| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,3-Dichloronaphthalene-1,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.828 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2902 2761 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H4Cl2O2 |
| Molar mass | 227.04 g·mol |
| Appearance | Yellow crystals |
| Melting point | 193 °C (379 °F; 466 K) |
| Solubility in water | 0.1 ppm |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H315, H317, H319, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P264+P265, P270, P272, P273, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P330, P332+P317, P333+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P391, P501 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Dichlone (trade names Phygon and Quintar) is a fungicide and algicide of the quinone class. It is a general use fungicide applied to fruits, vegetables, field crops, ornamentals, and residential and commercial outdoor areas. It is also used to control blue algae.
Dichlone is not persistent in soil and has moderate mammalian toxicity.
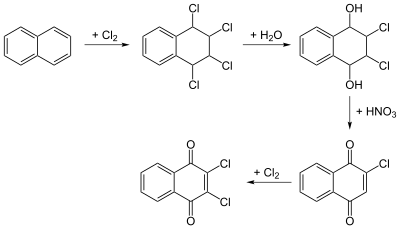
Dichlone can be manufactured by the chlorination and oxidation of naphthalene.
References
- ^ "Dichlone (Phygon, Quintar) Chemical Profile". Pesticide Management Education Program, Cornell Cooperative Extension.
- ^ "Dichlone". Pesticide Properties DataBase, University of Hertfordshire.
- Thomas A. Unger (1996). Pesticide Synthesis Handbook. William Andrew. p. 966. ISBN 0-8155-1853-6.