
A Data Matrix is a two-dimensional code consisting of black and white "cells" or dots arranged in either a square or rectangular pattern, also known as a matrix. The information to be encoded can be text or numeric data. Usual data size is from a few bytes up to 1556 bytes. The length of the encoded data depends on the number of cells in the matrix. Error correction codes are often used to increase reliability: even if one or more cells are damaged so it is unreadable, the message can still be read. A Data Matrix symbol can store up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters.
Data Matrix symbols are rectangular, usually square in shape and composed of square "cells" which represent bits. Depending on the coding used, a "light" cell represents a 0 and a "dark" cell is a 1, or vice versa. Every Data Matrix is composed of two solid adjacent borders in an "L" shape (called the "finder pattern") and two other borders consisting of alternating dark and light "cells" or modules (called the "timing pattern"). Within these borders are rows and columns of cells encoding information. The finder pattern is used to locate and orient the symbol while the timing pattern provides a count of the number of rows and columns in the symbol. As more data is encoded in the symbol, the number of cells (rows and columns) increases. Each code is unique. Symbol sizes vary from 10×10 to 144×144 in the new version ECC 200, and from 9×9 to 49×49 in the old version ECC 000 – 140.
Applications

The most popular application for Data Matrix is marking small items, due to the code's ability to encode fifty characters in a symbol that is readable at 2 or 3 mm (0.003 or 0.005 sq in) and the fact that the code can be read with only a 20% contrast ratio. A Data Matrix is scalable; commercial applications exist with images as small as 300 micrometres (0.012 in) (laser etched on a 600-micrometre (0.024 in) silicon device) and as large as a 1 metre (3 ft) square (painted on the roof of a boxcar). Fidelity of the marking and reading systems are the only limitation. The US Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) recommends using Data Matrix for labeling small electronic components.
Data Matrix codes are becoming common on printed media such as labels and letters. The code can be read quickly by a barcode reader which allows the media to be tracked, for example when a parcel has been dispatched to the recipient.
For industrial engineering purposes, Data Matrix codes can be marked directly onto components, ensuring that only the intended component is identified with the data-matrix-encoded data. The codes can be marked onto components with various methods, but within the aerospace industry these are commonly industrial ink-jet, dot-peen marking, laser marking, and electrolytic chemical etching (ECE). These methods give a permanent mark which can last up to the lifetime of the component.
Data Matrix codes are usually verified using specialist camera equipment and software. This verification ensures the code conforms to the relevant standards, and ensures readability for the lifetime of the component. After component enters service, the Data Matrix code can then be read by a reader camera, which decodes the Data Matrix data which can then be used for a number of purposes, such as movement tracking or inventory stock checks.

Data Matrix codes, along with other open-source codes such as 1D barcodes can also be read with mobile phones by downloading code specific mobile applications. Although many mobile devices are able to read 2D codes including Data Matrix Code, few extend the decoding to enable mobile access and interaction, whereupon the codes can be used securely and across media; for example, in track and trace, anti-counterfeit, e.govt, and banking solutions.
Food industry
Data Matrix codes are used in the food industry in autocoding systems to prevent food products being packaged and dated incorrectly. Codes are maintained internally on a food manufacturers database and associated with each unique product, e.g. ingredient variations. For each product run the unique code is supplied to the printer. Label artwork is required to allow the 2D Data Matrix to be positioned for optimal scanning. For black on white codes testing isn't required unless print quality is an issue, but all color variations need to be tested before production to ensure they are readable.
Art
In May 2006 a German computer programmer, Bernd Hopfengärtner, created a large Data Matrix in a wheat field (in a fashion similar to crop circles). The message read "Hello, World!". In June 2011 the Parisian tattoo artist K.A.R.L., as part of a promotion for Ballantine's scotch whisky, created the world's first animated tattoo utilizing a Data Matrix code in a collaborative process streamed live on Facebook.
Technical specifications

Data Matrix symbols are made up of modules arranged within a perimeter finder and timing pattern. It can encode up to 3,116 characters from the entire ASCII character set (with extensions). The symbol consists of data regions which contain modules set out in a regular array. Large symbols contain several regions. Each data region is delimited by a finder pattern, and this is surrounded on all four sides by a quiet zone border (margin). (Note: The modules may be round or square- no specific shape is defined in the standard. For example, dot-peened cells are generally round.)
Data Matrix ECC 200
ECC 200, the newer version of Data Matrix, uses Reed–Solomon codes for error and erasure recovery. ECC 200 allows the routine reconstruction of the entire encoded data string when the symbol has sustained 30% damage, assuming the matrix can still be accurately located. Data Matrix has an error rate of less than 1 in 10 million characters scanned.
Symbols have an even number of rows and an even number of columns. Most of the symbols are square with sizes from 10 × 10 to 144 × 144. Some symbols however are rectangular with sizes from 8×18 to 16×48 (even values only). All symbols using the ECC 200 error correction can be recognized by the upper-right corner module being the same as the background color. (binary 0).
Additional capabilities that differentiate ECC 200 symbols from the earlier standards include:
- Inverse reading symbols (light images on a dark background)
- Specification of the character set (via Extended Channel Interpretations)
- Rectangular symbols
- Structured append (linking of up to 16 symbols to encode larger amounts of data)
Data Matrix ECC 000–140
Older versions of Data Matrix include ECC 000, ECC 050, ECC 080, ECC 100, ECC 140. Instead of using Reed–Solomon codes like ECC 200, ECC 000–140 use a convolution-based error correction. Each varies in the amount of error correction it offers, with ECC 000 offering none, and ECC 140 offering the greatest. For error detection at decode time, even in the case of ECC 000, each of these versions also encode a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) on the bit pattern. As an added measure, the placement of each bit in the code is determined by bit-placement tables included in the specification. These older versions always have an odd number of modules, and can be made in sizes ranging from 9 × 9 to 49 × 49. All symbols utilizing the ECC 000 through 140 error correction can be recognized by the upper-right corner module being the inverse of the background color. (binary 1).
According to ISO/IEC 16022, "ECC 000–140 should only be used in closed applications where a single party controls both the production and reading of the symbols and is responsible for overall system performance."
Standards
Data Matrix was invented by International Data Matrix, Inc. (ID Matrix) which was merged into RVSI/Acuity CiMatrix, who were acquired by Siemens AG in October 2005 and Microscan Systems in September 2008. Data Matrix is covered today by several ISO/IEC standards and is in the public domain for many applications, which means it can be used free of any licensing or royalties.
- ISO/IEC 16022:2006—Data Matrix bar code symbology specification
- ISO/IEC 15415—2-D Print quality standard
- ISO/IEC 15418:2016—Symbol data format semantics (GS1 application identifiers and ASC MH10 data identifiers and maintenance)
- ISO/IEC 15424:2008—Data Carrier Identifiers (including Symbology Identifiers)
- ISO/IEC 15434:2006—Syntax for high-capacity ADC media (format of data transferred from scanner to software, etc.)
- ISO/IEC 15459—Unique identifiers
Error correction
Data Matrix codes use Reed–Solomon error correction over the finite field (or GF(2)), the elements of which are encoded as bytes of 8 bits; the byte with a standard numerical value encodes the field element where is taken to be a primitive element satisfying . The primitive polynomial is , corresponding to the polynomial number 301, with initial root = 1. The Reed–Solomon code uses one of 37 different polynomials over , with degrees ranging from 7 to 68, depending on how many error correction bytes the code adds.
The generator polynomial used to generate the codeword depends on number of error correction bytes. For example, in the 10 × 10 symbol, there are 3 data bytes and 5 error correction bytes. The generator polynomial is obtained as: ,
which gives: ,
or with decimal coefficients: .
Encoding

The encoding process is described in the ISO/IEC standard 16022:2006. Open-source software for encoding and decoding the ECC-200 variant of Data Matrix has been published.
The diagrams below illustrate the placement of the message data within a Data Matrix symbol. The message is "Misplaced Pages", and it is arranged in a somewhat complicated diagonal pattern starting near the upper-left corner. Some characters are split in two pieces, such as the initial W, and the third 'i' is in "corner pattern 2" rather than the usual L-shaped arrangement. Also shown are the end-of-message code (marked End), the padding (P) and error correction (E) bytes, and four modules of unused space (X).
The symbol is of size 16×16 (14×14 data area), with 12 data bytes (including 'End' and padding) and 12 error correction bytes. A (255,243,6) Reed Solomon code shortened to (12,12,6) is used. It can correct upto 6 byte errors or erasures.
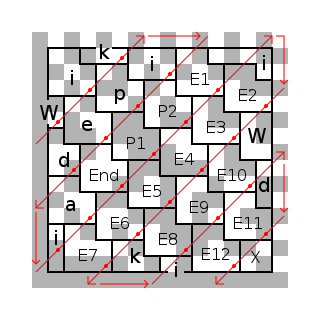
|

|
Multiple encoding modes are used to store different kinds of messages. The default mode stores one ASCII character per 8-bit codeword. Control codes are provided to switch between modes, as shown below.
| Codeword | Codeword hexadecimal | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Not used |
| 1–128 | 1-80 | ASCII data (ASCII value + 1) |
| 129 | 81 | End of message |
| 130–229 | 82-e5 | Digit pairs 00–99 |
| 230 | e6 | Begin C40 encoding |
| 231 | e7 | Begin Base 256 encoding |
| 232 | e8 | FNC1 |
| 233 | e9 | Structured append. Allows a message to be split across multiple symbols. |
| 234 | ea | Reader programming |
| 235 | eb | Set high bit of the following character |
| 236 | ec | 05 Macro |
| 237 | ed | 06 Macro |
| 238 | ee | Begin ANSI X12 encoding |
| 239 | ef | Begin Text encoding |
| 240 | f0 | Begin EDIFACT encoding |
| 241 | f1 | Extended Channel Interpretation code |
| 242–255 | f2-ff | Not used |
Text modes
The C40, Text and X12 modes are potentially more compact for storing text messages. They are similar to DEC Radix-50, using character codes in the range 0–39, and three of these codes are combined to make a number up to 40=64000, which is packed into two bytes (maximum value 65536) as follows:
- V = C1×1600 + C2×40 + C3 + 1
- B1 = floor(V/256)
- B2 = V mod 256
The resulting value of B1 is in the range 0–250. The special value 254 is used to return to ASCII encoding mode.
Character code interpretations are shown in the table below. The C40 and Text modes have four separate sets. Set 0 is the default, and contains codes that temporarily select a different set for the next character. The only difference is that they reverse upper-and lower-case letters. C40 is primarily upper-case, with lower-case letters in set 3; Text is the other way around. Set 1, containing ASCII control codes, and set 2, containing punctuation symbols are identical in C40 and Text mode.
| Code | set 0 | set 1 | set 2 | set 3 | X12 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C40 | Text | C40 | Text | ||||
| 0 | set 1 | NUL | ! | ` | CR | ||
| 1 | set 2 | SOH | " | a | A | * | |
| 2 | set 3 | STX | # | b | B | > | |
| 3 | space | ETX | $ | c | C | space | |
| 4 | 0 | EOT | % | d | D | 0 | |
| 5 | 1 | ENQ | & | e | E | 1 | |
| 6 | 2 | ACK | ' | f | F | 2 | |
| 7 | 3 | BEL | ( | g | G | 3 | |
| 8 | 4 | BS | ) | h | H | 4 | |
| 9 | 5 | HT | * | i | I | 5 | |
| 10 | 6 | LF | + | j | J | 6 | |
| 11 | 7 | VT | , | k | K | 7 | |
| 12 | 8 | FF | – | l | L | 8 | |
| 13 | 9 | CR | . | m | M | 9 | |
| 14 | A | a | SO | / | n | N | A |
| 15 | B | b | SI | : | o | O | B |
| 16 | C | c | DLE | ; | p | P | C |
| 17 | D | d | DC1 | < | q | Q | D |
| 18 | E | e | DC2 | = | r | R | E |
| 19 | F | f | DC3 | > | s | S | F |
| 20 | G | g | DC4 | ? | t | T | G |
| 21 | H | h | NAK | @ | u | U | H |
| 22 | I | i | SYN | [ | v | V | I |
| 23 | J | j | ETB | \ | w | W | J |
| 24 | K | k | CAN | ] | x | X | K |
| 25 | L | l | EM | ^ | y | Y | L |
| 26 | M | m | SUB | _ | z | Z | M |
| 27 | N | n | ESC | FNC1 | { | N | |
| 28 | O | o | FS | | | O | ||
| 29 | P | p | GS | } | P | ||
| 30 | Q | q | RS | hibit | ~ | Q | |
| 31 | R | r | US | DEL | R | ||
| 32 | S | s | S | ||||
| 33 | T | t | T | ||||
| 34 | U | u | U | ||||
| 35 | V | v | V | ||||
| 36 | W | w | W | ||||
| 37 | X | x | X | ||||
| 38 | Y | y | Y | ||||
| 39 | Z | z | Z | ||||
EDIFACT mode
EDIFACT mode uses six bits per character, with four characters packed into three bytes. It can store digits, upper-case letters, and many punctuation marks, but has no support for lower-case letters.
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0–30 | ASCII codes 64–94 |
| 31 | Return to ASCII mode |
| 32–63 | ASCII codes 32–63 |
Base 256 mode
Base 256 mode data starts with a length indicator, followed by a number of data bytes. A length of 1 to 249 is encoded as a single byte, and longer lengths are stored as two bytes.
- L1 = floor(length / 250) + 249, L2 = length mod 250
It is desirable to avoid long strings of zeros in the coded message, because they become large blank areas in the Data Matrix symbol, which may cause a scanner to lose synchronization. (The default ASCII encoding does not use zero for this reason.) In order to make that less likely, the length and data bytes are obscured by adding a pseudorandom value R(n), where n is the position in the byte stream.
- R(n) = (149 × n) mod 255 + 1
Patent issues
Prior to the expiration of US patent 5,612,524 in November 2007, intellectual property company Acacia Technologies claimed that Data Matrix was partially covered by its contents. As the patent owner, Acacia allegedly contacted Data Matrix users demanding license fees related to the patent.
Cognex Corporation, a large manufacturer of 2D barcode devices, filed a declaratory judgment complaint on 13 March 2006 after receiving information that Acacia had contacted its customers demanding licensing fees. On 19 May 2008 Judge Joan N. Ericksen of the U.S. District Court in Minnesota ruled in favor of Cognex. The ruling held that the '524 patent, which claimed to cover a system for capturing and reading 2D symbology codes, is both invalid and unenforceable due to inequitable conduct by the defendants during the procurement of the patent.
While the ruling was delivered after the patent expired, it precluded claims for infringement based on use of Data Matrix prior to November 2007.
A German patent application DE 4107020 was filed in 1991, and published in 1992. This patent is not cited in the above US patent applications and might invalidate them.
See also
- PDF417
- Aztec Code
- High Capacity Color Barcode
- MaxiCode
- Nintendo e-Reader
- QR Code
- Semacode
- SPARQCode
- Trusted paper key
References
- "Data Matrix Barcode". Archived from the original on 14 September 2017.
- Stevenson, Rick (December 2005). "Laser Marking Matrix Codes on PCBs" (PDF). Printed Circuit Design and Manufacture. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- Stefan, V. (2012). The use of 2D codes in the development of mobile applications with database. Valahian Journal of Economic Studies, 3(2), 105-114. Retrieved from https://econpapers.repec.org/article/vlhjournl/v_3a3_3ay_3a2012_3ai_3a2_3ap_3a105-114.htm
- "German man programs "Hello World" into wheat field". arstechnica.com. 11 June 2007. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "The World's First Animated Tattoo – Digital Buzz Blog". digitalbuzzblog.com. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "First Ever Animated Tattoo – By K.A.R.L." youtube.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2021. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "Facebook". facebook.com. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "Data Matrix and PDF417 Data Integrity Test" (PDF). idautomation.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 August 2019. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- Engin, Thomas. "QR Code scanner online". Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- ISO e-commerce page for this standard http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_catalogue/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=44230
- "GitHub – zxing/zxing: Official ZXing ("Zebra Crossing") project home". google.com. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "libdmtx Home". sourceforge.net. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- US 5612524, Sant'Anselmo, Carl; Sant'Anselmo, Robert & Hooper, David C., "Identification symbol system and method with orientation mechanism", published 1997-03-18, issued 1997-03-18
- "Cognex Invalidates Acacia Patent '524; Next? Suing for Business Defamation". Groklaw. 23 June 2008. Archived from the original on 5 May 2010.
External links
- GS1 DataMatrix Guideline: Overview and technical introduction to the use of GS1 DataMatrix
- Datamatrix Code Generator - Online Tool
| Barcodes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear barcodes |
| |||||
| Post office barcodes | ||||||
| 2D barcodes (stacked) | ||||||
| 2D barcodes (matrix) | ||||||
| Polar coordinate barcodes | ||||||
| Other | ||||||
| Technological issues | ||||||
| Other data tags | ||||||
| Related topics | ||||||
 (or GF(2)), the elements of which are encoded as
(or GF(2)), the elements of which are encoded as  with a standard numerical value
with a standard numerical value  encodes the field element
encodes the field element  where
where  is taken to be a primitive element satisfying
is taken to be a primitive element satisfying  . The primitive polynomial is
. The primitive polynomial is  , corresponding to the polynomial number 301, with initial root = 1. The Reed–Solomon code uses one of 37 different polynomials over
, corresponding to the polynomial number 301, with initial root = 1. The Reed–Solomon code uses one of 37 different polynomials over  ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.

