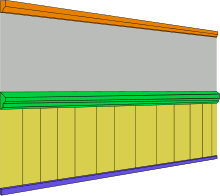
crown moulding dado rail dado skirting board
In architecture, the dado is the lower part of a wall, below the dado rail and above the skirting board. The word is borrowed from Italian meaning "dice" or "cube", and refers to "die", an architectural term for the middle section of a pedestal or plinth.
Decorative treatment
This area is given a decorative treatment different from that for the upper part of the wall; for example panelling, wainscoting or lincrusta. The purpose of the dado treatment to a wall is both aesthetic and functional. Historically, the panelling below the dado rail was installed to cover the lower part of the wall which was subject to stains associated with rising damp; additionally it provided protection from furniture and passing traffic. The dado rail itself is sometimes referred to as a chair rail, though this can be misleading since its function is principally aesthetic and not to protect the wall from chair backs.
Derivation

The name was first used in English as an architectural term for the part of a pedestal between the base and the cornice. As with many other architectural terms, the word is Italian in origin. The dado in a pedestal is roughly cubical in shape, and the word in Italian means "dice" or "cube" (ultimately Latin datum, meaning "something given", hence also a die for casting lots). By extension, the dado becomes the lower part of a wall when the pedestal is treated as being continuous along the wall, with the cornice becoming the dado rail.
Gallery
-
 Dado in carved oak, designed by W. S. Barber at Spring Hall, Halifax
Dado in carved oak, designed by W. S. Barber at Spring Hall, Halifax
-
Dado in a French chateau
-
 Dado in Taj Mahal
Dado in Taj Mahal
-
Dado in Leeds Central Library
See also
References
- "Dado - definition". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved March 10, 2013.
- ^ "Dado". Lexico. Archived from the original on September 20, 2021.
- ^ Chitham, Robert (2007). The Classical Orders of Architecture. Routledge. ISBN 9781136358951.
- Skeat, Walter W. (15 February 2013). An Etymological Dictionary of the English Language. Courier Corporation. pp. 152, 168–169. ISBN 9780486317656.
External links
 Media related to Dado (architecture) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Dado (architecture) at Wikimedia Commons