| This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. Please help clarify the article. There might be a discussion about this on the talk page. (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Colors of noise |
|---|
In audio engineering, electronics, physics, and many other fields, the color of noise or noise spectrum refers to the power spectrum of a noise signal (a signal produced by a stochastic process). Different colors of noise have significantly different properties. For example, as audio signals they will sound different to human ears, and as images they will have a visibly different texture. Therefore, each application typically requires noise of a specific color. This sense of 'color' for noise signals is similar to the concept of timbre in music (which is also called "tone color"; however, the latter is almost always used for sound, and may consider detailed features of the spectrum).
The practice of naming kinds of noise after colors started with white noise, a signal whose spectrum has equal power within any equal interval of frequencies. That name was given by analogy with white light, which was (incorrectly) assumed to have such a flat power spectrum over the visible range. Other color names, such as pink, red, and blue were then given to noise with other spectral profiles, often (but not always) in reference to the color of light with similar spectra. Some of those names have standard definitions in certain disciplines, while others are informal and poorly defined. Many of these definitions assume a signal with components at all frequencies, with a power spectral density per unit of bandwidth proportional to 1/f and hence they are examples of power-law noise. For instance, the spectral density of white noise is flat (β = 0), while flicker or pink noise has β = 1, and Brownian noise has β = 2. Blue noise has β = -1.
Technical definitions

Various noise models are employed in analysis, many of which fall under the above categories. AR noise or "autoregressive noise" is such a model, and generates simple examples of the above noise types, and more. The Federal Standard 1037C Telecommunications Glossary defines white, pink, blue, and black noise.
The color names for these different types of sounds are derived from a loose analogy between the spectrum of frequencies of sound wave present in the sound (as shown in the blue diagrams) and the equivalent spectrum of light wave frequencies. That is, if the sound wave pattern of "blue noise" were translated into light waves, the resulting light would be blue, and so on.
White noise
Main article: White noise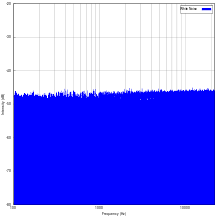
White noise is a signal (or process), named by analogy to white light, with a flat frequency spectrum when plotted as a linear function of frequency (e.g., in Hz). In other words, the signal has equal power in any band of a given bandwidth (power spectral density) when the bandwidth is measured in Hz. For example, with a white noise audio signal, the range of frequencies between 40 Hz and 60 Hz contains the same amount of sound power as the range between 400 Hz and 420 Hz, since both intervals are 20 Hz wide. Note that spectra are often plotted with a logarithmic frequency axis rather than a linear one, in which case equal physical widths on the printed or displayed plot do not all have the same bandwidth, with the same physical width covering more Hz at higher frequencies than at lower frequencies. In this case a white noise spectrum that is equally sampled in the logarithm of frequency (i.e., equally sampled on the X axis) will slope upwards at higher frequencies rather than being flat. However it is not unusual in practice for spectra to be calculated using linearly-spaced frequency samples but plotted on a logarithmic frequency axis, potentially leading to misunderstandings and confusion if the distinction between equally spaced linear frequency samples and equally spaced logarithmic frequency samples is not kept in mind.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Pink noise
Main article: Pink noise
The frequency spectrum of pink noise is linear in logarithmic scale; it has equal power in bands that are proportionally wide. This means that pink noise would have equal power in the frequency range from 40 to 60 Hz as in the band from 4000 to 6000 Hz. Since humans hear in such a proportional space, where a doubling of frequency (an octave) is perceived the same regardless of actual frequency (40–60 Hz is heard as the same interval and distance as 4000–6000 Hz), every octave contains the same amount of energy and thus pink noise is often used as a reference signal in audio engineering. The spectral power density, compared with white noise, decreases by 3.01 dB per octave (10 dB per decade); density proportional to 1/f. For this reason, pink noise is often called "1/f noise".
Since there are an infinite number of logarithmic bands at both the low frequency (DC) and high frequency ends of the spectrum, any finite energy spectrum must have less energy than pink noise at both ends. Pink noise is the only power-law spectral density that has this property: all steeper power-law spectra are finite if integrated to the high-frequency end, and all flatter power-law spectra are finite if integrated to the DC, low-frequency limit.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Brownian noise
Main article: Brownian noise
Brownian noise, also called Brown noise, is noise with a power density which decreases 6.02 dB per octave (20 dB per decade) with increasing frequency (frequency density proportional to 1/f) over a frequency range excluding zero (DC). It is also called "red noise", with pink being between red and white.
Brownian noise can be generated with temporal integration of white noise. "Brown" noise is not named for a power spectrum that suggests the color brown; rather, the name derives from Brownian motion, also known as "random walk" or "drunkard's walk".

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Blue noise

Blue noise is also called azure noise. Blue noise's power density increases 3.01 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f ) over a finite frequency range. In computer graphics, the term "blue noise" is sometimes used more loosely as any noise with minimal low frequency components and no concentrated spikes in energy. This can be good noise for dithering. Retinal cells are arranged in a blue-noise-like pattern which yields good visual resolution.
Cherenkov radiation is a naturally occurring example of almost perfect blue noise, with the power density growing linearly with frequency over spectrum regions where the permeability of index of refraction of the medium are approximately constant. The exact density spectrum is given by the Frank–Tamm formula. In this case, the finiteness of the frequency range comes from the finiteness of the range over which a material can have a refractive index greater than unity. Cherenkov radiation also appears as a bright blue color, for these reasons.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Violet noise

Violet noise is also called purple noise. Violet noise's power density increases 6.02 dB per octave with increasing frequency "The spectral analysis shows that GPS acceleration errors seem to be violet noise processes. They are dominated by high-frequency noise." (density proportional to f ) over a finite frequency range. It is also known as differentiated white noise, due to its being the result of the differentiation of a white noise signal.
Due to the diminished sensitivity of the human ear to high-frequency hiss and the ease with which white noise can be electronically differentiated (high-pass filtered at first order), many early adaptations of dither to digital audio used violet noise as the dither signal.
Acoustic thermal noise of water has a violet spectrum, causing it to dominate hydrophone measurements at high frequencies. "Predictions of the thermal noise spectrum, derived from classical statistical mechanics, suggest increasing noise with frequency with a positive slope of 6.02 dB octave." "Note that thermal noise increases at the rate of 20 dB decade"

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Grey noise
Main article: Grey noise
Grey noise is random white noise subjected to a psychoacoustic equal loudness curve (such as an inverted A-weighting curve) over a given range of frequencies, giving the listener the perception that it is equally loud at all frequencies. This is in contrast to standard white noise which has equal strength over a linear scale of frequencies but is not perceived as being equally loud due to biases in the human equal-loudness contour.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Velvet noise

Velvet noise is a sparse sequence of random positive and negative impulses. Velvet noise is typically characterised by its density in taps/second. At high densities it sounds similar to white noise; however, it is perceptually "smoother". The sparse nature of velvet noise allows for efficient time-domain convolution, making velvet noise particularly useful for applications where computational resources are limited, like real-time reverberation algorithms. Velvet noise is also frequently used in decorrelation filters.

Problems playing this file? See media help.
Informal definitions
There are also many colors used without precise definitions (or as synonyms for formally defined colors), sometimes with multiple definitions.
Red noise
- A synonym for Brownian noise, as above. That is, it is similar to pink noise, but with different spectral content and different relationships (i.e. 1/f for pink noise, while 1/f for red noise, or a decrease of 6.02 dB per octave).
- In areas where terminology is used loosely, "red noise" may refer to any system where power density decreases with increasing frequency.
Green noise

Problems playing this file? See media help.
- The mid-frequency component of white noise, used in halftone dithering
- Bounded Brownian noise
- Vocal spectrum noise used for testing audio circuits
- Joseph S. Wisniewski writes that "green noise" is marketed by producers of ambient sound effects recordings as "the background noise of the world". It simulates the spectra of natural settings, without human-made noises. It is similar to pink noise, but has more energy in the area of 500 Hz.
Black noise
- Silence
- Infrasound
- Noise with a 1/f spectrum, where β > 2. This formula is used to model the frequency of natural disasters.
- Noise that has a frequency spectrum of predominantly zero power level over all frequencies except for a few narrow bands or spikes. Note: An example of black noise in a facsimile transmission system is the spectrum that might be obtained when scanning a black area in which there are a few random white spots. Thus, in the time domain, a few random pulses occur while scanning.
- Noise with a spectrum corresponding to the blackbody radiation (thermal noise). For temperatures higher than about 3×10 K the peak of the blackbody spectrum is above the upper limit of human hearing range. In those situations, for the purposes of what is heard, black noise is well approximated as violet noise. At the same time, Hawking radiation of black holes may have a peak in hearing range, so the radiation of a typical stellar black hole with a mass equal to 6 solar masses will have a maximum at a frequency of 604.5 Hz – this noise is similar to green noise. A formula is: Hz. Several examples of audio files with this spectrum can be found here.
Noisy white
In telecommunication, the term noisy white has the following meanings:
- In facsimile or display systems, such as television, a nonuniformity in the white area of the image, i.e., document or picture, caused by the presence of noise in the received signal.
- A signal or signal level that is supposed to represent a white area on the object, but has a noise content sufficient to cause the creation of noticeable black spots on the display surface or record medium.
Noisy black
In telecommunication, the term noisy black has the following meanings:
- In facsimile or display systems, such as television, a nonuniformity in the black area of the image, i.e., document or picture, caused by the presence of noise in the received signal.
- A signal or signal level that is supposed to represent a black area on the object, but has a noise content sufficient to cause the creation of noticeable non-black spots on the display surface or record medium.
Generation
Colored noise can be computer-generated by first generating a white noise signal, Fourier-transforming it, then multiplying the amplitudes of the different frequency components with a frequency-dependent function. Matlab programs are available to generate power-law colored noise in one or any number of dimensions.
Identification of power law frequency noise
Identifying the dominant noise type in a time series has many applications including clock stability analysis and market forecasting. There are two algorithms based on autocorrelation functions that can identify the dominant noise type in a data set provided the noise type has a power law spectral density.
Lag(1) autocorrelation method (non-overlapped)
The first method for doing noise identification is based on a paper by W.J Riley and C.A Greenhall. First the lag(1) autocorrelation function is computed and checked to see if it is less than one third (which is the threshold for a stationary process):
where is the number of data points in the time series, are the phase or frequency values, and is the average value of the time series. If used for clock stability analysis, the values are the non-overlapped (or binned) averages of the original frequency or phase array for some averaging time and factor. Now discrete-time fractionally integrated noises have power spectral densities of the form which are stationary for . The value of is calculated using :
where is the lag(1) autocorrelation function defined above. If then the first differences of the adjacent time series data are taken times until . The power law for the stationary noise process is calculated from the calculated and the number of times the data has been differenced to achieve as follows:
where is the power of the frequency noise which can be rounded to identify the dominant noise type (for frequency data is the power of the frequency noise but for phase data the power of the frequency noise is ).
Lag(m) autocorrelation method (overlapped)
This method improves on the accuracy of the previous method and was introduced by Z. Chunlei, Z. Qi, Y. Shuhuana. Instead of using the lag(1) autocorrelation function the lag(m) correlation function is computed instead:
where is the "lag" or shift between the time series and the delayed version of itself. A major difference is that are now the averaged values of the original time series computed with a moving window average and averaging factor also equal to . The value of is computed the same way as in the pervious method and is again the criteria for a stationary process. The other major difference between this and the previous method is that the differencing used to make the time series stationary () is done between values that are spaced a distance apart:
The value of the power is calculated the same as the previous method as well.
See also
- Mains hum (also known as the AC power hum)
- Whittle likelihood
References
- "ATIS Telecom Glossary". atis.org. Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- "Federal Standard 1037C". Institute for Telecommunication Sciences. Institute for Telecommunication Sciences, National Telecommunications and Information Administration (ITS-NTIA). Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- Randall D. Peters (2 January 2012). "Tutorial on Power Spectral Density Calculations for Mechanical Oscillators".
- "Definition: pink noise". its.bldrdoc.gov. Archived from the original on 8 June 2021.
- "Definition: blue noise". its.bldrdoc.gov. Archived from the original on 8 June 2021.
- Mitchell, Don P. (1987). "Generating antialiased images at low sampling densities". Proceedings of the 14th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. Vol. 21. pp. 65–72. doi:10.1145/37401.37410. ISBN 0897912276. S2CID 207582968.
- Yellott, John I. Jr (1983). "Spectral Consequences of Photoreceptor Sampling in the Rhesus Retina". Science. 221 (4608): 382–85. Bibcode:1983Sci...221..382Y. doi:10.1126/science.6867716. PMID 6867716.
- Transactions of the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers 1968 Quote: 'A "purple noise," accordingly, is a noise the spectrum level of which rises with frequency.'
- Zhang, Q. J.; Schwarz, K.-P. (April 1996). "Estimating double difference GPS multipath under kinematic conditions". Proceedings of the Position Location and Navigation Symposium – PLANS '96. Position Location and Navigation Symposium – PLANS '96. Atlanta, GA, USA: IEEE. pp. 285–91. doi:10.1109/PLANS.1996.509090.
- Hildebrand, John A. (2009). "Anthropogenic and natural sources of ambient noise in the ocean". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 395: 478–480. Bibcode:2009MEPS..395....5H. doi:10.3354/meps08353.
- Mellen, R. H. (1952). "The Thermal-Noise Limit in the Detection of Underwater Acoustic Signals". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 24 (5): 478–80. Bibcode:1952ASAJ...24..478M. doi:10.1121/1.1906924.
- Välimäki, Vesa; Lehtonen, Heidi-Maria; Takanen, Marko (2013). "A Perceptual Study on Velvet Noise and Its Variants at Different Pulse Densities". IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing. 21 (7): 1481–1488. doi:10.1109/TASL.2013.2255281. S2CID 17173495.
- Järveläinen, Hanna; Karjalainen, Matti (March 2007). Reverberation Modeling Using Velvet Noise. 30th International Conference: Intelligent Audio Environments. Helsinki, Finland: AES.
- "The Switched Convolution Reverberator, Lee et. al".
- Alary, Benoit; Politis, Archontis; Välimäki, Vesa (September 2017). Velvet-Noise Decorrelator. 20th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-17). Edinburgh, UK.
- "Index: Noise (Disciplines of Study [DoS])". Archived from the original on 22 May 2006.
- Gilman, D. L.; Fuglister, F. J.; Mitchell Jr., J. M. (1963). "On the power spectrum of "red noise"". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 20 (2): 182–84. Bibcode:1963JAtS...20..182G. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0182:OTPSON>2.0.CO;2.
- Daniel L. Rudnick, Russ E. Davis (2003). "Red noise and regime shifts" (PDF). Deep-Sea Research Part I. 50 (6): 691–99. Bibcode:2003DSRI...50..691R. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(03)00053-0.
- Lau, Daniel Leo; Arce, Gonzalo R.; Gallagher, Neal C. (1998). "Green-noise digital halftoning". Proceedings of the IEEE. 86 (12): 2424–42. doi:10.1109/5.735449.
- ^ Joseph S. Wisniewski (7 October 1996). "Colors of noise pseudo FAQ, version 1.3". Newsgroup: comp.dsp. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- "David Bowie and the Black Noise". The Vigilant Citizen Forums. 21 May 2017.
- Schroeder, Manfred (2009). Fractals, Chaos, Power Laws: Minutes from an Infinite Paradise. Courier Dover. pp. 129–30. ISBN 978-0486472041.
- "Definition of "black noise" – Federal Standard 1037C". Archived from the original on 12 December 2008. Retrieved 28 April 2008.
- "Definition: noisy white". its.bldrdoc.gov. Archived from the original on 8 June 2021.
- "Definition: noisy black". its.bldrdoc.gov. Archived from the original on 8 June 2021.
- Das, Abhranil (2022). Camouflage detection & signal discrimination: theory, methods & experiments (corrected) (PhD). The University of Texas at Austin. doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.32016.07683.
- Riley, W.J.; Greenhal, C.A. (2004). "Power law noise identification using the lag 1 autocorrelation". 18th European Frequency and Time Forum (EFTF 2004). IEE. pp. 576–580. doi:10.1049/cp:20040932. ISBN 978-0-86341-384-1.
- Zhou Chunlei; Zhang Qi; Yan Shuhua (August 2011). "Power law noise identification using the LAG 1 autocorrelation by overlapping samples". IEEE 2011 10th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments. IEEE. pp. 110–113. doi:10.1109/icemi.2011.6037776. ISBN 978-1-4244-8158-3.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 22 January 2022.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 22 January 2022.
External links
- Some colored noise definitions
- Online Colored Noise Generator and True Grey Noise Generator
- Black Noise and Population Persistence
| Timbre | |
|---|---|
 3.01 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f ) over a finite frequency range. In computer graphics, the term "blue noise" is sometimes used more loosely as any noise with minimal low frequency components and no concentrated spikes in energy. This can be good noise for
3.01 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f ) over a finite frequency range. In computer graphics, the term "blue noise" is sometimes used more loosely as any noise with minimal low frequency components and no concentrated spikes in energy. This can be good noise for  Hz. Several examples of audio files with this spectrum can be found
Hz. Several examples of audio files with this spectrum can be found 
 is the number of data points in the time series,
is the number of data points in the time series,  are the phase or frequency values, and
are the phase or frequency values, and  is the average value of the time series. If used for clock stability analysis, the
is the average value of the time series. If used for clock stability analysis, the  which are stationary for
which are stationary for  . The value of
. The value of  is calculated using
is calculated using  :
:

 then the first differences of the adjacent time series data are taken
then the first differences of the adjacent time series data are taken  times until
times until 
 is the power of the frequency noise which can be rounded to identify the dominant noise type (for frequency data
is the power of the frequency noise which can be rounded to identify the dominant noise type (for frequency data  ).
).

 is the "lag" or shift between the time series and the delayed version of itself. A major difference is that
is the "lag" or shift between the time series and the delayed version of itself. A major difference is that 