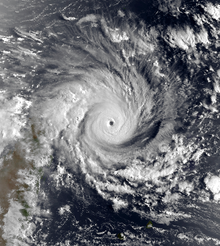
 Cyclone Nadia near peak intensity on 22 March Cyclone Nadia near peak intensity on 22 March | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 16 March 1994 (1994-03-16) |
| Dissipated | 1 April 1994 (1994-04-01) |
| Intense tropical cyclone | |
| 10-minute sustained (MFR) | |
| Highest winds | 175 km/h (110 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 925 hPa (mbar); 27.32 inHg |
| Category 4-equivalent tropical cyclone | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 220 km/h (140 mph) |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 252 total |
| Damage | $20.2 million (1994 USD) |
| Areas affected | Madagascar, Mozambique, Malawi |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1993–94 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
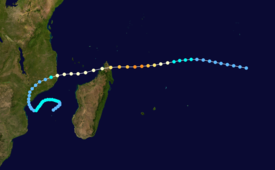
Intense Tropical Cyclone Nadia was a powerful tropical cyclone that struck both Madagascar and Mozambique in March 1994. It formed on 16 March and moved westward for the first ten days of its duration. Warm waters and low wind shear allowed for the storm to gradually strengthen. After developing a well-defined eye, Nadia intensified to reach winds of 175 km/h (110 mph (10 minute sustained)) early on 22 March, according to Météo-France (MF). In contrast, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimated winds of about 220 km/h (140 mph 1 minute sustained). On 23 March, the cyclone struck northern Madagascar, causing flooding and localized damage where it moved ashore. There were 12 deaths in the country. Nadia emerged into the Mozambique Channel as a weakened storm, although it reintensified slightly before making landfall in northeastern Mozambique on 24 March. The storm turned southward through the country, emerging over water on 26 March. It turned to the northeast and meandered over waters before dissipating on 1 April.
Damage was heaviest in Mozambique, estimated at $20 million (1994 USD). Cyclone Nadia severely affected four provinces in the country, primarily Nampula Province where it moved ashore. There, 85% of the houses were destroyed, and across its path, the cyclone left 1.5 million people homeless. High winds caused widespread power outages, left areas without water, and significantly damaged crops, notably the cashew crop. The storm struck before the harvest, and lack of food resulted in 300 deaths in the months after the storm. Across Mozambique, Nadia directly caused 240 deaths and injured thousands. Effects spread as far inland as Malawi.
Meteorological history
Map key Saffir–Simpson scale Tropical depression (≤38 mph, ≤62 km/h)
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown Storm type
 Tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone  Subtropical cyclone
Subtropical cyclone  Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression
Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression A disturbance in the Indian Ocean Intertropical Convergence Zone became evident southeast of the Chagos Archipelago on 16 March after two cyclones moved away from the region. Based on analysis from Météo-France, the system slowly organized while moving westward, its movement influenced by a subtropical ridge to the south. On 17 March, the JTWC also began tracking the system. Due to cool, dry air, the system initially did not intensify, although its passage over warmer sea surface temperatures on 19 March allowed for strengthening. That same day, MF classified the disturbance as Tropical Storm Nadia after rainbands developed. A day later, the JTWC designated Nadia as Tropical Cyclone 23S.
After becoming a tropical storm, Nadia quickly intensified, developing a central dense overcast and later an eye. With minimal wind shear, the storm strengthened into a tropical cyclone early on 21 March. That day, the JTWC estimated winds of 120 km/h (75 mph 1-minute sustained), or the equivalent of a minimal hurricane, and later that day, MF upgraded Nadia into an intense tropical cyclone. While the cyclone was approaching northern Madagascar on 22 March, MF estimated that Nadia attained maximum sustained winds of 175 km/h (110 mph (10 minute sustained)). At around the same time, the JTWC estimated winds of about 220 km/h (140 mph (1-minute sustained)). While at peak intensity, Nadia had well-defined outflow and an eye no larger than 30 km (19 mi). At about 0100 UTC on 23 March, Nadia made landfall on northern Madagascar near Vohemar, having weakened slightly from its peak.
While located over Madagascar, Nadia weakened into a tropical storm due to the mountainous terrain. With warm temperatures, the storm re-intensified slightly after entering the Mozambique Channel, and it passed about 100 km (62 mi) south of Mayotte at 1900 UTC on 23 March. At 1700 UTC the next day, Nadia made its second landfall on Mozambique, about halfway between Nacala and Moçambique. Shortly thereafter, the JTWC discontinued advisories. Despite moving further inland, Nadia retained a well-organized circulation and convection. The storm turned to the south and re-emerged into the Mozambique Channel late on 26 March near the mouth of the Zambezi River. Nadia gradually re-intensified while curving to the southeast, and it re-intensified into a tropical storm on 28 March, the same day the JTWC resumed issuing advisories. The storm strengthened to reach a secondary peak intensity of 85 km/h (50 mph (10 minute sustained)), according to MF. After reaching a position about halfway between Mozambique and Madagascar, Nadia turned to the southwest on 1 April and lost its remaining convection. The JTWC and MF discontinued advisories that day, and the circulation dissipated a day later.
Impact and aftermath

While crossing northern Madagascar, Nadia produced widespread flooding. In Vohemar where it moved ashore, the storm destroyed most public buildings, although local churches provided assistance in the aftermath. Across the region, the storm downed power lines and destroyed more than 540 tonnes (600 tons) of rice. The cyclone killed 12 people and caused about $200,000 damage (1994 USD).
Upon striking Mozambique, Nadia produced heavy rains and strong wind gusts, causing widespread tree damage and flooding. The city of Nampula recorded 126 mm (4.96 in) of rainfall in a 24‑hour period. Damage was heaviest in Nampula, Zambezia, Manica, and Sofala provinces. In Nampula Province, Nadia destroyed 85% of the houses and 75% of the crops, mostly cashew trees. The city of Nacala was heavily damaged, with about 170,000 people losing their houses. Many residents evacuated Nacala, and temporary shelters were provided for those who stayed. At the port in Nacala, the local harbor was wrecked and two ships sank; one of the damaged ships spilled oil into the Bay of Nacala. The city lost power and water, and its primary hospital was destroyed. About 130 km (81 mi) of power lines were cut between Nampula and Nacala, and widespread road and bridge damage disrupted transportation. In the area along Nadia's path, over 120 schools were damaged destroyed, affecting over 46,864 students. Across the country, roughly 1.5 million people were left homeless. A World Food Programme building in the city was destroyed, wrecking 642 tonnes (708 tons) of stored food. Overall, Nadia killed 240 people in Mozambique and injured thousands. Damage was estimated at $20 million (1994 USD).
Damage from Nadia extended as far inland as Malawi.
Aftermath
After the storm, about 300,000 people in Nampula Province in Mozambique required food and other goods. Officials sent relief to the affected areas, including iron sheeting and medical teams. Due to damage to sanitation facilities, there were outbreaks of diarrhea and cholera in the weeks after the storm. By April 20, most primary roads were cleared, bridge reconstruction had commenced, and power was being restored. Heavy crop damage depleted food supplies, The cyclone struck shortly before the annual harvest, causing heavy crop damage that depleted food supplies. Some residents who evacuated during the country's civil war returned late to assist in harvesting the remaining crops. In the six months after the storm, about 300 people died due to starvation. Many secondary roads remained blocked in the weeks after the storm, forcing relief supplies to be transported by boat. The country appealed to the international community for assistance, and by 6 May, various international agencies and governments donated about $1.4 million in cash (1994 USD). The French government sent $48,000 worth of medicine, blankets, and food, the United Kingdom sent $373,134 for generators, water tanks, and roofing materials, and the Spanish government sent about $117,000 worth of food and tents. The charity organization Concern Worldwide sent 54,000 sets of clothing to the country. The government of Japan sent 6,000 blankets and 1,800 bars of soap, while the Italian government sent five generators, eight water tanks, and 1,150 agricultural tools. Donated generators assisted in restoring water in Nacala. In June 1994, the World Bank provided $20 million in assistance to the country due to the storm. Cyclone Nadia contributed to fishing exports decreasing by $11 million during the year.
See also
References
- ^ Guy Le Goff (1994). "1993–1994 Cyclone Season in the South-West Indian Ocean". Météo-France. pp. 75–76. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center. "Tropical Cyclone 23S (Nadia) best track analysis". United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on 17 September 2012. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center; Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center. Chapter 4 — Summary of South Pacific and South Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclones (PDF) (1994 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report). United States Navy, United States Air Force. p. 246. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 February 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- "Donnees De Nadia" (in French). Météo-France. 2004. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- Jane Scobie (1996). Mitigating the Millennium. Intermediate Technology. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-7881-7465-0. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- "Five killed by cyclone in Madagascar". United Press International. 25 March 1994.
- EM-DAT: The OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database (2009). EM-DAT (Report). Université Catholique de Louvain, Brussels (Belgium). Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ UN Department of Humanitarian Affairs (1994). Mozambique: Cyclone Mar 1994 UN DHA Situation Reports 1 - 8 (Report). ReliefWeb. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Jack Beven. "Tropical Cyclone Weekly Summary #138 (March 20 - 27, 1994)". Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Kenya News Agency (5 April 1994). "Ships damaged by Cyclone Nadia threaten to pollute Bay of Nacala". British Broadcasting Corporation.
- OFDA Annual Report FY 1994 (PDF) (Report). Office of United States Foreign Disaster Assistance. p. 28. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- ^ International Organisation for Migration (1996). Health impact of large post-conflict migratory movements: The experience of Mozambique (PDF) (Report). p. 63. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- "Natural Disasters in Africa". International Perspectives on Natural Disasters: Occurrence, Mitigation, and Consequences. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publisher. 2004. p. 239. ISBN 978-1-4020-2850-2. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- "World Bank credit to Mozambique formalised". Agence France-Presse. 21 June 1994.
- "Fishing industry exports decline in 1994". British Broadcasting Corporation. 21 March 1995.
External links
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) Archived 2015-08-09 at the Wayback Machine.
- Météo France (RSMC La Réunion).
- World Meteorological Organization
| Tropical cyclones of the 1993–94 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
|---|---|
| MTSAlexina STSBettia STSCecilia TCDaisy STSEdmea TCPearl-Farah ITCGeralda TCHollanda TCIvy TDJulita MTSKelvina ITCLitanne STSMariola ITCNadia ITCOdille | |