For a topical guide, see Imperial and US customary measurement systems.
| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2020) |


Both the British imperial measurement system and United States customary systems of measurement derive from earlier English unit systems used prior to 1824 that were the result of a combination of the local Anglo-Saxon units inherited from Germanic tribes and Roman units.
Having this shared heritage, the two systems are quite similar, but there are differences. The US customary system is based on English systems of the 18th century, while the imperial system was defined in 1824, almost a half-century after American independence.
Volume
Volume may be measured either in terms of units of cubic length or with specific volume units. The units of cubic length (the cubic inch, cubic foot, cubic mile, etc.) are the same in the imperial and US customary systems, but they differ in their specific units of volume (the bushel, gallon, fluid ounce, etc.). The US customary system has one set of units for fluids and another set for dry goods. The imperial system has only one set defined independently of, and subdivided differently from, its US counterparts.
By the end of the 18th century, various systems of volume measurement were in use throughout the British Empire. Wine was measured with units based on the wine gallon of 231 cubic inches (3.785 L), beer was measured with units based on an ale gallon of 282 cubic inches (4.621 L) and grain was measured with the Winchester measure with a gallon of approximately 268.8 cubic inches (one eighth of a Winchester bushel or 4.405 L). In 1824, these units were replaced with a single system based on the imperial gallon. Originally defined as the volume of 10 pounds (4.54 kg) of distilled water (under certain conditions), then redefined by the Weights and Measures Act 1985 to be exactly 4.54609 L (277.4 cu in), the imperial gallon is close in size to the old ale gallon.
The Winchester measure was made obsolete in the British Empire but remained in use in the US. The Winchester bushel was replaced with an imperial bushel of eight imperial gallons. The subdivisions of the bushel were maintained. As with US dry measures, the imperial system divides the bushel into 4 pecks, 8 gallons, 32 quarts or 64 pints. Thus, all of these imperial measures are about 3% larger than are their US dry-measure counterparts.
Fluid measure is not as straightforward. The American colonists adopted a system based on the 231-cubic-inch wine gallon for all fluid purposes. This became the US fluid gallon. Both the imperial and US fluid gallon are divided into 4 quarts, 8 pints or 32 gills. However, whereas the US gill is divided into four US fluid ounces, the imperial gill is divided into five imperial fluid ounces. So whilst the imperial gallon, quart, pint and gill are about 20% larger than are their US fluid measure counterparts, the fluid ounce is about 4% smaller. One avoirdupois ounce of water has an approximate volume of one imperial fluid ounce at 62 °F (16.67 °C). This convenient fluid-ounce-to-avoirdupois-ounce relation does not exist in the US system.
One noticeable comparison between the imperial system and the US system is between some Canadian and American beer bottles. Many Canadian brewers package beer in a 12-imperial-fluid-ounce bottles, which are 341 mL each. American brewers package their beer in 12-US-fluid-ounce bottles, which are 355 mL each. As a result, Canadian bottles are labelled as 11.5 fl oz in US units when imported into the United States. Because the standard size of Canadian beer bottles predates the adoption of the metric system in Canada, the bottles are still sold and labelled in Canada as 341 mL. Canned beer in Canada is sold and labelled in 355 mL cans, and when exported to the US, they are labelled as 12 fl oz.
Notes:
| ||||
| Unit name | Imperial measures | US fluid measures | US dry measures | Metric measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fluid ounces | ||||
| Imperial fluid ounce (fl oz) |
≡ 1 imp fl oz |
≈ 0.96075994040 US fl oz |
≡ 28.4130625 mL | |
| US fluid ounce (customary) (fl oz) |
≈ 1.04084273079 imp fl oz |
≡ 1 US fl oz |
≡ 29.5735295625 mL | |
| US fluid ounce (food nutrition labelling) (fl oz) (food) |
≈ 1.05585239184 imp fl oz |
≈ 1.01442068106 US fl oz |
≡ 30 mL | |
pints | ||||
| Imperial pint (pt) |
≡ 20 imp fl oz |
≈ 19.2151988081 US fl oz |
≈ 1.03205674349 US dry pt |
≡ 568.26125 mL |
| US liquid pint (pt) |
≈ 16.6534836926 imp fl oz |
≡ 16 US fl oz |
≈ 0.859367007375 US dry pt |
≡ 473.176473 mL |
| US dry pint (pt) |
≈ 19.3787794384 imp fl oz |
≈ 18.6183549784 US fl oz |
≡ 1 US dry pt |
≡ 550.6104713575 mL |
quarts | ||||
| Imperial quart (qt) |
≡ 40 imp fl oz |
≈ 38.4303976162 US fl oz |
≈ 1.03205674349 US dry qt |
≡ 1136.5225 mL |
| US liquid quart (qt) |
≈ 33.3069673852 imp fl oz |
≡ 32 US fl oz |
≈ 0.859367007375 US dry qt |
≡ 946.352946 mL |
| US dry quart (qt) |
≈ 38.7575588768 imp fl oz |
≈ 37.2367099567 US fl oz |
≡ 1 US dry qt |
≡ 1101.220942715 mL |
gallons | ||||
| Imperial gallon (gal) |
≡ 160 imp fl oz |
≈ 153.721590465 US fl oz |
≈ 4.12822697395 US dry qt |
≡ 4546.09 mL |
| US liquid gallon (gal) |
≈ 133.227869541 imp fl oz |
≡ 128 US fl oz |
≈ 3.437468029501 US dry qt |
≡ 3785.411784 mL |
| US dry gallon (gal) |
≈ 155.030235507 imp fl oz |
≈ 148.946839827 US fl oz |
≡ 4 US dry qt |
≡ 4404.88377086 mL |
metric | ||||
| litre (l or L or dm) |
≈ 35.1950797279 imp fl oz |
≈ 33.8140227018 US fl oz |
≈ 0.90808298427 US dry qt |
≡ 1000 mL |
Length
The international yard is defined as exactly 0.9144 metres. This definition was approved by the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand through the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, and corresponds with the previous 1930s British and American definitions of 1 inch being 25.4 mm. In all systems, a yard is 36 inches.
