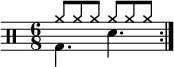| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Duple and quadruple metre" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Duple metre (or Am. duple meter, also known as duple time) is a musical metre characterized by a primary division of 2 beats to the bar, usually indicated by 2 and multiples (simple) or 6 and multiples (compound) in the upper figure of the time signature, with
2 (cut time),
4, and
8 (at a fast tempo) being the most common examples.
Shown below are a simple and a compound duple drum pattern.
Though the upper number must be divisible by 2, the mere fact that 2 evenly divides the upper figure does not in and of itself indicate a duple metre; it is only a prerequisite.
The most common time signature in rock, blues, country, funk, and pop is
4. Although jazz writing has become more adventurous since Dave Brubeck's Time Out, the majority of jazz and jazz standards are still in "common time" (
4).
Duple time is common in many styles including the polka, well known for its obvious "oom-pah" duple feel. Compare to the waltz.
Quadruple metre
Quadruple metre (also quadruple time) is a musical metre characterized in modern practice by a primary division of 4 beats to the bar, usually indicated by 4 in the upper figure of the time signature, with
4 (common time, also notated as ![]() ) being the most common example.
) being the most common example.
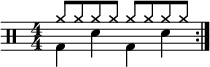
Shown below are a simple and a compound quadruple drum pattern.
Sources
- Schroedl, Scott (2001). Play Drums Today!. Hal Leonard. p. 42. ISBN 0-634-02185-0.
- Sadie, S.; Tyrrell, J., eds. (2001). "Quadruple time". The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians (2nd ed.). London, UK: Macmillan.
| Musical meters | |
|---|---|
| Musical notation | |
|---|---|
| Staff | |
| Musical notes | |
| Articulation | |
| Sheet music | |
| Other systems | |
| Related | |