| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (3S,3′S,5R,5′R,6S,6′S)-5,6:5′,6′-Diepoxy-5,5′,6,6′-tetrahydro-β,β-carotene-3,3′-diol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1R,1′R,3S,3′S,6S,6′S)-6,6′-bis(1,5,5-trimethyl-7-oxabicycloheptan-3-ol) | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| E number | E161e (colours) |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C40H56O4 |
| Molar mass | 600.884 g·mol |
| Appearance | Orange crystals |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
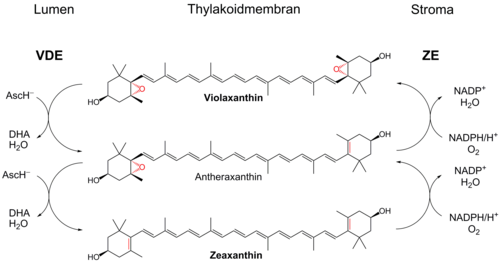
Violaxanthin is a xanthophyll pigment with an orange color found in a variety of plants. Violaxanthin is the product of the epoxidation of zeaxanthin where the oxygen atoms are from reactive oxygen species (ROS). Such ROS's arise when a plant is subject to solar radiation so intense that the light cannot all be absorbed by the chlorophyll.
Food coloring
Violaxanthin is used as a food coloring under the E number E161e and INS number 161e. The coloring is not approved for use in food in the EU or the United States, but is allowed in Australia and New Zealand.
Violaxanthin cycle
Violaxanthin is a participant in the violaxanthin cycle.
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9902.
- Bassi, Roberto; Dall'Osto, Luca (2021). "Dissipation of Light Energy Absorbed in Excess: The Molecular Mechanisms". Annual Review of Plant Biology. 72: 47–76. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-071720-015522. PMID 34143647. S2CID 235480018.
- UK Food Standards Agency: "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code"Standard 1.2.4 - Labelling of ingredients". 8 September 2011. Retrieved 2011-10-27.
| Carotenoids | |
|---|---|
| Carotenes (C40) | |
| Xanthophylls (C40) | |
| Apocarotenoids (C<40) | |
| Vitamin A retinoids (C20) | |
| Retinoid drugs | |