
In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon where celestial objects exhibit an apparent motion about their true positions based on the velocity of the observer: It causes objects to appear to be displaced towards the observer's direction of motion. The change in angle is of the order of v/c where c is the speed of light and v the velocity of the observer. In the case of "stellar" or "annual" aberration, the apparent position of a star to an observer on Earth varies periodically over the course of a year as the Earth's velocity changes as it revolves around the Sun, by a maximum angle of approximately 20 arcseconds in right ascension or declination.
The term aberration has historically been used to refer to a number of related phenomena concerning the propagation of light in moving bodies. Aberration is distinct from parallax, which is a change in the apparent position of a relatively nearby object, as measured by a moving observer, relative to more distant objects that define a reference frame. The amount of parallax depends on the distance of the object from the observer, whereas aberration does not. Aberration is also related to light-time correction and relativistic beaming, although it is often considered separately from these effects.
Aberration is historically significant because of its role in the development of the theories of light, electromagnetism and, ultimately, the theory of special relativity. It was first observed in the late 1600s by astronomers searching for stellar parallax in order to confirm the heliocentric model of the Solar System. However, it was not understood at the time to be a different phenomenon. In 1727, James Bradley provided a classical explanation for it in terms of the finite speed of light relative to the motion of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun, which he used to make one of the earliest measurements of the speed of light. However, Bradley's theory was incompatible with 19th-century theories of light, and aberration became a major motivation for the aether drag theories of Augustin Fresnel (in 1818) and G. G. Stokes (in 1845), and for Hendrik Lorentz's aether theory of electromagnetism in 1892. The aberration of light, together with Lorentz's elaboration of Maxwell's electrodynamics, the moving magnet and conductor problem, the negative aether drift experiments, as well as the Fizeau experiment, led Albert Einstein to develop the theory of special relativity in 1905, which presents a general form of the equation for aberration in terms of such theory.
Explanation
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Aberration" astronomy – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Aberration may be explained as the difference in angle of a beam of light in different inertial frames of reference. A common analogy is to consider the apparent direction of falling rain. If rain is falling vertically in the frame of reference of a person standing still, then to a person moving forwards the rain will appear to arrive at an angle, requiring the moving observer to tilt their umbrella forwards. The faster the observer moves, the more tilt is needed.
The net effect is that light rays striking the moving observer from the sides in a stationary frame will come angled from ahead in the moving observer's frame. This effect is sometimes called the "searchlight" or "headlight" effect.
In the case of annual aberration of starlight, the direction of incoming starlight as seen in the Earth's moving frame is tilted relative to the angle observed in the Sun's frame. Since the direction of motion of the Earth changes during its orbit, the direction of this tilting changes during the course of the year, and causes the apparent position of the star to differ from its true position as measured in the inertial frame of the Sun.
While classical reasoning gives intuition for aberration, it leads to a number of physical paradoxes observable even at the classical level (see history). The theory of special relativity is required to correctly account for aberration. The relativistic explanation is very similar to the classical one however, and in both theories aberration may be understood as a case of addition of velocities.
Classical explanation
In the Sun's frame, consider a beam of light with velocity equal to the speed of light , with x and y velocity components and , and thus at an angle such that . If the Earth is moving at velocity in the x direction relative to the Sun, then by velocity addition the x component of the beam's velocity in the Earth's frame of reference is , and the y velocity is unchanged, . Thus the angle of the light in the Earth's frame in terms of the angle in the Sun's frame is
In the case of , this result reduces to , which in the limit may be approximated by .
Relativistic explanation
The reasoning in the relativistic case is the same except that the relativistic velocity addition formulas must be used, which can be derived from Lorentz transformations between different frames of reference. These formulas are
where , giving the components of the light beam in the Earth's frame in terms of the components in the Sun's frame. The angle of the beam in the Earth's frame is thus
In the case of , this result reduces to , and in the limit this may be approximated by . This relativistic derivation keeps the speed of light constant in all frames of reference, unlike the classical derivation above.
Relationship to light-time correction and relativistic beaming

Aberration is related to two other phenomena, light-time correction, which is due to the motion of an observed object during the time taken by its light to reach an observer, and relativistic beaming, which is an angling of the light emitted by a moving light source. It can be considered equivalent to them but in a different inertial frame of reference. In aberration, the observer is considered to be moving relative to a (for the sake of simplicity) stationary light source, while in light-time correction and relativistic beaming the light source is considered to be moving relative to a stationary observer.
Consider the case of an observer and a light source moving relative to each other at constant velocity, with a light beam moving from the source to the observer. At the moment of emission, the beam in the observer's rest frame is tilted compared to the one in the source's rest frame, as understood through relativistic beaming. During the time it takes the light beam to reach the observer the light source moves in the observer's frame, and the 'true position' of the light source is displaced relative to the apparent position the observer sees, as explained by light-time correction. Finally, the beam in the observer's frame at the moment of observation is tilted compared to the beam in source's frame, which can be understood as an aberrational effect. Thus, a person in the light source's frame would describe the apparent tilting of the beam in terms of aberration, while a person in the observer's frame would describe it as a light-time effect.
The relationship between these phenomena is only valid if the observer and source's frames are inertial frames. In practice, because the Earth is not an inertial rest frame but experiences centripetal acceleration towards the Sun, many aberrational effects such as annual aberration on Earth cannot be considered light-time corrections. However, if the time between emission and detection of the light is short compared to the orbital period of the Earth, the Earth may be approximated as an inertial frame and aberrational effects are equivalent to light-time corrections.
Types
The Astronomical Almanac describes several different types of aberration, arising from differing components of the Earth's and observed object's motion:
- Stellar aberration: "The apparent angular displacement of the observed position of a celestial body resulting from the motion of the observer. Stellar aberration is divided into diurnal, annual, and secular components."
- Annual aberration: "The component of stellar aberration resulting from the motion of the Earth about the Sun."
- Diurnal aberration: "The component of stellar aberration resulting from the observer's diurnal motion about the center of the Earth due to the Earth's rotation."
- Secular aberration: "The component of stellar aberration resulting from the essentially uniform and almost rectilinear motion of the entire solar system in space. Secular aberration is usually disregarded."
- Planetary aberration: "The apparent angular displacement of the observed position of a solar system body from its instantaneous geocentric direction as would be seen by an observer at the geocenter. This displacement is caused by the aberration of light and light-time displacement."
Annual aberration


Annual aberration is caused by the motion of an observer on Earth as the planet revolves around the Sun. Due to orbital eccentricity, the orbital velocity of Earth (in the Sun's rest frame) varies periodically during the year as the planet traverses its elliptic orbit and consequently the aberration also varies periodically, typically causing stars to appear to move in small ellipses.
Approximating Earth's orbit as circular, the maximum displacement of a star due to annual aberration is known as the constant of aberration, conventionally represented by . It may be calculated using the relation substituting the Earth's average speed in the Sun's frame for and the speed of light . Its accepted value is 20.49552 arcseconds (sec) or 0.000099365 radians (rad) (at J2000).
Assuming a circular orbit, annual aberration causes stars exactly on the ecliptic (the plane of Earth's orbit) to appear to move back and forth along a straight line, varying by on either side of their position in the Sun's frame. A star that is precisely at one of the ecliptic poles (at 90° from the ecliptic plane) will appear to move in a circle of radius about its true position, and stars at intermediate ecliptic latitudes will appear to move along a small ellipse.
For illustration, consider a star at the northern ecliptic pole viewed by an observer at a point on the Arctic Circle. Such an observer will see the star transit at the zenith, once every day (strictly speaking sidereal day). At the time of the March equinox, Earth's orbit carries the observer in a southwards direction, and the star's apparent declination is therefore displaced to the south by an angle of . On the September equinox, the star's position is displaced to the north by an equal and opposite amount. On either solstice, the displacement in declination is 0. Conversely, the amount of displacement in right ascension is 0 on either equinox and at maximum on either solstice.
In actuality, Earth's orbit is slightly elliptic rather than circular, and its speed varies somewhat over the course of its orbit, which means the description above is only approximate. Aberration is more accurately calculated using Earth's instantaneous velocity relative to the barycenter of the Solar System.
Note that the displacement due to aberration is orthogonal to any displacement due to parallax. If parallax is detectable, the maximum displacement to the south would occur in December, and the maximum displacement to the north in June. It is this apparently anomalous motion that so mystified early astronomers.
Solar annual aberration
A special case of annual aberration is the nearly constant deflection of the Sun from its position in the Sun's rest frame by towards the west (as viewed from Earth), opposite to the apparent motion of the Sun along the ecliptic (which is from west to east, as seen from Earth). The deflection thus makes the Sun appear to be behind (or retarded) from its rest-frame position on the ecliptic by a position or angle .
This deflection may equivalently be described as a light-time effect due to motion of the Earth during the 8.3 minutes that it takes light to travel from the Sun to Earth. The relation with is : x = 8.3167 min ≈ 8 min 19 sec = 499 sec. This is possible since the transit time of sunlight is short relative to the orbital period of the Earth, so the Earth's frame may be approximated as inertial. In the Earth's frame, the Sun moves, at a mean velocity v = 29.789 km/s, by a distance ≈ 14,864.7 km in the time it takes light to reach Earth, ≈ 499 sec for the orbit of mean radius = 1 AU = 149,597,870.7 km. This gives an angular correction ≈ 0.000099364 rad = 20.49539 sec, which can be solved to give ≈ 0.000099365 rad = 20.49559 sec, very nearly the same as the aberrational correction (here is in radian and not in arcsecond).
Diurnal aberration
Diurnal aberration is caused by the velocity of the observer on the surface of the rotating Earth. It is therefore dependent not only on the time of the observation, but also the latitude and longitude of the observer. Its effect is much smaller than that of annual aberration, and is only 0.32 arcseconds in the case of an observer at the Equator, where the rotational velocity is greatest.
Secular aberration
The secular component of aberration, caused by the motion of the Solar System in space, has been further subdivided into several components: aberration resulting from the motion of the solar system barycenter around the center of our Galaxy, aberration resulting from the motion of the Galaxy relative to the Local Group, and aberration resulting from the motion of the Local Group relative to the cosmic microwave background. Secular aberration affects the apparent positions of stars and extragalactic objects. The large, constant part of secular aberration cannot be directly observed and "It has been standard practice to absorb this large, nearly constant effect into the reported" positions of stars.
In about 200 million years, the Sun circles the galactic center, whose measured location is near right ascension (α = 266.4°) and declination (δ = −29.0°). The constant, unobservable, effect of the solar system's motion around the galactic center has been computed variously as 150 or 165 arcseconds. The other, observable, part is an acceleration toward the galactic center of approximately 2.5 × 10 m/s, which yields a change of aberration of about 5 μas/yr. Highly precise measurements extending over several years can observe this change in secular aberration, often called the secular aberration drift or the acceleration of the Solar System, as a small apparent proper motion.
Recently, highly precise astrometry of extragalactic objects using both Very Long Baseline Interferometry and the Gaia space observatory have successfully measured this small effect. The first VLBI measurement of the apparent motion, over a period of 20 years, of 555 extragalactic objects towards the center of our galaxy at equatorial coordinates of α = 263° and δ = −20° indicated a secular aberration drift 6.4 ±1.5 μas/yr. Later determinations using a series of VLBI measurements extending over almost 40 years determined the secular aberration drift to be 5.83 ± 0.23 μas/yr in the direction α = 270.2 ± 2.3° and δ = −20.2° ± 3.6°. Optical observations using only 33 months of Gaia satellite data of 1.6 million extragalactic sources indicated an acceleration of the solar system of 2.32 ± 0.16 × 10 m/s and a corresponding secular aberration drift of 5.05 ± 0.35 μas/yr in the direction of α = 269.1° ± 5.4°, δ = −31.6° ± 4.1°. It is expected that later Gaia data releases, incorporating about 66 and 120 months of data, will reduce the random errors of these results by factors of 0.35 and 0.15. The latest edition of the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF3) adopted a recommended galactocentric aberration constant of 5.8 μas/yr and recommended a correction for secular aberration to obtain the highest positional accuracy for times other than the reference epoch 2015.0.
Planetary aberration
See also: Light-time correctionPlanetary aberration is the combination of the aberration of light (due to Earth's velocity) and light-time correction (due to the object's motion and distance), as calculated in the rest frame of the Solar System. Both are determined at the instant when the moving object's light reaches the moving observer on Earth. It is so called because it is usually applied to planets and other objects in the Solar System whose motion and distance are accurately known.
Discovery and first observations
The discovery of the aberration of light was totally unexpected, and it was only by considerable perseverance and perspicacity that Bradley was able to explain it in 1727. It originated from attempts to discover whether stars possessed appreciable parallaxes.
Search for stellar parallax
The Copernican heliocentric theory of the Solar System had received confirmation by the observations of Galileo and Tycho Brahe and the mathematical investigations of Kepler and Newton. As early as 1573, Thomas Digges had suggested that parallactic shifting of the stars should occur according to the heliocentric model, and consequently if stellar parallax could be observed it would help confirm this theory. Many observers claimed to have determined such parallaxes, but Tycho Brahe and Giovanni Battista Riccioli concluded that they existed only in the minds of the observers, and were due to instrumental and personal errors. However, in 1680 Jean Picard, in his Voyage d'Uranibourg, stated, as a result of ten years' observations, that Polaris, the Pole Star, exhibited variations in its position amounting to 40″ annually. Some astronomers endeavoured to explain this by parallax, but these attempts failed because the motion differed from that which parallax would produce. John Flamsteed, from measurements made in 1689 and succeeding years with his mural quadrant, similarly concluded that the declination of Polaris was 40″ less in July than in September. Robert Hooke, in 1674, published his observations of γ Draconis, a star of magnitude 2 which passes practically overhead at the latitude of London (hence its observations are largely free from the complex corrections due to atmospheric refraction), and concluded that this star was 23″ more northerly in July than in October.
James Bradley's observations

Consequently, when Bradley and Samuel Molyneux entered this sphere of research in 1725, there was still considerable uncertainty as to whether stellar parallaxes had been observed or not, and it was with the intention of definitely answering this question that they erected a large telescope at Molyneux's house at Kew. They decided to reinvestigate the motion of γ Draconis with a telescope constructed by George Graham (1675–1751), a celebrated instrument-maker. This was fixed to a vertical chimney stack in such manner as to permit a small oscillation of the eyepiece, the amount of which (i.e. the deviation from the vertical) was regulated and measured by the introduction of a screw and a plumb line.
The instrument was set up in November 1725, and observations on γ Draconis were made starting in December. The star was observed to move 40″ southwards between September and March, and then reversed its course from March to September. At the same time, 35 Camelopardalis, a star with a right ascension nearly exactly opposite to that of γ Draconis, was 19" more northerly at the beginning of March than in September. The asymmetry of these results, which were expected to be mirror images of each other, were completely unexpected and inexplicable by existing theories.
Early hypotheses


Bradley and Molyneux discussed several hypotheses in the hope of finding the solution. Since the apparent motion was evidently caused neither by parallax nor observational errors, Bradley first hypothesized that it could be due to oscillations in the orientation of the Earth's axis relative to the celestial sphere – a phenomenon known as nutation. 35 Camelopardalis was seen to possess an apparent motion which could be consistent with nutation, but since its declination varied only one half as much as that of γ Draconis, it was obvious that nutation did not supply the answer (however, Bradley later went on to discover that the Earth does indeed nutate). He also investigated the possibility that the motion was due to an irregular distribution of the Earth's atmosphere, thus involving abnormal variations in the refractive index, but again obtained negative results.
On August 19, 1727, Bradley embarked upon a further series of observations using a telescope of his own erected at the Rectory, Wanstead. This instrument had the advantage of a larger field of view and he was able to obtain precise positions of a large number of stars over the course of about twenty years. During his first two years at Wanstead, he established the existence of the phenomenon of aberration beyond all doubt, and this also enabled him to formulate a set of rules that would allow the calculation of the effect on any given star at a specified date.
Development of the theory of aberration
Bradley eventually developed his explanation of aberration in about September 1728 and this theory was presented to the Royal Society in mid January the following year. One well-known story was that he saw the change of direction of a wind vane on a boat on the Thames, caused not by an alteration of the wind itself, but by a change of course of the boat relative to the wind direction. However, there is no record of this incident in Bradley's own account of the discovery, and it may therefore be apocryphal.
The following table shows the magnitude of deviation from true declination for γ Draconis and the direction, on the planes of the solstitial colure and ecliptic prime meridian, of the tangent of the velocity of the Earth in its orbit for each of the four months where the extremes are found, as well as expected deviation from true ecliptic longitude if Bradley had measured its deviation from right ascension:
| Month | Direction of tangential velocity of Earth on the plane of the solstitial colure | Deviation from true declination of γ Draconis | Direction of tangential velocity of Earth on the plane of the ecliptic prime meridian | Expected deviation from true ecliptic longitude of γ Draconis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| December | zero | none | ← (moving toward perihelion at fast velocity) | decrease of more than 20.2" |
| March | ← (moving toward aphelion) | 19.5" southward | zero | none |
| June | zero | none | → (moving toward aphelion at slow velocity) | increase of less than 20.2" |
| September | → (moving toward perihelion) | 19.5" northward | zero | none |
Bradley proposed that the aberration of light not only affected declination, but right ascension as well, so that a star in the pole of the ecliptic would describe a little ellipse with a diameter of about 40", but for simplicity, he assumed it to be a circle. Since he only observed the deviation in declination, and not in right ascension, his calculations for the maximum deviation of a star in the pole of the ecliptic are for its declination only, which will coincide with the diameter of the little circle described by such star. For eight different stars, his calculations are as follows:
| Star | Annual Variation (") | Maximum deviation in declination of a star in the pole of the ecliptic (") |
|---|---|---|
| γ Draconis | 39 | 40.4 |
| β Draconis | 39 | 40.2 |
| η Ursa Maj. | 36 | 40.4 |
| α Cass. | 34 | 40.8 |
| τ Persei | 25 | 41.0 |
| α Persei | 23 | 40.2 |
| 35 Camel. | 19 | 40.2 |
| Capella | 16 | 40.0 |
| MEAN | 40.4 |
Based on these calculations, Bradley was able to estimate the constant of aberration at 20.2", which is equal to 0.00009793 radians, and with this was able to estimate the speed of light at 183,300 miles (295,000 km) per second. By projecting the little circle for a star in the pole of the ecliptic, he could simplify the calculation of the relationship between the speed of light and the speed of the Earth's annual motion in its orbit as follows:
Thus, the speed of light to the speed of the Earth's annual motion in its orbit is 10,210 to one, from whence it would follow, that light moves, or is propagated as far as from the Sun to the Earth in 8 minutes 12 seconds.
The original motivation of the search for stellar parallax was to test the Copernican theory that the Earth revolves around the Sun. The change of aberration in the course of the year demonstrates the relative motion of the Earth and the stars.
Retrodiction on Descartes' lightspeed argument
In the prior century, René Descartes argued that if light were not instantaneous, then shadows of moving objects would lag; and if propagation times over terrestrial distances were appreciable, then during a lunar eclipse the Sun, Earth, and Moon would be out of alignment by hours' motion, contrary to observation. Huygens commented that, on Rømer's lightspeed data (yielding an earth-moon round-trip time of only seconds), the lag angle would be imperceptible. What they both overlooked is that aberration (as understood only later) would exactly counteract the lag even if large, leaving this eclipse method completely insensitive to light speed. (Otherwise, shadow-lag methods could be made to sense absolute translational motion, contrary to a basic principle of relativity.)
Historical theories of aberration
The phenomenon of aberration became a driving force for many physical theories during the 200 years between its observation and the explanation by Albert Einstein.
The first classical explanation was provided in 1729, by James Bradley as described above, who attributed it to the finite speed of light and the motion of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. However, this explanation proved inaccurate once the wave nature of light was better understood, and correcting it became a major goal of the 19th century theories of luminiferous aether. Augustin-Jean Fresnel proposed a correction due to the motion of a medium (the aether) through which light propagated, known as "partial aether drag". He proposed that objects partially drag the aether along with them as they move, and this became the accepted explanation for aberration for some time. George Stokes proposed a similar theory, explaining that aberration occurs due to the flow of aether induced by the motion of the Earth. Accumulated evidence against these explanations, combined with new understanding of the electromagnetic nature of light, led Hendrik Lorentz to develop an electron theory which featured an immobile aether, and he explained that objects contract in length as they move through the aether. Motivated by these previous theories, Albert Einstein then developed the theory of special relativity in 1905, which provides the modern account of aberration.
Bradley's classical explanation

Bradley conceived of an explanation in terms of a corpuscular theory of light in which light is made of particles. His classical explanation appeals to the motion of the earth relative to a beam of light-particles moving at a finite velocity, and is developed in the Sun's frame of reference, unlike the classical derivation given above.
Consider the case where a distant star is motionless relative to the Sun, and the star is extremely far away, so that parallax may be ignored. In the rest frame of the Sun, this means light from the star travels in parallel paths to the Earth observer, and arrives at the same angle regardless of where the Earth is in its orbit. Suppose the star is observed on Earth with a telescope, idealized as a narrow tube. The light enters the tube from the star at angle and travels at speed taking a time to reach the bottom of the tube, where it is detected. Suppose observations are made from Earth, which is moving with a speed . During the transit of the light, the tube moves a distance . Consequently, for the particles of light to reach the bottom of the tube, the tube must be inclined at an angle different from , resulting in an apparent position of the star at angle . As the Earth proceeds in its orbit it changes direction, so changes with the time of year the observation is made. The apparent angle and true angle are related using trigonometry as:
- .
In the case of , this gives . While this is different from the more accurate relativistic result described above, in the limit of small angle and low velocity they are approximately the same, within the error of the measurements of Bradley's day. These results allowed Bradley to make one of the earliest measurements of the speed of light.
Luminiferous aether
See also: Luminiferous aether
In the early nineteenth century the wave theory of light was being rediscovered, and in 1804 Thomas Young adapted Bradley's explanation for corpuscular light to wavelike light traveling through a medium known as the luminiferous aether. His reasoning was the same as Bradley's, but it required that this medium be immobile in the Sun's reference frame and must pass through the earth unaffected, otherwise the medium (and therefore the light) would move along with the earth and no aberration would be observed. He wrote:
Upon consideration of the phenomena of the aberration of the stars I am disposed to believe that the luminiferous aether pervades the substance of all material bodies with little or no resistance, as freely perhaps as the wind passes through a grove of trees.
— Thomas Young, 1804
However, it soon became clear Young's theory could not account for aberration when materials with a non-vacuum refractive index were present. An important example is of a telescope filled with water. The speed of light in such a telescope will be slower than in vacuum, and is given by rather than where is the refractive index of the water. Thus, by Bradley and Young's reasoning the aberration angle is given by
- .
which predicts a medium-dependent angle of aberration. When refraction at the telescope's objective is taken into account this result deviates even more from the vacuum result. In 1810 François Arago performed a similar experiment and found that the aberration was unaffected by the medium in the telescope, providing solid evidence against Young's theory. This experiment was subsequently verified by many others in the following decades, most accurately by Airy in 1871, with the same result.
Aether drag models
See also: Aether drag hypothesisFresnel's aether drag
In 1818, Augustin Fresnel developed a modified explanation to account for the water telescope and for other aberration phenomena. He explained that the aether is generally at rest in the Sun's frame of reference, but objects partially drag the aether along with them as they move. That is, the aether in an object of index of refraction moving at velocity is partially dragged with a velocity bringing the light along with it. This factor is known as "Fresnel's dragging coefficient". This dragging effect, along with refraction at the telescope's objective, compensates for the slower speed of light in the water telescope in Bradley's explanation. With this modification Fresnel obtained Bradley's vacuum result even for non-vacuum telescopes, and was also able to predict many other phenomena related to the propagation of light in moving bodies. Fresnel's dragging coefficient became the dominant explanation of aberration for the next decades.

Stokes' aether drag
However, the fact that light is polarized (discovered by Fresnel himself) led scientists such as Cauchy and Green to believe that the aether was a totally immobile elastic solid as opposed to Fresnel's fluid aether. There was thus renewed need for an explanation of aberration consistent both with Fresnel's predictions (and Arago's observations) as well as polarization.
In 1845, Stokes proposed a 'putty-like' aether which acts as a liquid on large scales but as a solid on small scales, thus supporting both the transverse vibrations required for polarized light and the aether flow required to explain aberration. Making only the assumptions that the fluid is irrotational and that the boundary conditions of the flow are such that the aether has zero velocity far from the Earth, but moves at the Earth's velocity at its surface and within it, he was able to completely account for aberration. The velocity of the aether outside of the Earth would decrease as a function of distance from the Earth so light rays from stars would be progressively dragged as they approached the surface of the Earth. The Earth's motion would be unaffected by the aether due to D'Alembert's paradox.
Both Fresnel and Stokes' theories were popular. However, the question of aberration was put aside during much of the second half of the 19th century as focus of inquiry turned to the electromagnetic properties of aether.
Lorentz' length contraction
See also: Lorentz ether theoryIn the 1880s once electromagnetism was better understood, interest turned again to the problem of aberration. By this time flaws were known to both Fresnel's and Stokes' theories. Fresnel's theory required that the relative velocity of aether and matter to be different for light of different colors, and it was shown that the boundary conditions Stokes had assumed in his theory were inconsistent with his assumption of irrotational flow. At the same time, the modern theories of electromagnetic aether could not account for aberration at all. Many scientists such as Maxwell, Heaviside and Hertz unsuccessfully attempted to solve these problems by incorporating either Fresnel or Stokes' theories into Maxwell's new electromagnetic laws.
Hendrik Lorentz spent considerable effort along these lines. After working on this problem for a decade, the issues with Stokes' theory caused him to abandon it and to follow Fresnel's suggestion of a (mostly) stationary aether (1892, 1895). However, in Lorentz's model the aether was completely immobile, like the electromagnetic aethers of Cauchy, Green and Maxwell and unlike Fresnel's aether. He obtained Fresnel's dragging coefficient from modifications of Maxwell's electromagnetic theory, including a modification of the time coordinates in moving frames ("local time"). In order to explain the Michelson–Morley experiment (1887), which apparently contradicted both Fresnel's and Lorentz's immobile aether theories, and apparently confirmed Stokes' complete aether drag, Lorentz theorized (1892) that objects undergo "length contraction" by a factor of in the direction of their motion through the aether. In this way, aberration (and all related optical phenomena) can be accounted for in the context of an immobile aether. Lorentz' theory became the basis for much research in the next decade, and beyond. Its predictions for aberration are identical to those of the relativistic theory.
Special relativity
See also: History of special relativityLorentz' theory matched experiment well, but it was complicated and made many unsubstantiated physical assumptions about the microscopic nature of electromagnetic media. In his 1905 theory of special relativity, Albert Einstein reinterpreted the results of Lorentz' theory in a much simpler and more natural conceptual framework which disposed of the idea of an aether. His derivation is given above, and is now the accepted explanation. Robert S. Shankland reported some conversations with Einstein, in which Einstein emphasized the importance of aberration:
He continued to say the experimental results which had influenced him most were the observations of stellar aberration and Fizeau's measurements on the speed of light in moving water. "They were enough," he said.
Other important motivations for Einstein's development of relativity were the moving magnet and conductor problem and (indirectly) the negative aether drift experiments, already mentioned by him in the introduction of his first relativity paper. Einstein wrote in a note in 1952:
My own thought was more indirectly influenced by the famous Michelson-Morley experiment. I learned of it through Lorentz' path breaking investigation on the electrodynamics of moving bodies (1895), of which I knew before the establishment of the special theory of relativity. Lorentz' basic assumption of a resting ether did not seem directly convincing to me, since it led to an interpretation of the Michelson-Morley experiment, which seemed unnatural to me. My direct path to the sp. th. rel. was mainly determined by the conviction that the electromotive force induced in a conductor moving in a magnetic field is nothing other than an electric field. But the result of Fizeau's experiment and the phenomenon of aberration also guided me.
While Einstein's result is the same as Bradley's original equation except for an extra factor of , Bradley's result does not merely give the classical limit of the relativistic case, in the sense that it gives incorrect predictions even at low relative velocities. Bradley's explanation cannot account for situations such as the water telescope, nor for many other optical effects (such as interference) that might occur within the telescope. This is because in the Earth's frame it predicts that the direction of propagation of the light beam in the telescope is not normal to the wavefronts of the beam, in contradiction with Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism. It also does not preserve the speed of light c between frames. However, Bradley did correctly infer that the effect was due to relative velocities.
See also
- Apparent place
- Stellar parallax
- Astronomical nutation
- Proper motion
- Timeline of electromagnetism and classical optics
- Relativistic aberration
Notes
- More in detail, Fresnel explains that the incoming light of angle is first refracted at the end of the telescope, to a new angle within the telescope. This may be accounted for by Snell's law, giving . Then drag must be accounted for. Without drag, the x and y components of the light in the telescope are and , but drag modifies the x component to if the Earth moves with velocity . If is angle and is the velocity of the light with these velocity components, then by Bradley's reasoning where is the modified path length through the water and t is the time it takes the light to travel the distance h, . Upon solving these equations for in terms of one obtains Bradley's vacuum result.
-
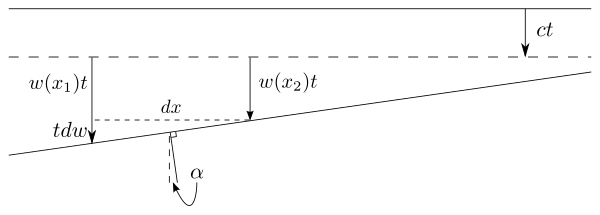
The propagating wavefront moving through the aether. Stokes' derivation may be summarized as follows: Consider a wavefront moving in the downwards z direction. Say the aether has velocity field as a function of . Now, motion of the aether in the x and y directions does not affect the wavefront, but the motion in the z direction advances it (in addition to the amount it advances at speed c). If the z velocity of the aether varies over space, for example if it is slower for higher x as shown in the figure, then the wavefront becomes angled, by an angle . Now, say in time t the wavefront has moved by a span (assuming the speed of the aether is negligible compared to the speed of light). Then for each distance the ray descends, it is bent by an angle , and so the total angle by which it has changed after travelling through the entire fluid is
If the fluid is irrotational it will satisfy the Cauchy–Riemann equations, one of which is
- .
Inserting this into the previous result gives an aberration angle where the s represent the x component of the aether's velocity at the start and end of the ray. Far from the earth the aether has zero velocity, so and at the surface of the earth it has the earth's velocity . Thus we finally get
which is the known aberration result.
References
- ^ Schaffner, Kenneth F. (1972). Nineteenth-century aether theories. Oxford: Pergamon Press. pp. 99–117 und 255–273. ISBN 0-08-015674-6.
- Williams, M. E. W. (1979). "Flamsteed's Alleged Measurement of Annual Parallax for the Pole Star". Journal for the History of Astronomy. 10 (2): 102–116. Bibcode:1979JHA....10..102W. doi:10.1177/002182867901000203. S2CID 118565124.
- ^ Bradley, James (1727–1728). "A Letter from the Reverend Mr. James Bradley Savilian Professor of Astronomy at Oxford, and F.R.S. to Dr.Edmond Halley Astronom. Reg. &c. Giving an Account of a New Discovered Motion of the Fix'd Stars". Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 35 (406): 637–661. Bibcode:1727RSPT...35..637B. doi:10.1098/rstl.1727.0064.
- ^ Hirschfeld, Alan (2001). Parallax:The Race to Measure the Cosmos. New York, New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 0-8050-7133-4.
- ^ Norton, John D. (2004). "Einstein's Investigations of Galilean Covariant Electrodynamics prior to 1905". Archive for History of Exact Sciences. 59 (1): 45–105. Bibcode:2004AHES...59...45N. doi:10.1007/s00407-004-0085-6. S2CID 17459755. Archived from the original on 2009-01-11.
- Richard A. Mould (2001). Basic Relativity (2nd ed.). Springer. p. 8. ISBN 0-387-95210-1.
- In fact, the light source doesn't need to be stationary, consider for example eclipsing binary stars: they are rotating with high speed —and ever changing and different velocity vectors— around each other, but they appear as one spot all the time.
- U.S. Nautical Almanac Office (21 March 2014). "Glossary". Astronomical Almanac for the Year 2015 and Its Companion, The Astronomical Almanac Online. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office (published 2014). p. M1. ISBN 9780707741499.
- ^ Kovalevsky, Jean & Seidelmann, P. Kenneth (2004). Fundamentals of Astrometry. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-64216-7.
- Newcomb, Simon (1960). A Compendium of Spherical Astronomy. Macmillan, 1906 – republished by Dover.
- ^ Charlot, P.; Jacobs, C. S.; Gordon, D.; Lambert, S.; et al. (2020). "The third realization of the International Celestial Reference Frame by very long baseline interferometry". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 644: A159. arXiv:2010.13625. Bibcode:2020A&A...644A.159C. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202038368. S2CID 225068756.
- ^ MacMillan, D. S.; Fey, A.; Gipson, J. M.; et al. (2019). "Galactocentric acceleration in VLBI analysis". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 630: A93. Bibcode:2019A&A...630A..93M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935379. S2CID 198471325.
- Hagihara, Yusuke (1933). "On the Theory of Secular Aberration". Proceedings of the Physico-Mathematical Society of Japan. 3rd Series. 15 (3–6): 175. doi:10.11429/ppmsj1919.15.3-6_155.
the correction of star places with secular aberration is not at all necessary and is even inconvenient, so long as the solar motion remains uniform and rectilinear.
- Kovalevsky, J. (2003). "Aberration in proper motions". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 404 (2): 743–747. Bibcode:2003A&A...404..743K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030560.
- Kopeikin, S.; Makarov, V. (2006). "Astrometric effects of secular aberration". The Astronomical Journal (USA). 131 (3): 1471–1478. arXiv:astro-ph/0508505. Bibcode:2006AJ....131.1471K. doi:10.1086/500170.
- ^ Titov, O.; Lambert, S. B.; Gontier, A.-M. (2011). "VLBI measurement of the secular aberration drift". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 529: A91. arXiv:1009.3698. Bibcode:2011A&A...529A..91T. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015718. S2CID 119305429.
- "Gaia's measurement of the solar system acceleration with respect to the distant universe". esa.int. European Space Agency. 3 December 2020. Retrieved 14 September 2022.
- Gaia Collaboration; Klioner, S. A.; et al. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Acceleration of the Solar System from Gaia astrometry". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A9. arXiv:2012.02036. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...9G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039734.
- ^ Eppenstein (1911), p. 54.
- Bradley, James; Rigaud, Stephen Peter (1832). Miscellaneous works and correspondence of the Rev. James Bradley, D.D., F.R.S. Oxford: University Press. p. 11.
- ^ Eppenstein (1911), p. 55.
- ^ Berry, Arthur (1961) . A Short History of Astronomy. Dover. ISBN 9780486202105.
- Hoiberg, Dale H., ed. (2010). "aberration, constant of". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. I: A-ak Bayes (15th ed.). Chicago, IL: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. pp. 30. ISBN 978-1-59339-837-8.
- ^ James Bradley (1729). "An account of a new discovered motion of the fixed stars". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. 35: 637–661. doi:10.1098/rstl.1727.0064.
- Sakellariadis, Spyros (1982). "Descartes' Experimental Proof of the Infinite Velocity of Light and Huygens' Rejoinder". Archive for History of Exact Sciences. 26 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1007/BF00348308. ISSN 0003-9519. JSTOR 41133639. S2CID 118187860.
- Encyclopædia Britannica Archived 2013-11-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Whittaker, Edmund Taylor (1910). A History of the theories of aether and electricity (1. ed.). Dublin: Longman, Green and Co. Archived from the original on 2016-02-15.
Whittaker, Edmund Taylor (1953). A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity (2. ed.). T. Nelson. - Janssen, Michel & Stachel, John (2010). "The Optics and Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies" (PDF). In John Stachel (ed.). Going Critical. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-1308-9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- Darrigol, Olivier (2000). Electrodynamics from Ampére to Einstein. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-850594-9.
- Shankland, R. S. (1963). "Conversations with Albert Einstein". American Journal of Physics. 31 (1): 47–57. Bibcode:1963AmJPh..31...47S. doi:10.1119/1.1969236.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Eppenstein, Otto (1911). "Aberration". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). pp. 54–61.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Eppenstein, Otto (1911). "Aberration". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). pp. 54–61.
Further reading
- P. Kenneth Seidelmann (Ed.), Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac (University Science Books, 1992), 127–135, 700.
- Stephen Peter Rigaud, Miscellaneous Works and Correspondence of the Rev. James Bradley, D.D. F.R.S. (1832).
- Charles Hutton, Mathematical and Philosophical Dictionary (1795).
- H. H. Turner, Astronomical Discovery (1904).
- Thomas Simpson, Essays on Several Curious and Useful Subjects in Speculative and Mix'd Mathematicks (1740).
- de:August Ludwig Busch, Reduction of the Observations Made by Bradley at Kew and Wansted to Determine the Quantities of Aberration and Nutation (1838).
External links
- Courtney Seligman on Bradley's observations
 , with x and y velocity components
, with x and y velocity components  and
and  , and thus at an angle
, and thus at an angle  such that
such that  . If the Earth is moving at velocity
. If the Earth is moving at velocity  in the x direction relative to the Sun, then by velocity addition the x component of the beam's velocity in the Earth's frame of reference is
in the x direction relative to the Sun, then by velocity addition the x component of the beam's velocity in the Earth's frame of reference is  , and the y velocity is unchanged,
, and the y velocity is unchanged,  . Thus the angle of the light in the Earth's frame in terms of the angle in the Sun's frame is
. Thus the angle of the light in the Earth's frame in terms of the angle in the Sun's frame is

 , this result reduces to
, this result reduces to  , which in the limit
, which in the limit  may be approximated by
may be approximated by  .
.


 , giving the components of the light beam in the Earth's frame in terms of the components in the Sun's frame. The angle of the beam in the Earth's frame is thus
, giving the components of the light beam in the Earth's frame in terms of the components in the Sun's frame. The angle of the beam in the Earth's frame is thus

 , and in the limit
, and in the limit  constant in all frames of reference, unlike the classical derivation above.
constant in all frames of reference, unlike the classical derivation above.
 . It may be calculated using the relation
. It may be calculated using the relation  substituting the Earth's average speed in the Sun's frame for
substituting the Earth's average speed in the Sun's frame for  ≈ 14,864.7 km in the time it takes light to reach Earth,
≈ 14,864.7 km in the time it takes light to reach Earth,  ≈ 499 sec for the orbit of mean radius
≈ 499 sec for the orbit of mean radius  = 1 AU = 149,597,870.7 km. This gives an angular correction
= 1 AU = 149,597,870.7 km. This gives an angular correction  ≈ 0.000099364 rad = 20.49539 sec, which can be solved to give
≈ 0.000099364 rad = 20.49539 sec, which can be solved to give  ≈ 0.000099365 rad = 20.49559 sec, very nearly the same as the aberrational correction (here
≈ 0.000099365 rad = 20.49559 sec, very nearly the same as the aberrational correction (here 
 to reach the bottom of the tube, where it is detected. Suppose observations are made from Earth, which is moving with a speed
to reach the bottom of the tube, where it is detected. Suppose observations are made from Earth, which is moving with a speed  . Consequently, for the particles of light to reach the bottom of the tube, the tube must be inclined at an angle
. Consequently, for the particles of light to reach the bottom of the tube, the tube must be inclined at an angle  different from
different from  .
. rather than
rather than  is the refractive index of the water. Thus, by Bradley and Young's reasoning the aberration angle is given by
is the refractive index of the water. Thus, by Bradley and Young's reasoning the aberration angle is given by
 .
. bringing the light along with it. This factor is known as "Fresnel's dragging coefficient". This dragging effect, along with refraction at the telescope's objective, compensates for the slower speed of light in the water telescope in Bradley's explanation. With this modification Fresnel obtained Bradley's vacuum result even for non-vacuum telescopes, and was also able to predict many other phenomena related to the propagation of light in moving bodies. Fresnel's dragging coefficient became the dominant explanation of aberration for the next decades.
bringing the light along with it. This factor is known as "Fresnel's dragging coefficient". This dragging effect, along with refraction at the telescope's objective, compensates for the slower speed of light in the water telescope in Bradley's explanation. With this modification Fresnel obtained Bradley's vacuum result even for non-vacuum telescopes, and was also able to predict many other phenomena related to the propagation of light in moving bodies. Fresnel's dragging coefficient became the dominant explanation of aberration for the next decades.
 in the direction of their motion through the aether. In this way, aberration (and all related optical phenomena) can be accounted for in the context of an immobile aether. Lorentz' theory became the basis for much research in the next decade, and beyond. Its predictions for aberration are identical to those of the relativistic theory.
in the direction of their motion through the aether. In this way, aberration (and all related optical phenomena) can be accounted for in the context of an immobile aether. Lorentz' theory became the basis for much research in the next decade, and beyond. Its predictions for aberration are identical to those of the relativistic theory.
 , Bradley's result does not merely give the classical limit of the relativistic case, in the sense that it gives incorrect predictions even at low relative velocities. Bradley's explanation cannot account for situations such as the water telescope, nor for many other optical effects (such as interference) that might occur within the telescope. This is because in the Earth's frame it predicts that the direction of propagation of the light beam in the telescope is not normal to the wavefronts of the beam, in contradiction with
, Bradley's result does not merely give the classical limit of the relativistic case, in the sense that it gives incorrect predictions even at low relative velocities. Bradley's explanation cannot account for situations such as the water telescope, nor for many other optical effects (such as interference) that might occur within the telescope. This is because in the Earth's frame it predicts that the direction of propagation of the light beam in the telescope is not normal to the wavefronts of the beam, in contradiction with  within the telescope. This may be accounted for by
within the telescope. This may be accounted for by  . Then drag must be accounted for. Without drag, the x and y components of the light in the telescope are
. Then drag must be accounted for. Without drag, the x and y components of the light in the telescope are  and
and  , but drag modifies the x component to
, but drag modifies the x component to  if the Earth moves with velocity
if the Earth moves with velocity  is angle and
is angle and  is the velocity of the light with these velocity components, then by Bradley's reasoning
is the velocity of the light with these velocity components, then by Bradley's reasoning
 where
where  is the modified path length through the water and t is the time it takes the light to travel the distance h,
is the modified path length through the water and t is the time it takes the light to travel the distance h,  . Upon solving these equations for
. Upon solving these equations for  as a function of
as a function of  . Now, motion of the aether in the x and y directions does not affect the wavefront, but the motion in the z direction advances it (in addition to the amount it advances at speed c). If the z velocity of the aether varies over space, for example if it is slower for higher x as shown in the figure, then the wavefront becomes angled, by an angle
. Now, motion of the aether in the x and y directions does not affect the wavefront, but the motion in the z direction advances it (in addition to the amount it advances at speed c). If the z velocity of the aether varies over space, for example if it is slower for higher x as shown in the figure, then the wavefront becomes angled, by an angle  . Now, say in time t the wavefront has moved by a span
. Now, say in time t the wavefront has moved by a span  (assuming the speed of the aether is negligible compared to the speed of light). Then for each distance
(assuming the speed of the aether is negligible compared to the speed of light). Then for each distance  the ray descends, it is bent by an angle
the ray descends, it is bent by an angle  , and so the total angle by which it has changed after travelling through the entire fluid is
, and so the total angle by which it has changed after travelling through the entire fluid is

 .
. where the
where the  s represent the x component of the aether's velocity at the start and end of the ray. Far from the earth the aether has zero velocity, so
s represent the x component of the aether's velocity at the start and end of the ray. Far from the earth the aether has zero velocity, so  and at the surface of the earth it has the earth's velocity
and at the surface of the earth it has the earth's velocity 