The US survey foot and survey mile were maintained as separate units for surveying purposes to avoid the accumulation of error that would follow replacing them with the international versions, particularly with State Plane Coordinate Systems. The choice of unit for surveying purposes is based on the unit used when the overall framework or geodetic datum for the region was established; for example, much of the former British empire still uses the Clarke foot for surveying.
The US survey foot is defined so that 1 metre is exactly 39.37 inches, making the international foot of 0.3048 metres exactly two parts per million shorter. This is a difference of just over 3.2 mm, or a little more than one-eighth of an inch per mile. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the survey foot is obsolete as of 1 January 2023, and its use discouraged.
The main units of length (inch, foot, yard and international mile) were the same in the US, though the US rarely uses some of the intermediate units today, such as the (surveyor's) chain (22 yards) and the furlong (220 yards).
At one time, the definition of the nautical mile was based on the surface area of the Clarke ellipsoid. While the US used the full value of 1853.256 metres, in the British Commonwealth, this was rounded to 6080 feet (1853.184 m). These have been replaced by the international version (which rounds the 60th part of the 45° to the nearest metre) of 1852 metres.
Weight and mass
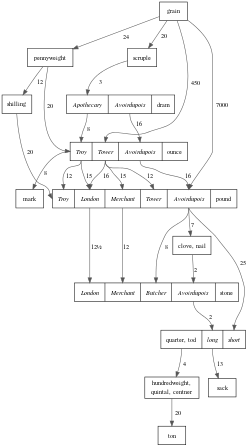
Traditionally, both Britain and the US used three different weight systems: troy weight for precious metals, apothecaries' weight for medicines and avoirdupois weight for almost all other purposes. However, apothecaries' weight has now been superseded by the metric system.
One important difference is the widespread use in Britain of the stone of 14 pounds (6.35029318 kg) for body weight; this unit is not used in the United States, although flour was sold by a barrel of 196 pounds (14 stone) until World War II.
Another difference arose when Britain abolished the troy pound (373.2417216 g) on 1 January 1879, leaving only the troy ounce (31.1034768 g) and its decimal subdivisions, whereas the troy pound (of 12 troy ounces) and pennyweight are still legal in the United States, although they are no longer widely used.
In all of these systems, the fundamental unit is the pound (lb), and all other units are defined as fractions or multiples of a pound. The tables of imperial troy mass and apothecaries' mass are the same as the corresponding United States tables, except for the British spelling "drachm" in the table of apothecaries' mass. The table of imperial avoirdupois mass is the same as the United States table up to one pound, but above that point, the tables differ.
The imperial system has a hundredweight, defined as eight stone of 14 lb each, or 112 lb (50.80234544 kg), whereas a US hundredweight is 100 lb (45.359237 kg). In both systems, 20 hundredweights make a ton. In the US, the terms long ton (2240 lb, 1016.0469088 kg) and short ton (2000 lb; 907.18474 kg) are used. The metric ton is the name used for the tonne (1000 kg, 2204.62262 lb), which is about 1.6% less than the long ton.
The US customary system also includes the kip, equivalent to 1,000 pounds of force, which is also occasionally used as a unit of weight of 1,000 pounds (usually in engineering contexts).
See also
Notes
- Wine gallons, however, continued to be used for tax purposes in the UK until the late 1990s.
- The water was to be weighed in air with brass weights with the barometer standing at 30 inches of mercury (102 kPa) at a temperature of 62 °F (17 °C). In 1963 these conditions were redefined such that the water was to have a density of 0.998859 g/mL and to be weighed in air of density 0.001217 g/mL against weights of density 8.136 g/mL.
- Originally defined as the volume of a cylinder 18+1⁄2 inches (470 mm) in diameter and 8 inches (200 mm) deep, the Winchester bushel was redefined in the US as 2150.42 cubic inches.
- The gill is no longer in common use.
- The now rarely used apothecaries' system of fluid measures further divides the fluid ounce into 8 fluid drams or 480 minims. Also in the imperial system there is a fluid scruple of 20 minims which is absent from the US customary system. Like the fluid ounce the dram and minim are about 4% smaller in the imperial system.
- 160 imperial fluid ounces is equivalent to one imperial gallon, which is the approximate volume of 10 pounds or 160 avoirdupois ounces of water at 62 °F.
References
- "U.S. Survey Foot". NIST. 26 July 2019.
| Imperial units | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison with US customary system | |||||||
| Length | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
| Volume |
| ||||||
| Speed | |||||||
| Mass | |||||||
| Pressure | |||||||
| Other units and measures | |||||||
| Related systems | |||||||
| United States customary units | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison with imperial unit system | |||||||||
| Length | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| Volume |
| ||||||||
| Speed | |||||||||
| Mass | |||||||||
| Force | |||||||||
| Pressure | |||||||||
| Other units and measures | |||||||||
| Related systems | |||||||||
| Systems of measurement | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current |
| ||||||||||||
| Background |
| ||||||||||||
| Historic |
| ||||||||||||
| Ancient | |||||||||||||
| List articles | |||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||