| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Duchy of Mecklenburg-GüstrowHertzogtum Mecklenburg-Güstrow (German) Hertogdom Mekelenborch-Güstrow (Low German) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1480–1483 1520–1610 1621–1695 | |||||||||
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||
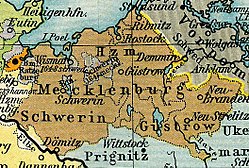 Mecklenburg circa 1648, showing the division between Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Güstrow Mecklenburg circa 1648, showing the division between Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Güstrow | |||||||||
| Status | Duchy | ||||||||
| Capital | Güstrow | ||||||||
| Duke | |||||||||
| • 1520–1547 | Albert VII | ||||||||
| • 1556–1603 | Ulrich III | ||||||||
| • 1628–1631 | Albrecht von Wallenstein | ||||||||
| • 1636–1695 | Gustav Adolph | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| • Death of Henry IV | 1477 | ||||||||
| • First partition of Mecklenburg | 1480 | ||||||||
| • Reunited | 1483 | ||||||||
| • Neubrandenburg Treaty | 1520 | ||||||||
| • Ruppin dictum | 1556 | ||||||||
| • Third partition of Mecklenburg | 1621 | ||||||||
| • Emp. Ferdinand II stripped duchies | 1628–1631 | ||||||||
| • Acquired secularised Bp Ratzeburg | 1648 | ||||||||
| • Ducal line extinct, to M-Schwerin | 1695 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| a: De jure partition was from 1556 to 1603. b: Between 1628 and 1631, the duchies of Mecklenburg-Güstrow and Mecklenburg-Schwerin were stripped from the ducal brothers and awarded to Albrecht von Wallenstein by Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor. c: Second de facto partition. d: Second de jure partition. | |||||||||
Mecklenburg-Güstrow was a state of the Holy Roman Empire in Northern Germany, that existed on three occasions ruled by the House of Mecklenburg at Güstrow.
History

A first short-lived predecessor existed after the death of Henry IV, Duke of Mecklenburg in 1477 and the subsequent partition of his lands among his sons in 1480. Albert VI received the estates of the former Lordship of Werle around Güstrow. However, Albert died without issue in 1483 and his lands were inherited by his younger brother Magnus II, Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin.
When Magnus died in 1503, his sons Henry V and Albert VII at first ruled jointly over the entire Mecklenburg duchy until its renewed division by the 1520 Neubrandenburg Treaty. Albert, a fierce opponent of the Protestant Reformation, had insisted on the partition and became duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow, while his brother Henry retained Mecklenburg-Schwerin. However Mecklenburg de jure remained undivided; both brothers held the title of Duke of Mecklenburg and, as Henry only left one insane son when he died in 1552, the Schwerin lands fell back to Albert's sons Ulrich III and John Albert I.
At this time John Albert and Ulrich had ruled jointly over the Güstrow lands, but now came into conflict over the inherited Schwerin part. The controversy was finally decided in 1556 by the Ruppin dictum of Joachim II Hector, Elector of Brandenburg: John Albert I received Schwerin while Ulrich remained Duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow. Ulrich died without heirs in 1603 and Güstrow fell back to John Albert's grandchildren Adolf Frederick I and John Albert II, joint rulers of Mecklenburg-Schwerin from 1610 onwards.
Mecklenburg-Güstrow was created for a third and final time with the partition of 1621, when John Albert II received the Güstrow part of Mecklenburg. In 1628 he and his brother at Schwerin were stripped of their duchies by order of Emperor Ferdinand II von Habsburg in favour of his Generalissimo Albrecht von Wallenstein. Officially the dukes were reproached for having secretly sided with Christian IV, King of Denmark, while in fact Mecklenburg was given in compensation of the enormous expenses Wallenstein had paid in building up Imperial troops. He took his residence at Güstrow but was dismissed by the Emperor three years later under pressure from the Prince-electors, while the dukes with the support of Swedish troops were restored.
The House of Mecklenburg-Güstrow had assumed the administration of the former Catholic Prince-Bishopric of Ratzeburg after its conversion to Lutheranism in 1554. By the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, the diocese was finally secularised and adjudicated to the last administrator, Duke Gustav Adolph.
Gustav Adolph's death in 1695 led to an inheritance dispute between his son-in-law Adolphus Frederick II, younger son of Adolf Frederick I and his nephew Frederick William, Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, which would lead to the creation of Mecklenburg-Strelitz in 1701.
Dukes of Mecklenburg-Güstrow
- Albert VI 1480–1483
Güstrow reunited with Mecklenburg 1483–1520
- Albert VII 1520–1547
- John Albert I 1547–1556, son
- Ulrich III 1556–1603, brother
- Charles I 1603–1610, brother, custodian for:
- John Albert II 1610–1628, jointly with his brother
- Albrecht von Wallenstein (non-dynast) 1628–1631
- John Albert II (restored) 1631–1636
- Gustav Adolph 1636–1695, son
References
- Regnal chronologies
- Marek, Miroslav. "Genealogy of the House of Mecklenburg". Genealogy.EU.
- Map of Mecklenburg-Güstrow in 1600, Euratlas.net
| Ecclesiastical |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Secular | ||
| Cities | ||
| until 1648. until 1701. from 1648. until 1731. until 1705. until 1596. from 1708. until 1773. until 1640. until 1695. from 1701. until 1734.
Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon Circles est. 1512: Austrian, Burgundian, Upper Saxon, Electoral Rhenish · Unencircled territories | ||
53°47′38″N 12°10′35″E / 53.79389°N 12.17639°E / 53.79389; 12.17639
Categories:- States and territories established in 1480
- 1480 establishments in Europe
- 1695 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1520
- States and territories disestablished in 1695
- Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire
- House of Mecklenburg
- Former principalities
- History of Mecklenburg
- Former states and territories of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
- 1520 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire