| This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (November 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 The Hindenburgdamm Rail Causeway across the Wadden Sea to the island of Sylt in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany The Hindenburgdamm Rail Causeway across the Wadden Sea to the island of Sylt in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany | |
| Ancestor | None. (See Ford (crossing)) |
|---|---|
| Related | None. (See Step-stone bridge) |
| Descendant | None. (See Viaduct) |
| Carries | Traffic, Rail, Cyclists, Pedestrians |
| Material | Concrete, Masonry, Earth-fill |
| Movable | No |
| Design effort | medium |
| Falsework required | No |
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Track in the Somerset Levels, England, which dates from the Neolithic age. Timber causeways may also be described as both boardwalks and bridges.
Etymology
When first used, the word causeway appeared in a form such as "causey way", making clear its derivation from the earlier form "causey". This word seems to have come from the same source by two different routes. It derives ultimately, from the Latin for heel, calx, and most likely comes from the trampling technique to consolidate earthworks.
Originally, the construction of a causeway used earth that had been trodden upon to compact and harden it as much as possible, one layer at a time, often by slaves or flocks of sheep. Today, this work is done by machines. The same technique would have been used for road embankments, raised river banks, sea banks and fortification earthworks.
The second derivation route is simply the hard, trodden surface of a path. The name by this route came to be applied to any firmly surfaced road. It is now little-used except in dialect and in the names of roads which were originally notable for their solidly made surface. The 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica states: "causey, a mound or dam, which is derived, through the Norman-French caucie (cf. modern chaussée), from the late Latin via calciata, a road stamped firm with the feet (calcare, to tread)."
The word is comparable in both meanings with the French chaussée, from a form of which it reached English by way of Norman French. The French adjective chaussée carries the meaning of having been given a hardened surface and is used to mean either paved or shod. As a noun chaussée is used on the one hand for a metalled carriageway, and on the other for an embankment with or without a road.
Other languages have a noun with similar dual meaning. In Welsh, it is sarn. The Welsh is relevant here, as it also has a verb sarnu, meaning to trample. The trampling and ramming technique for consolidating earthworks was used in fortifications and there is a comparable, outmoded form of wall construction technique, used in such work and known as pisé, a word derived not from trampling but from ramming or tamping. The Welsh word cawsai translates directly to the English word 'causeway'; it is possible that, with Welsh being a lineal linguistic descendant of the original native British tongues, the English word derives from the Welsh.
A transport corridor that is carried instead on a series of arches, perhaps approaching a bridge, is a viaduct; a short stretch of viaduct is called an overpass. The distinction between the terms causeway and viaduct becomes blurred when flood-relief culverts are incorporated, though generally a causeway refers to a roadway supported mostly by earth or stone, while a bridge supports a roadway between piers (which may be embedded in embankments). Some low causeways across shore waters become inaccessible when covered at high tide.
History
The Aztec city-state of Tenochtitlan had causeways supporting roads and aqueducts. One of the oldest engineered roads yet discovered is the Sweet Track in England. Built in 3807 or 3806 BC, the track was a walkway consisting mainly of planks of oak laid end-to-end, supported by crossed pegs of ash, oak, and lime, driven into the underlying peat.
In East Africa, the Husuni Kubwa (the "Great Fort"), situated outside the town of Kilwa, was an early 14th-century sultan's palace and emporium that contained causeways and platforms at the entrance of the Harbour made from blocks of reef and coral nearly a meter high. These acted as breakwaters, allowing mangroves to grow which is one of the ways the breakwater can be spotted from a distance. Some parts of the causeway are made from the bedrock, but usually the bedrock was used as a base. Coral stone was also used to build up the causeways, with sand and lime being used to cement the cobbles together. However, some of the stones were left loose.
In Scotland, the skirmish known as Clense the Calsey, or Cleanse the Causeway, took place in the High Street of Edinburgh in 1520.
In the 18th century, Dahomey lacked an effective navy hence it built causeways for naval purposes starting in 1774.
Engineering
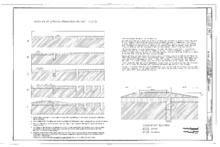
The modern embankment may be constructed within a cofferdam: two parallel steel sheet pile or concrete retaining walls, anchored to each other with steel cables or rods. This construction may also serve as a dyke that keeps two bodies of water apart, such as bodies with a different water level on each side, or with salt water on one side and fresh water on the other. This may also be the primary purpose of a structure, the road providing a hardened crest for the dike, slowing erosion in the event of an overflow. It also provides access for maintenance as well perhaps, as a public service.
Examples

Notable causeways include those that connect Singapore and Malaysia (the Johor-Singapore Causeway), Bahrain and Saudi Arabia (25-km long King Fahd Causeway) and Venice to the mainland, all of which carry roadways and railways. In the Netherlands there are a number of prominent dikes which also double as causeways, including the Afsluitdijk, Brouwersdam, and Markerwaarddijk. In the Republic of Panama a causeway connects the islands of Perico, Flamenco, and Naos to Panama City on the mainland. It also serves as a breakwater for ships entering the Panama Canal.
Causeways are also common in Florida, where low bridges may connect several human-made islands, often with a much higher bridge (or part of a single bridge) in the middle so that taller boats may pass underneath safely. Causeways are most often used to connect the barrier islands with the mainland. In the case of the Courtney Campbell Causeway, however, the mainland (Hillsborough County) is connected by a causeway to a peninsula (Pinellas County). A well-known causeway is the NASA Causeway connecting the town of Titusville on the Florida mainland to the rocket-launching facility at the Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island.
The Churchill Barriers in Orkney are some of the most notable sets of causeways in Europe. Constructed in waters up to 18 metres deep, the four barriers link five islands on the eastern side of the natural harbour at Scapa Flow. They were built during World War II as military defences for the harbour, on the orders of Winston Churchill.
The Estrada do Istmo connecting the islands of Taipa and Coloane in Macau was initially built as a causeway. The sea on both sides of the causeway then became shallower as a result of silting, and mangroves began to conquer the area. Later, land reclamation took place on both sides of the road and the area has subsequently been named Cotai and become home to several casino complexes.
Specific causeways around the world
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2009) |
Various causeways in the world:
- Adam's Bridge, historic causeway which existed till 1480 CE
- Afsluitdijk, Netherlands.
- Canso Causeway, Nova Scotia, Canada (45°38′39″N 61°25′06″W / 45.6443°N 61.4184°W / 45.6443; -61.4184)
- Churchill Barriers, 4 causeways in Orkney, Scotland
- Colaba Causeway, Mumbai, India 18°55′N 72°49′E / 18.91°N 72.81°E / 18.91; 72.81
- Courtney Campbell Causeway, Tampa Bay, Florida, United States
- Gaoji Causeway, Xiamen, China
- Hindenburgdamm, 11km rail link between the island of Sylt and the German mainland (54°53′07″N 8°32′25″E / 54.8852°N 8.5404°E / 54.8852; 8.5404)
- Johor–Singapore Causeway (1°27′07″N 103°46′12″E / 1.4520°N 103.7700°E / 1.4520; 103.7700)
- King Fahd Causeway, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia (26°11′03″N 50°19′27″E / 26.1841°N 50.3241°E / 26.1841; 50.3241)
- Lake Cuitzeo Causeway, Michoacán, Mexico (19.9380°N 101.1547°W)
- Lake Pontchartrain Causeway, Metairie, Louisiana, Southern; Mandeville, Louisiana, Northern, United States
- Lucin Cutoff railroad causeway across the Great Salt Lake in Utah, USA
- MacArthur Causeway, Florida, United States
- Mahim Causeway, Mumbai, India 19°02′55″N 72°50′17″E / 19.04871°N 72.83816°E / 19.04871; 72.83816
- Pulaski Skyway
- Robert Moses Causeway, Bay Shore, Long Island, New York, United States ()
- Rømødæmningen, 9km link between Rømø, and the Danish mainland
- Sanibel Causeway, Sanibel, Florida, United States
- Sloedam, Zeeland, Netherlands
- Swarkestone causeway, Derby, England, United Kingdom
- The Causeway, Western Australia
- Venice (45°27′13″N 12°17′56″E / 45.4535°N 12.2990°E / 45.4535; 12.2990)
- Yolo Causeway, California, USA
- Ponte Conde de Linhares, Panjim, Goa, India. The 3.2 km route was the longest causeway in Asia at the time of its completion in 1634.
- Cherkasy Dam (uk:Черкаська дамба), Ukraine
- Cayo Santa María Causeway, Cuba
- Cayo Coco Causeway, Cuba
Disadvantages

Unlike tunnels or bridges, causeways do not permit shipping through the strait which can cause problems. In some cases, causeways were built with "gates" or other facilities to permit shipping to pass through.
Ecological consequences
Causeways affect currents and may therefore be involved in beach erosion or changed deposition patterns; this effect has been a problem at the Hindenburgdamm in northern Germany. During hurricane seasons, the winds and rains of approaching tropical storms—as well as waves generated by the storm in the surrounding bodies of water—make traversing causeways problematic at best and impossibly dangerous during the fiercest parts of the storms. For this reason (and related reasons, such as the need to minimize traffic jams on both the roads approaching the causeway and the causeway itself), emergency evacuation of island residents is a high priority for local, regional, and even national authorities.
Causeways can separate populations of wildlife, putting further pressure on endangered species.
Causeways can cause a mineral imbalance between portions of a body of water. For example, a causeway built in the Great Salt Lake has caused the northern half of the lake to have much higher salinity, to the point that the two halves show a major color imbalance (as can be seen in the image at right). Furthermore, the difference in salinity has become so severe that native brine shrimp cannot survive in much of the waters, with the northern part being too salty and the southern part being insufficiently salty.
Gallery
-
 The Julia Tuttle Causeway, one of the major arteries connecting Miami and Miami Beach in Florida
The Julia Tuttle Causeway, one of the major arteries connecting Miami and Miami Beach in Florida
-
 Afsluitdijk with the North Sea on the left and the IJsselmeer on the right
Afsluitdijk with the North Sea on the left and the IJsselmeer on the right
-
 Aerial view of the Lucin Cutoff trestle before removal. The 1950s causeway can be seen to the right of the trestle.
Aerial view of the Lucin Cutoff trestle before removal. The 1950s causeway can be seen to the right of the trestle.
-
 The causeway to Antelope Island in the Great Salt Lake, Utah
The causeway to Antelope Island in the Great Salt Lake, Utah
-
 The Johor–Singapore Causeway is an important road which connects Singapore to Malaysia
The Johor–Singapore Causeway is an important road which connects Singapore to Malaysia
-
The Sorell Causeway in Tasmania, Australia
-
 Lake Pontchartrain Causeway bridge in New Orleans
Lake Pontchartrain Causeway bridge in New Orleans
-
 Causeway across Colwyn Bay Beach, Wales, United Kingdom
Causeway across Colwyn Bay Beach, Wales, United Kingdom
-
 The King Fahd Causeway from satellite photo
The King Fahd Causeway from satellite photo
-
 Causeway in St. George's, Bermuda
Causeway in St. George's, Bermuda
-
 Causeway that connects Victor Harbor with Granite Island in Australia (Completed in 1867)
Causeway that connects Victor Harbor with Granite Island in Australia (Completed in 1867)
-
 Canso Causeway from Cape Breton Island
Canso Causeway from Cape Breton Island
See also
References
- Oxford English Dictionary 1971.
- Williams, Robin; Williams, Romey (1992). The Somerset Levels. Bradford on Avon: Ex Libris Press. pp. 35–36. ISBN 0-948578-38-6.
- Wedgwood, Hensleigh (1855). "On False Etymologies". Transactions of the Philological Society (6): 66.
- "Causeway" . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
- Brunning, Richard (February 2001). "The Somerset Levels". Current Archaeology. XV (4) (172 (Special issue on Wetlands)): 139–143.
- Pollard, Edward (2008). "Inter-Tidal Causeways and Platforms of the 13th- to 16th-Century City-States of Kilwa Kisiwani, Tanzania". The International Journal of Nautical Archaeology. 1 (37): 98–114. Bibcode:2008IJNAr..37...98P. doi:10.1111/j.1095-9270.2007.00167.x. S2CID 161753263.
- "Cleanse Causeway". Battle of Linlithgow Bridge. Retrieved 13 November 2024.
- Coetzee, DanielJ.M.; Eysturlid, Lee W. (2013). Philosophers of War: The Evolution of History's Greatest Military Thinkers [2 Volumes]: The Evolution of History's Greatest Military Thinkers. ABC-CLIO. p. 353. ISBN 9780313070334.
Further reading
- Oxford English Dictionary. 1971. ASIN B01JXP1GBY.
- Collins Robert French Dictionary (5th ed.). 1998. ISBN 0-00-470526-2.
- Nouveau Petit Larousse Illustré (in French). Paris. 1934.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Grape, W. (1994). The Bayeux Tapestry. Munich: Prestel. ISBN 3-7913-1365-7.
- Evans, H. M.; Thomas, W. O. (1953). The New Welsh Dictionary (Y Geiriadur Newydd). Llandybie: Llyfrau'r Dryw.
External links
 Media related to causeways at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to causeways at Wikimedia Commons
| Infrastructure | |
|---|---|
| Geotechnical engineering | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offshore geotechnical engineering | |||||||
| Investigation and instrumentation |
| ||||||
| Soil |
| ||||||
| Structures (Interaction) |
| ||||||
| Mechanics |
| ||||||
| Numerical analysis software | |||||||
| Related fields | |||||||