 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4548-G05 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H26O10 |
| Molar mass | 546.528 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
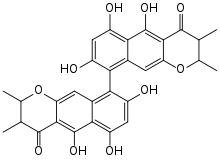
Chaetochromin, also known as 4548-G05, is an orally active, small-molecule, selective agonist of the insulin receptor. It has potent and long-lasting antidiabetic activity in vivo in mice. The drug may represent a novel potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes which is more convenient and tolerable to administer than injected insulin. It was discovered in 1981 in Chaetomium gracile fungi, and its interaction with the insulin receptor was identified in 2014.
Stereochemistry
Chaetochromin A and B are stereoisomers of this structure, while chaetochromin C and D are related but different compounds. It is not known whether the insulin mimetic effect was found in chaetochromin A or B, or in a mixture.
See also
References
- ^ Qiang G, Xue S, Yang JJ, Du G, Pang X, Li X, et al. (April 2014). "Identification of a small molecular insulin receptor agonist with potent antidiabetes activity". Diabetes. 63 (4): 1394–1409. doi:10.2337/db13-0334. PMC 3964510. PMID 24651808.
- Sekita S, Yoshihira K, Natori S, Udagawa S, Muroi T, Sugiyama Y, et al. (August 1981). "Mycotoxin production by Chaetomium spp. and related fungi". Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 27 (8): 766–772. doi:10.1139/m81-119. PMID 7296410.
- "Chaetochromin". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine.