| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Deuterated acetone" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (1,1,1,3,3,3-H6)Propan-2-one | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 1702935 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.514 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1090 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
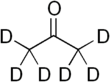
| Chemical formula | C3H6O or C3D6O | ||
| Molar mass | 64.1161 g mol | ||
| Density | 0.872 g cm | ||
| Melting point | −94 °C (−137 °F; 179 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 56 °C (133 °F; 329 K) | ||
| Vapor pressure | 24.5-25.3 kPa (at 20°C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H225, H319, H336 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Flash point | −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds | Acetone | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
Deuterated acetone ((CD3)2CO), also known as acetone-d6, is a form (isotopologue) of acetone (CH3)2CO in which the hydrogen atom (H) is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope (H or D). Deuterated acetone is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
Properties
As with all deuterated compounds, the properties of deuterated acetone are virtually identical to those of regular acetone.
Manufacture
Deuterated acetone is prepared by the reaction of acetone with heavy water, H2O or D2O, in the presence of a base. In this case, the base used is deuterated lithium hydroxide:
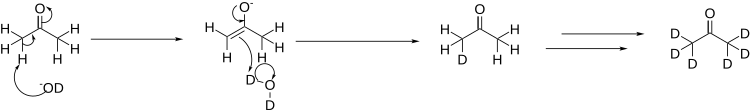
In order to fully deuterate the acetone, the process is repeated several times, distilling off the acetone from the heavy water, and re-running the reaction in a fresh batch of heavy water.
References
- ^ Paulsen, P. J.; Cooke, W. D. (1963). "Preparation of Deuterated Solvents for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry. 35 (10): 1560. doi:10.1021/ac60203a072.
| Deuterated NMR solvents | |
|---|---|
| |
|
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This nuclear magnetic resonance–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |