You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (September 2023) Click for important translation instructions.
|
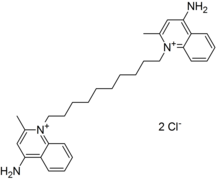 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dequadin, Fluomizin, Vablys, others |
| Routes of administration | By mouth intravaginal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.575 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H40N4 |
| Molar mass | 456.678 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Dequalinium is a quaternary ammonium cation and bolaamphiphile commonly available as the dichloride salt. It is useful as an antiseptic and disinfectant. The bromide, iodide, acetate, and undecenoate salts are known as well. Dequalinium chloride is the active ingredient of several medications.
The dequalinium dication is symmetrical, containing two quaternary quinolinium units linked by an N-decylene chain.
Medical uses
Dequalinium chloride 0.25 mg is available as an over-the-counter throat lozenge under brand names such as Dequadin and SP Troche. Mouthwash and buccal sprays at 0.5 % concentration are also available. In this form is it used to treat minor infections of the mouth and throat. It can help with tonsillitis but is not effective in cases of streptococci infections.
The product is also available as a 10 mg prescription vaginal tablet for treating vaginal bacterial conditions (i.e. bacterial Vaginosis and aerobic vaginitis). Brand names include Fluomizin and Vablys.
In Austria, dequalinium chloride is combined with bacitracin and diphenylpyraline in Eucillin "B", an antibiotic cream. This cream is the first dequalinium-containing product to enter Austria in 1967.
Spectrum of activity
Dequalinium salts have broad bactericidal and fungicidal activity. In OTC oral products containing a low concentration, the product is instead described as a bacteriostat.
Dequalinium salts may have antimalarial activities.
Adverse effects
Dequalinium may cause skin necrosis "if administered on intertriginous skin areas under occlusive conditions".
History
Dequalinium was first described by M Babbs and colleagues in 1956, as the first agent of the bisquaternary ammonium chemical class.
References
- "Health product highlights 2021: Annexes of products approved in 2021". Health Canada. 3 August 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- "Fluomizin Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 12 October 2022. Retrieved 14 April 2024.
- ^ "Dequalinium". DrugBank Online.
- Krämer W (April 1977). "". Fortschritte der Medizin (in German). 95 (16): 1108–1110. PMID 856702.
- Mendling W, Weissenbacher ER, Gerber S, Prasauskas V, Grob P (March 2016). "Use of locally delivered dequalinium chloride in the treatment of vaginal infections: a review". Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics. 293 (3): 469–484. doi:10.1007/s00404-015-3914-8. PMC 4757629. PMID 26506926.
- ^ Tischer M, Pradel G, Ohlsen K, Holzgrabe U (January 2012). "Quaternary ammonium salts and their antimicrobial potential: targets or nonspecific interactions?". ChemMedChem. 7 (1): 22–31. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201100404. PMID 22113995. S2CID 26326417.
- Babbs M, Collier HO, Austin WC, Potter MD, Taylor EP (February 1956). "Salts of decamethylene-bis-4-aminoquinaldinium (dequadin); a new antimicrobial agent". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 8 (2): 110–119. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1956.tb12138.x. PMID 13307403. S2CID 30103639.
Further reading
- Gamboa-Vujicic G, Emma DA, Liao SY, Fuchtner C, Manetta A (March 1993). "Toxicity of the mitochondrial poison dequalinium chloride in a murine model system". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 82 (3): 231–235. doi:10.1002/jps.2600820302. PMID 8450414.
External links
| Antiseptics and disinfectants (D08) | |
|---|---|
| Acridine derivatives | |
| Biguanides and amidines | |
| Phenol and derivatives | |
| Nitrofuran derivatives | |
| Iodine products | |
| Quinoline derivatives | |
| Quaternary ammonium compounds | |
| Mercurial products | |
| Silver compounds | |
| Alcohols | |
| Other | |
| |
| Gynecological anti-infectives and antiseptics (G01) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | |||||||||
| Arsenic compounds | |||||||||
| Quinoline derivatives | |||||||||
| Organic acids | |||||||||
| Sulfonamides | |||||||||
| Antifungals |
| ||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |