| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
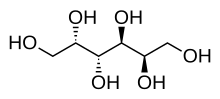
| IUPAC name D-Galactitol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3S,4R,5S)-hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol | |
| Other names Dulcitol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.242 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H14O6 |
| Molar mass | 182.172 g/mol |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -112.40·10 cm/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Galactitol (dulcitol) is a sugar alcohol, the reduction product of galactose. It has a slightly sweet taste. In people with galactokinase deficiency, a form of galactosemia, excess dulcitol forms in the lens of the eye leading to cataracts.
Galactitol is produced from galactose in a reaction catalyzed by aldose reductase.
The other common galactose metabolism defect is a defect in galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase, an autosomal recessive disorder, which also causes a buildup of galactitol as a result of increased concentrations of galactose-1-phosphate and galactose. This disorder leads to cataracts caused by galactitol buildup.
References
- ^ "Galactitol - Compound Summary". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2008-08-06.
- Roth, KS (September 10, 2007). "Galactokinase Deficiency". eMedicine. WebMD. Retrieved 2008-08-08.
External links
 Media related to Galactitol at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Galactitol at Wikimedia Commons
| Fructose and galactose metabolic intermediates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fructose | |||||||
| Galactose | |||||||
| Mannose | |||||||