| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Choline hydroxide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium hydroxide | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | ChOH |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.206 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
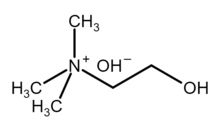
| Chemical formula | [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]OH |
| Molar mass | 121.180 g·mol |
| Appearance | Viscous colorless deliquescent liquid or white granular powder |
| Odor | Unpleasant, like trimethylamine |
| Density | 1.073 g/cm at 25 °C (46% water solution by weight) |
| Solubility in water | Very soluble |
| Solubility | 48-50% solution of choline hydroxide in water (by weight) is insoluble in toluene. Choline hydroxide
is soluble in ethanol, insoluble in diethyl ether and chloroform. |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4304 (46% water solution by weight) |
| Structure | |
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral at the nitrogen atom |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H314, H335, H372 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302, P304+P340, P305, P316, P317, P319, P321, P338, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | 92 °F (33 °C) |
| Autoignition temperature |
380 °C (716 °F) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 21.4 mg/kg (mouse, intravenous) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Choline chloride |
| Other cations | Tetraethylammonium hydroxide |
| Related compounds | Choline |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Choline hydroxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]OH. It is also known as choline base. It is used as solutions in water or alcohols, which are colorless and very alkaline.
Properties
It is hygroscopic and thus often encountered as a colorless viscous hydrated syrup that smells of trimethylamine (TMA). Aqueous solutions of choline are stable, but the compound slowly breaks down to ethylene glycol, polyethylene glycols, and TMA.
Chemistry
Choline hydroxide is a quaternary ammonium salt, consisting of choline cations ([(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]) and hydroxide anions (OH). It is bifunctional compound, meaning, it contains both quaternary ammonium functional group and a hydroxyl functional group. Choline hydroxide forms an ionic liquid.
Occurrence
The cation of this salt, choline, occurs in nature in living beings.
Uses
Choline hydroxide is used in industry as a pH regulating agent and as an eco-friendly, biodegradable, recyclable and efficient catalyst with high yields for synthesis of certain organic compounds (2-amino-3-nitro-4H-chromene derivatives) in an aqueous solution at room temperatures.

Safety
Choline hydroxide irritates skin, eyes and respiratory system. It can cause serious injuries to the eyes. Causes serious skin and eye burns. Inhalation of this chemical may cause dyspnea and corrosive injuries to upper respiratory system and lungs, which can lead to pneumonia. May react violently with strong oxidizing agents.
References
- ^ "Choline hydroxide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Krishnammagari, Suresh Kumar; Lim, Kwon Taek; Cho, Byung Gwon; Tae Jeong, Yeon (January 1, 2018). "Choline hydroxide: An efficient and biodegradable catalyst for the synthesis of 2-amino-3-nitro-4H-chromene derivatives in an aqueous medium". Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon and the Related Elements. 193 (9): 574–581. doi:10.1080/10426507.2018.1469489. S2CID 105825055 – via www.sciencedirect.com.
- ^ Kirk RE, et al. (2000). Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. Vol. 6 (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 100–102. ISBN 9780471484943.
- ^ "Choline hydroxide | 123-41-1". ChemicalBook.
- ^ https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/GB/en/product/aldrich/292257
- ^ https://www.carlroth.com/medias/SDB-3406-GB-EN.pdf?context=bWFzdGVyfHNlY3VyaXR5RGF0YXNoZWV0c3wzMTA3NDN8YXBwbGljYXRpb24vcGRmfHNlY3VyaXR5RGF0YXNoZWV0cy9oMjcvaGFmLzkwNjA5OTcxMzY0MTQucGRmfGVmOTEwZTlkM2E0YTVjN2U4NWI0YzUxZWExNjRkYzFlYmE2YzYzMzRmOTU1NTc4MDA1NTBkZDkxY2U4NDY3M2Y
- Rucker RB, Zempleni J, Suttie JW, McCormick DB (2007). Handbook of vitamins (4th ed.). Taylor & Francis. pp. 459–477. ISBN 9780849340222.
- "Choline". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University. February 2015. Retrieved 11 November 2019.