Paraphyly of the widespread generalist red fox (Vulpes vulpes): introgression rather than recent divergence of the arid-adapted Rüppell's fox (Vulpes rueppellii)?". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 138 (4): 453–469. doi:10.1093/biolinnean/blad001.
- Basuony, A. E.; Saleh, M.; Hailer, F. (2024). "Mitogenomic analysis of Rüppell's fox (Vulpes rueppellii) confirms phylogenetic placement within the Palaearctic clade shared with its sister species, the red fox (Vulpes vulpes)". Mitochondrial DNA Part A. 34: 1–7. doi:10.1080/24701394.2024.2332320. PMID 38584459.
- Lindblad-Toh, K.; Wade, C. M.; Mikkelsen, T. S.; et al. (2005). "Genome sequence, comparative analysis and haplotype structure of the domestic dog". Nature. 438 (7069): 803–819. Bibcode:2005Natur.438..803L. doi:10.1038/nature04338. PMID 16341006.
- ^ Kurtén, Björn (1968). Pleistocene Mammals of Europe. Weidenfeld & Nicolson.
- PaleoDatabase collection No. 35369, authorized by Alan Turner, Liverpool John Moores University. Entry by H. O'Regan, 8 December 2003
- David M. Alba, Saverio Bartolini Lucenti, Joan Madurell Malapeira, 2021, Middle Pleistocene fox from the Vallparadís Section (Vallès-Penedès Basin, NE Iberian Peninsula) and the earliest records of the extant red fox Archived 26 October 2021 at the Wayback Machine, Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia, Vol.127, pp.179-187, DOI:10.13130/2039-4942/15229, Retrieved on 26 October 2021
- ^ Spagnesi & De Marina Marinis 2002, p. 222
- ^ Aubry, Keith B.; Statham, Mark J.; Sacks, Benjamin N.; Perrines, John D. & Wisely, Samantha M. (2009). "Phylogeography of the North American red fox: Vicariance in Pleistocene forest refugia" (PDF). Molecular Ecology. 18 (12): 2668–2686. Bibcode:2009MolEc..18.2668A. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04222.x. PMID 19457180. S2CID 11518843. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- Statham, Mark J.; Murdoch, James; Janecka, Jan; Aubry, Keith B.; Edwards, Ceiridwen J.; Soulsbury, Carl D.; Berry, Oliver; Wang, Zhenghuan; et al. (2014). "Range-wide multilocus phylogeography of the red fox reveals ancient continental divergence, minimal genomic exchange and distinct demographic histories". Molecular Ecology. 23 (19): 4813–4830. Bibcode:2014MolEc..23.4813S. doi:10.1111/mec.12898. PMID 25212210. S2CID 25466489.
- Feldman, Rodney; Hackathorn, Merriane (1996). Fossils of Ohio. Columbus: State of Ohio, Dept. of Natural Resources, Division of Geological Survey. ISBN 0931079055.
- Kurtén, B. & Anderson, E. (1980). Pleistocene Mammals of North America. Columbia University Press. pp. 96, 174. ISBN 9780231037334.
- Mark J. Statham; Benjamin N. Sacks; Keith B. Aubry; John D. Perrine & Samantha M. Wisely (2012). "The origin of recently established red fox populations in the United States: translocations or natural range expansions?". Journal of Mammalogy. 93 (1): 58. doi:10.1644/11-MAMM-A-033.1.
- Sacks, B. N.; Moore, M.; Statham, M. J. & Wittmer, H. U. (2011). "A restricted hybrid zone between native and introduced red fox Vulpes vulpes populations suggests reproductive barriers and competitive exclusion". Molecular Ecology. 20 (2): 326–341. Bibcode:2011MolEc..20..326S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294x.2010.04943.x. PMID 21143330. S2CID 2995171.
- Volkmann, Logan A.; Statham, Mark J.; Mooers, Arne Ø. & Sacks, Benjamin N. (2015). "Genetic distinctiveness of red foxes in the Intermountain West as revealed through expanded mitochondrial sequencing". Journal of Mammalogy. 96 (2): 297–307. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyv007.
- Sacks, Benjamin N.; Statham, Mark J.; Perrine, John D.; Wisely, Samantha M. & Aubry, Keith B. (2010). "North American montane red foxes: Expansion, fragmentation, and the origin of the Sacramento Valley red fox" (PDF). Conservation Genetics. 11 (4): 1523–1539. Bibcode:2010ConG...11.1523S. doi:10.1007/s10592-010-0053-4. S2CID 7164254. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 October 2020. Retrieved 3 September 2019.
- Castello, Jose, 2018. Canids of the World. Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ.
- ^ Dale, Thomas Francis (1906). The Fox. London, New York, Bombay: Longmans, Green, and Co. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- Teacher, Amber G. F.; Thomas, Jessica A. & Barnes, Ian (2011). "Modern and ancient red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in Europe show an unusual lack of geographical and temporal structuring, and differing responses within the carnivores to historical climatic change". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 11 (214): 214. Bibcode:2011BMCEE..11..214T. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-214. PMC 3154186. PMID 21774815.
- Kutschera, Verena E.; Lecomte, Nicolas; Janke, Axel; Selva, Nuria; Sokolov, Alexander A.; Haun, Timm; Steyer, Katharina; Nowak, Carsten & Hailer, Frank (2013). "A range-wide synthesis and timeline for phylogeographic events in the red fox (Vulpes vulpes)". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 13 (114): 114. Bibcode:2013BMCEE..13..114K. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-114. PMC 3689046. PMID 23738594.
- Allen, S. H. & Sargeant, A. B. (1993). "Dispersal Patterns of Red Foxes Relative to Population Density". Journal of Wildlife Management. 57 (3): 526–533. doi:10.2307/3809277. JSTOR 3809277. Archived from the original on 18 October 2020. Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- Preble, Edward Alexander (1908). "Mammals". A biological investigation of the Athabaska-Mackenzie region. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 217.
- ^ Merriam, Clinton Hart (1900). Preliminary Revision of the North American Red Foxes. Washington Academy of Sciences. pp. 663–669. ISBN 9780665167928.
- Cook, Joseph A.; MacDonald, Stephen O. (2010). Recent Mammals of Alaska. University of Alaska Press. p. 162. ISBN 9781602231160.
- ^ Spagnesi & De Marina Marinis 2002, p. 221
- ^ Pocock, Reginald Innes (1941). The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma: Mammalia Volume 2, Carnivora: Aeluroidea, Arctoidea. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- Allen, G. M. (1938). The mammals of China and Mongolia. Volume 1. New York: American Museum of Natural History.
- Hoath, Richard (2009). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Egypt. American Univ in Cairo Press. ISBN 978-977-416-254-1.
- ^ Osborn, Dale J. & Helmy, Ibrahim (1980). The Contemporary Land Mammals of Egypt (including Sinai). Field Museum of Natural History. pp. 376, 679. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
- Miller, Gerrit Smith (1912). Catalogue of the Mammals of Western Europe (Europe Exclusive of Russia) in the Collection of the British Museum, British Museum (Natural History). Department of Zoology.
- Allen 1938, p. 353
- ^ Larivière, Serge & Pasitschniak-Arts, Maria (1996). Vulpes vulpes (PDF). American Society of Mammalogists. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 October 2005. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
- ^ Sillero-Zubiri, Hoffman & MacDonald 2004, pp. 132–133
- Sillero-Zubiri, Hoffman & MacDonald 2004, p. 129
- ^ Macdonald, David (1987). Running with the Fox. Unwin Hyman, London. ISBN 9780044401995.
- Nowak, Ronald M. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. Vol. 1. JHU Press. p. 636. ISBN 978-0-8018-5789-8.
- Burnie, D. & Wilson, D. E. (eds.), Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. DK Adult (2005), ISBN 0789477645
- Sillero-Zubiri, Hoffman & MacDonald 2004, p. 130
- Wilkes, David (5 March 2012). "'Largest fox killed in UK' shot on Aberdeenshire farm". BBC News Online. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- Klir, J. J. & Heath, J. E. (1992). "An infrared thermographic study of surface temperature in relation to external thermal stress in three species of foxes: The Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes), Arctic Fox (Alopex lagopus), and Kit Fox (Vulpes macrotis)". Physiological Zoology. 65 (5): 1011–1021. doi:10.1086/physzool.65.5.30158555. S2CID 87183522.
- Albone, E. S. & Grönnerberg, T. O. "Lipids of the anal sac secretions of the red fox, Vulpes vulpes and of the lion, Panthera leo". Journal of Lipid Research. 18.4 (1977): 474–479.
- Rinck, M., R., J. (1 June 2000). "Morphometrische Analbeutelmessungen beim Rotfuchs (Vulpes vulpes, Linné 1758)". Zeitschrift für Jagdwissenschaft. 46 (117–119): 118. doi:10.1007/BF02241575. S2CID 35030583 – via SpringerLink.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Hazardous Substances and New Organisms Act 2003 – Schedule 2 Prohibited new organisms". New Zealand Government. Archived from the original on 16 June 2012. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- "Impacts of Feral Animals". Game Council of New South Wales. Archived from on 18 April 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - Bostanci, A. (2005). "Wildlife Biology: A Devil of a Disease". Science. 307 (5712): 1035. doi:10.1126/science.307.5712.1035. PMID 15718445. S2CID 54100368.
- Short, J. (1998). "The extinction of rat-kangaroos (Marsupialia: Potoroidae) in New South Wales, Australia". Biological Conservation. 86 (3): 365–377. Bibcode:1998BCons..86..365S. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(98)00026-3.
- Threat Abatement Plan for Predation by the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes) (PDF) (Report). NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service. 2001. ISBN 0731364244. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 March 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- Millen, Tracey (October–November 2006). "Call for more dingoes to restore native species" (PDF). ECOS. 133. Archived from the original on 16 April 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2007. (Refers to the book Australia's Mammal Extinctions: A 50,000 Year History. Christopher N. Johnson. ISBN 978-0-521-68660-0.)
- "Latest Physical Evidence of Foxes in Tasmania". Department of Primary Industries and Water, Tasmania website. 18 July 2013. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- Fawcett, John K.; Fawcett, Jeanne M. & Soulsbury, Carl D. (2012). "Seasonal and sex differences in urine marking rates of wild red foxes Vulpes vulpes". Journal of Ethology. 31 (1): 41–47. doi:10.1007/s10164-012-0348-7. S2CID 15328275.
- Macdonald, D. W. (1979). "Some observations and field experiments on the urine marking behaviour of the red fox, Vulpes vulpes L." (PDF). Zeitschrift für Tierpsychologie. 51 (1): 1–22. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0310.1979.tb00667.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2020.
- Walters, M.; Bang, P. & Dahlstrøm, P. (2001). Animal Tracks and Signs. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 202–203. ISBN 978-0-19-850796-3.
- Henry, J. D. (1977). "The use of urine marking in the scavenging behavior of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes)". Behaviour. 61 (1/2): 82–106. doi:10.1163/156853977X00496. JSTOR 4533812. PMID 869875. S2CID 36332457.
- Andersen, K. F. & Vulpius, T. (1999). "Urinary volatile constituents of the lion, Panthera leo". Chemical Senses. 24 (2): 179–189. doi:10.1093/chemse/24.2.179. PMID 10321819.
- Fawcett, J.; Fawcett, J. & Soulsbury, C. (2013). "Seasonal and sex differences in urine marking rates of wild red foxes Vulpes vulpes". Journal of Ethology. 31 (1): 41–47. doi:10.1007/s10164-012-0348-7. S2CID 254144483.
- Elbroch, L. M.; Kresky, M. R. & Evans, J. W. (2012). Field Guide to Animal Tracks and Scat of California. University of California Press. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-520-25378-0.
- Iossa, G.; Soulsbury, C.D.; Baker, P.J. & Harris, S. (2008). "Body mass, territory size, and life-history tactics in a socially monogamous canid, the red fox Vulpes vulpes". Journal of Mammalogy. 89 (6): 1481–1490. doi:10.1644/07-mamm-a-405.1.
- ^ Hunter, L. (2011). Carnivores of the World. Princeton University Press. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-691-15227-1.
- Holland, Jennifer S. (July 2011). "40 winks?". National Geographic. 220 (1).
- Contesse, P.; Hegglin, D.; Gloor, S.; Bontadina, F.; Deplazes, P. (1 February 2004). "The diet of urban foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and the availability of anthropogenic food in the city of Zurich, Switzerland". Mammalian Biology. 69 (2): 81–95. Bibcode:2004MamBi..69...81C. doi:10.1078/1616-5047-00123. ISSN 1616-5047.
- Morton, F. Blake; Gartner, Marieke; Norrie, Ellie-Mae; Haddou, Yacob; Soulsbury, Carl D.; Adaway, Kristy A. (1 September 2023). "Urban foxes are bolder but not more innovative than their rural conspecifics". Animal Behaviour. 203: 101–113. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2023.07.003. ISSN 0003-3472.
- Fox, David L. (2007). "Vulpes vulpes Red fox". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- Asa, C. S. & Mech, D. (1995). "A review of the sensory organs in wolves and their importance to life history," in Ecology and Conservation of Wolves in a Changing World eds. Carbyn, L. D.; Fritts, S. H. & Seip, D. R. (Edmonton: Canadian Circumpolar Institute): 287–291.
- Osterholm, H. (1964). "The significance of distance reception in the feeding behaviour of fox (Vulpes vulpes L.)". Acta Zoologica Fennica. 106 1–31.
- Wells, M. C. (1978). "Coyote senses in predation – environmental influences on their relative use". Behavioural Processes. 3: 149–158 doi:10.1016/0376-6357(78)90041-4
- Wells, M. C. & Lehner, P. N. (1978). "Relative importance of distance senses in Coyote predatory behavior". Animal Behaviour. 26: 251–258 doi:10.1016/0003-3472(78)90025-8
- Yong, Ed (11 January 2011). "Foxes use the Earth's magnetic field as a targeting system - Not Exactly Rocket Science". Discover Magazine. Archived from the original on 13 December 2018. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- Červený, Jaroslav; Begall, Sabine; Koubek, Petr; Nováková, Petra & Burda, Hynek (12 January 2011). "Directional preference may enhance hunting accuracy in foraging foxes". Biology Letters. 7 (3): 355–357. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2010.1145. PMC 3097881. PMID 21227977.
- Heptner & Naumov 1998, pp. 453–454
- Mech, L. David & Boitani, Luigi (2003). Wolves: Behaviour, Ecology and Conservation. University of Chicago Press. p. 269. ISBN 978-0-226-51696-7.
- Sargeant, Alan B & Allen, Stephen H. (1989). "Observed interactions between coyotes and red foxes". Journal of Mammalogy. 70 (3): 631–633. doi:10.2307/1381437. JSTOR 1381437. Archived from the original on 14 November 2007.
- Scheinin, Shani; Yom-Tov, Yoram; Motro, Uzi & Geffen, Eli (2006). "Behavioural responses of red foxes to an increase in the presence of golden jackals: A field experiment" (PDF). Animal Behaviour. 71 (3): 577–584. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2005.05.022. S2CID 38578736. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2018. Retrieved 24 August 2007.
- Böcker, F; Weber, H; Arnold, J; Collet, S; Hatlauf, J (2024). "Interspecific social interaction between golden jackal (Canis aureus) and red fox (Vulpes vulpes)". Mammal Research. 69 (2): 319–324. doi:10.1007/s13364-024-00737-2.
- ^ Sillero-Zubiri, Hoffman & MacDonald 2004, p. 134
- Heptner, V. G. (2002). Mammals of the Soviet Union. Leiden u.a.: Brill. pp. 1280. ISBN 978-1886106819.
- Heptner, V. G. (2002). Mammals of the Soviet Union. Leiden u.a.: Brill. pp. 952. ISBN 978-1886106819.
- Jankowiak, L. & Tryjanowski, P. (2013). "Cooccurrence and food niche overlap of two common predators (red fox Vulpes vulpes and common buzzard Buteo buteo) in an agricultural landscape". Turkish Journal of Zoology. 37 (2): 157–162.
- Ziesemer, F. (1981). "Methods of assessing goshawk predation". Understanding the goshawk, 144–150.
- Watson, J. (2010). The Golden Eagle (Second ed.). A&C Black. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-4081-1420-9.
- Sulkava, Seppo, et al. "Changes in the diet of the Golden Eagle Aquila chrysaetos and small game populations in Finland in 1957-96." Ornis Fennica 76 (1999): 1-16.
- Lewis, C. F. (1957). Wedge-tailed eagle takes a fox. Victorian Naturalist, 74, 89-90.
- Heptner, Vladimir G., ed. Mammals of the Soviet Union, Volume 2 Part 2 Carnivora (Hyenas and Cats). Vol. 2. Brill, 1989.
- Vrezec, A.; Bordjan, D.; Perušek, M. & Hudoklin, A. (2009). "Population and ecology of the White-tailed Eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) and its conservation status in Slovenia". Denisia. 27: 103–114.
- Utekhina, I.; Potapov, E. & McGrady, M.J. (2000). "Diet of the Steller's Sea Eagle in the northern Sea of Okhotsk". In Ueta, M. & McGrady, M.J. (eds.). First Symposium on Steller's and White-tailed Sea Eagles in East Asia. Tokyo, Japan: Wild Bird Society of Japan. pp. 71–92.
- Larivière, S., & Pasitschniak-Arts, M. (1996). Vulpes vulpes. Mammalian species, (537), 1-11.
- "Eurasian Eagle Owl (Bubo bubo) - Information, Pictures, Sounds". The Owl Pages. 23 October 2015. Archived from the original on 20 November 2015. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- Skrifter. (1963). Norway: I Kommisjon Hos Jacob Dybwad.
- Dixon, Charles C. (1970). "Red Fox Predated by Snowy Owl". Blue Jay. 33 (2).
- Lalošević, V.; Lalošević, D.; Čapo, I.; Simin, V.; Galfi, A. & Traversa, D. (2013). "High infection rate of zoonotic Eucoleus aerophilus infection in foxes from Serbia". Parasite. 20 (3): 3. doi:10.1051/parasite/2012003. PMC 3718516. PMID 23340229.
- Mechouk, N.; Deak, G.; Ionică, A. M.; Toma, C. G.; Bouslama, Z.; Daniel Mihalca, A. (2023). "First report of Crenosoma vulpis in Africa and Eucoleus aerophilus in Algeria". International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife. 20: 187–191. doi:10.1016/j.ijppaw.2023.03.003. PMC 10023903. PMID 36941973.
- Smith, H. J. (1978). "Parasites of red foxes in New Brunswick and Nova Scotia". Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 14 (3): 366–370. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-14.3.366. PMID 691132.
- Tavakol, Sareh; Amin, Omar M.; Luus-Powell, Wilmien J.; Halajian, Ali (22 October 2015). "The acanthocephalan fauna of Iran, a check list". Zootaxa. 4033 (2): 237–258. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4033.2.3. PMID 26624401.
- Gomes, Ana Paula N.; Amin, Omar M.; Olifiers, Natalie; Bianchi, Rita de Cassia; Souza, Joyce G. R.; Barbosa, Helene S.; Maldonado, Arnaldo (2019). "A New Species of Pachysentis Meyer, 1931 (Acanthocephala: Oligacanthorhynchidae) in the Brown-Nosed Coati Nasua nasua (Carnivora: Procyonidae) from Brazil, with Notes on the Genus and a Key to Species". Acta Parasitologica. 64 (3): 587–595. doi:10.2478/s11686-019-00080-6. PMC 6814649. PMID 31286360.
- Ancient Greek: Τευμησ(σ)ία ἀλώπηξ (Teumēs(s)íā alôpēx),gen.: Τευμησίας ἀλώπεκος, also known as ἀλώπηξ τῆς Τευμησσοῦ "fox of Teumessos"; Teumessos was an ancient city in Boeotia.
- Wallen, Martin (2006). Fox. Reaktion Books. p. 40. ISBN 978-1-86189-297-3.
- Monaghan, Patricia (2004). The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folklore. Infobase Publishing. pp. 199–200. ISBN 978-0-8160-4524-2.
- Goff, Janet (1997). "Foxes in Japanese culture: Beautiful or beastly?" (PDF). Japan Quarterly. 44 (2). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- Smyers, Karen Ann (1999). The Fox and the Jewel: Shared and Private Meanings in Contemporary Japanese Inari Worship. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-2102-9.
- Bright, Michael (2006). Beasts of the Field: The Revealing Natural History of Animals in the Bible. London: Robson Books. pp. 120–127. ISBN 978-1-86105-831-7.
- Bastian, Dawn Elaine & Mitchell, Judy K. (2004). Handbook of Native American Mythology. ABC-CLIO. pp. 99–100. ISBN 978-1-85109-533-9.
- ^ Potts, Allen (1912). Fox Hunting in America. Washington: The Carnahan Press. pp. 7, 38. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
- Dexter, Margaret (8 December 2009). Trapping Harvest Statistics (PDF). Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. p. 282 (Table 5). Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 August 2014. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- "NAFA February 2013 Fur Auction Results". Trapping Today. 22 February 2013. Archived from the original on 26 June 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- Jones, Lucy (7 May 2016). "Why we love keeping foxes at home - despite the smell". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- Karim, Fariha (8 September 2016). "Why having Mr Fox to stay is not such a fantastic idea after all". The Times. Archived from the original on 8 September 2016. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- Trut, Lyudmila N. (1999). "Early canid domestication: The farm-fox experiment" (PDF). American Scientist. 87 (2): 160–169. Bibcode:1999AmSci..87.....T. doi:10.1511/1999.20.813. S2CID 120981396. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 February 2010.
- "Urban foxes: Overview". The fox website. Archived from the original on 16 September 2013. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Harris, Stephen (1986). Urban Foxes. London: Whittet Books. ISBN 978-0905483474.
- "10,000 Foxes Roam London". National Geographic. 28 October 2010. Archived from the original on 8 September 2006. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- "Fieldsports Britain: How to call in great big bucks". Fieldsports Channel. 24 October 2012. Archived from the original on 15 December 2021.
- "BBC Two - Winterwatch, Urban Fox Diary: Part 2". BBC. 23 January 2014. Archived from the original on 9 December 2018. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- "Fleet the Sussex fox breaks British walking record". BBC. 22 January 2014. Archived from the original on 15 September 2019. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
Further reading
- Osborn, Dale. J. & Helmy, Ibrahim (1980). "The contemporary land mammals of Egypt (including Sinai)". Fieldiana. New Series (5). Field Museum of Natural History.
- Sillero-Zubiri, Claudio; Hoffman, Michael & MacDonald, David W. (2004). Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs – 2004 Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN/SSC Canid Specialist Group. ISBN 978-2-8317-0786-0. Archived from the original on 6 October 2011.
- Spagnesi, Mario & De Marina Marinis, Maria (2002). "Mammiferi d'Italia". Quaderni di Conservazione della Natura. ISSN 1592-2901.
External links
- "Vulpes vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758)". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 18 March 2006.
- Red Fox, National Geographic
- Natural History of the Red Fox, Wildlife Online
- Sacramento Valley red fox info1
- Red Fox, Fletcher Wildlife Garden
| Game animals and shooting in North America | ||
|---|---|---|
| Game birds |  | |
| Waterfowl | ||
| Big game | ||
| Other quarry | ||
| See also | ||
| Game animals and shooting in the United Kingdom | |
|---|---|
| Game birds | |
| Quarry species | |
| Deer | |
| Other quarry | |
| Opponents | |
| Law | |
| See also | |
| Rarely shot because of declining numbers. | |
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Vulpes vulpes |
|
| Canis vulpes | |
Categories:
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- NatureServe secure species
- Vulpes
- Holarctic fauna
- Carnivorans of Asia
- Carnivorans of Europe
- Carnivorans of North America
- Mammals of the Arctic
- Arctic land animals
- Introduced mammals of Australia
- Mammals described in 1758
- Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
- Symbols of Mississippi
- Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances





























