| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Dimethylmagnesium | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C2H6Mg |
| Molar mass | 54.375 g·mol |
| Density | 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Reacts |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Dibutylmagnesium |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethylmagnesium is an organomagnesium compound. It is a white pyrophoric solid. Dimethylmagnesium is used in the synthesis of organometallic compounds.
Preparation
Like other dialkylmagnesium compounds, dimethylmagnesium is prepared by adding dioxane to a solution of methylmagnesium halide:
- 2 CH3MgX + 2 dioxane ⇌ (CH3)2Mg + MgX2(μ-dioxane)2↓
In such procedures, the dimethylmagnesium exists as the ether adduct, not the polymer.
Addition of 1,4-dioxane causes precipitation of solid MgX2(μ-dioxane)2, a coordination polymer. This precipitation drives the Schlenk equilibrium toward (CH3)2Mg. Related methods have been applied to other dialkylmagnesium compounds.
Dimethylmagnesium can also be prepared by combining dimethylmercury and magnesium.
Properties
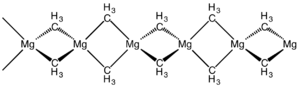
The structure of this compound has been determined by X-ray crystallography. The material is a polymer with the same connectivity as silicon disulfide, featuring tetrahedral magnesium centres, each surrounded by bridging methyl groups. The Mg-C distances are 224 pm.
Related compounds
The linear chain structure seen for dimethylmagnesium is also observed for diethylmagnesium and dimethylberyllium. Di(tert-butyl)magnesium is however a dimer.
References
- Cope, A. C. (1935). "The Preparation of Dialkylmagnesium Compounds from Grignard Reagents". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (11): 2238–2240. doi:10.1021/ja01314a059.
- Anteunis, M. (1962). "Studies of the Grignard Reaction. II. Kinetics of the Reaction of Dimethylmagnesium with Benzophenone and of Methylmagnesium Bromide-Magnesium Bromide with Pinacolone". J. Org. Chem. 27 (2): 596–598. doi:10.1021/jo01049a060.
- ^ Richard A. Andersen, Geoffrey Wilkinson (1979). "Bis[(Trimethylsilyl)Methyl] Magnesium". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 19. pp. 262–265. doi:10.1002/9780470132500.ch61. ISBN 978-0-471-04542-7.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Fischer, Reinald; Görls, Helmar; Meisinger, Philippe R.; Suxdorf, Regina; Westerhausen, Matthias (2019). "Structure–Solubility Relationship of 1,4-Dioxane Complexes of Di(hydrocarbyl)magnesium". Chemistry – A European Journal. 25 (55): 12830–12841. doi:10.1002/chem.201903120. PMC 7027550. PMID 31328293.
- Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. XIII/2a, 4th Edition Organometallic Compounds of Group II of the Periodic Table (except mercury) (in German), Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, p. 215, ISBN 978-3-13-180654-3
- Jane E. Macintyre (1994), Dictionary of Organometallic Compounds (in German), CRC Press, p. 2273, ISBN 978-0-412-43060-2
- Weiss, E. (1964). "Die Kristallstruktur des Dimethylmagnesiums". J. Organomet. Chem. 2 (4): 314–321. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)82217-2.
- Snow, A.I.; Rundle, R.E. (1951). "Structure of Dimethylberyllium". Acta Crystallographica. 4 (4): 348–52. Bibcode:1951AcCry...4..348S. doi:10.1107/S0365110X51001100. hdl:2027/mdp.39015095081207.
- Starowieyski, Kazimierz B.; Lewinski, Janusz; Wozniak, Robert; Lipkowski, Janusz; Chrost, Andrzej (2003). "Di- tert -butylmagnesium: Synthesis and Structure". Organometallics. 22 (12): 2458–2463. doi:10.1021/om030091j.