| |
| Continent | North America |
| Subregion | Caribbean |
| Geographic coordinates | 18°15′N 63°10′W / 18.250°N 63.167°W / 18.250; -63.167 |
| Area - Total - Water |
Ranked 227th 91 km² 0 km |
| Coastline | 61 km |
| Land boundaries | 0 km |
| Highest point | Crocus Hill, 73 m |
| Lowest point | Caribbean Sea, 0 m |
| Largest inland body of water | Road Bay Pond |
| Land Use - Arable land - Permanent crops - Other |
0 % 0 % 100 % (2012 est.) |
| Climate: | tropical; moderated by northeast trade winds |
| Terrain: | flat and low-lying island of coral and limestone |
| Natural resources | salt, fish, lobster |
| Natural hazards | hurricanes, tropical storms (June to November) |
| Environmental issues | low water supplies |
Anguilla is an island in the Leeward Islands. It has numerous bays, including Barnes, Little, Rendezvous, Shoal, and Road Bays.
Statistics
Location: Caribbean, island in the Caribbean Sea, east of Puerto Rico
Geographic coordinates: 18°15′ N, 63°10′ W
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area:
- total: 91 km (35 sq mi)
- land: 91 km (35 sq mi)
- water: 0 km (0 sq mi)
Area – comparative: about half the size of Washington, D.C.
Coastline: 61 km
Maritime claims:
- exclusive fishing zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- territorial sea: 3 nmi (5.6 km; 3.5 mi)
Climate: tropical moderated by northeast trade winds
Terrain: flat and low-lying island of coral and limestone
Elevation extremes:
- lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
- highest point: Crocus Hill 73 m
Natural resources: salt, fish, lobster
Land use:
- arable land: 0%
- permanent crops: 0%
- permanent pastures: 0%
- forests and woodland: 61.1%
- other: 38.9% (mostly rock with some commercial salt ponds)
Natural hazards: frequent hurricanes and other tropical storms (July to October)
Environment – current issues: supplies of potable water sometimes cannot meet increasing demand largely because of poor distribution system.
Islands and cays

The territory of Anguilla consists of the island of Anguilla itself (by far the largest), as well as numerous other islands and cays, most of which are very small and uninhabited. These include:
- Anguillita
- Blowing Rock
- Cove Cay
- Crocus Cay
- Deadman's Cay
- Dog Island
- East Cay
- Little Island
- Little Scrub Island
- Mid Cay
- North Cay
- Prickly Pear Cays
- Rabbit Island
- Sandy Island, also known as Sand Island
- Scilly Cay
- Scrub Island
- Seal Island
- Sombrero, also known as Hat Island
- South Cay
- South Wager Island
- West Cay
Districts
Anguilla is divided into fourteen districts:
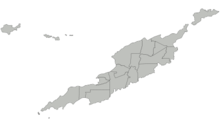
| District | Population (2011) |
|---|---|
| Blowing Point | 870 |
| East End | 671 |
| George Hill | 879 |
| Island Harbour | 988 |
| North Hill | 464 |
| North Side | 1980 |
| Sandy Ground | 230 |
| Sandy Hill | 636 |
| South Hill | 1722 |
| Stoney Ground | 1549 |
| The Farrington | 624 |
| The Quarter | 959 |
| The Valley | 1067 |
| West End | 813 |
Climate
Anguilla features a tropical wet and dry climate under the Köppen climate classification. The island has a rather dry climate, moderated by northeast trade winds. Temperatures vary little throughout the year. Average daily maxima range from about 27 °C (80.6 °F) in December to 30 °C (86 °F) in July. With no mountains to slow or trap clouds, rainfall is erratic, averaging about 900 mm (35.4 in) per year, the wettest months being September and October, and the driest February and March. Anguilla is vulnerable to hurricanes from June to November, peak season August to mid-October. The island suffered damage from Hurricane Luis in 1995, severe flooding of 1.5 to 6 metres (5 to 19.5 feet) from Hurricane Lenny in 1999 and severe damage from Hurricane Irma in 2017, which remains the most powerful hurricane to hit the island.
| Climate data for The Valley - capital of Anguilla | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
28 (82) |
28 (82) |
28 (82) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
30 (86) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26 (79) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
27 (81) |
27 (81) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
27 (81) |
26 (79) |
27 (81) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
| Average precipitation cm (inches) | 7 (2.8) |
4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
7 (2.8) |
9 (3.5) |
7 (2.8) |
8 (3.1) |
11 (4.3) |
11 (4.3) |
9 (3.5) |
11 (4.3) |
9 (3.5) |
102 (40) |
| Source: Weatherbase | |||||||||||||
Vegetation
Anguilla's coral and limestone terrain provide no subsistence possibilities for forests, woodland, pastures, crops, or arable lands. Its dry climate and thin soil hamper commercial agricultural development. In Anguilla forest cover is around 61% of the total land area, equivalent to 5,500 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, which was unchanged from 1990.
See also
References
- "Districts of Anguilla". Archived from the original on 2017-02-13. Retrieved 2015-03-23.
- "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for The Valley".
- Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023.
- "Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Anguilla". Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
External links
- Caribbean-On-Line.com provides detailed maps of Anguilla.
- Districts of Anguilla, Statoids.com
- Anguilla 2001 Census, Government of Anguilla
| Geography of North America | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states |  | |
| Dependencies and other territories | ||
| Anguilla | ||
|---|---|---|
| History | ||
| Districts | ||
| Education |
| |
| Transport | ||
| Landmarks | ||
| Symbols | ||
| This list is incomplete. | ||
| Climate of North America | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |
| Dependencies and other territories | |
| List of islands of the Caribbean | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Indies | |||||
| Caribbean Sea | |||||
| Caribbean continental zone |
| ||||
| Wider groupings may include: |
| ||||
| N.B.: Territories in italics are parts of transregional sovereign states or non-sovereign dependencies.
These three form the SSS islands that with the ABC islands comprise the Dutch Caribbean, of which the BES islands are not direct Kingdom constituents but subsumed with the country of the Netherlands. Physiographically, these continental islands are not part of the volcanic Windward Islands arc, although sometimes grouped with them culturally and politically. Disputed territories administered by Guyana. Disputed territories administered by Colombia. Bermuda is an isolated North Atlantic oceanic island, physiographically not part of the Lucayan Archipelago, Antilles, Caribbean Sea nor North American continental nor South American continental islands. It is grouped with the Northern American region, but occasionally also with the Caribbean region culturally. | |||||