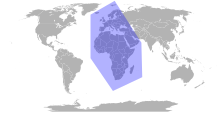
Europe, the Middle East and Africa, commonly known by its acronym EMEA among the North American business spheres, is a geographical region used by institutions, governments and global spheres of marketing, media and business when referring to this region. The acronym EMEA is a shorthand way of referencing the two continents (Africa and Europe) and the Middle Eastern sub-continent all at once.
As the name suggests, the region includes all of the countries found on the continents of Africa and Europe, as well as the countries that make up the Middle East. The region is generally accepted to include all European nations and all African nations, and extends east to Iran, including part of Russia. Typically, the acronym does not include overseas territories of mainland countries in the region, such as French Guiana. However, the term is not completely clear, and while it usually refers to Europe, the Middle East and Africa, it is not uncommon for businesses and other institutions to slightly tweak the countries they include under this umbrella term.
One of the reasons why the term is commonly used is because it is useful for business purposes, as most of the region falls within four time zones, which facilitates communication and travel.
The related term "EAA" refers to "Europe, Africa, and Asia".
Historical influence
The historical influence and interdependence of Europe on the Middle East and Africa in relation to trade routes contributed to the development of the term EMEA. The establishment of the Suez Canal in 1869 impacted international commerce. It directly linked Europe to the Indian Ocean and East Asian trade routes. The direct channel between Britain and India enabled Britain to gradually gain authority over Egypt. This authority was reinforced via the development and maintenance of the Pax Britannica which gave Britain naval power and control over the world's maritime trade routes during the late nineteenth century period of peace.
Related regions
- Eastern Europe, Middle East and Africa (EEMEA). Some companies separate their Eastern European business from the rest of Europe, and refer to the EEMEA region separately from the Western/Central European (EU/EFTA) region
- Southern Europe, Middle East and Africa (SEMEA)
- Southeastern Europe, Middle East and Africa (SEEMEA)
- Central and Eastern Europe (CEE)
- Central Europe, Middle East and Africa (CEMEA)
- The Middle East and Africa (MEA)
- The Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
- The Middle East, Turkey and Africa (META)
- The Middle East, North Africa, Afghanistan and Pakistan (MENAP)
- Europe and the Middle East (EME)
- Europe, the Middle East and North Africa (EUMENA or EMENA)
- Europe, the Middle East, India and Africa (EMEIA or EMIA)
- Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Russia (EMEAR)
- Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Commonwealth of Independent States (EMEACIS)
- Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Caribbean (EMEAC)
- The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), around the Black Sea and Caspian Sea
- North Atlantic and Central Europe (NACE)
- Central and Eastern Europe, the Middle East and Africa (CEMA)
- Europe, Latin America, Africa, Arab world
Component areas
The EMEA region generally includes:
Europe
Central and Eastern Europe
 Belarus
Belarus Bulgaria
Bulgaria Czech Republic
Czech Republic Georgia
Georgia Hungary
Hungary Moldova
Moldova Poland
Poland Romania
Romania Russia
Russia Slovakia
Slovakia Ukraine
Ukraine Armenia
Armenia Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Tajikistan
Tajikistan Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Northern Europe
Southern Europe
 Albania
Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Croatia
Croatia Cyprus
Cyprus Greece
Greece Italy
Italy Kosovo
Kosovo Malta
Malta Montenegro
Montenegro North Macedonia
North Macedonia Portugal
Portugal Serbia
Serbia Slovenia
Slovenia Spain
Spain Turkey
Turkey
Western Europe
Middle East, North Africa (MENA)
 Algeria
Algeria Bahrain
Bahrain Egypt
Egypt Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Israel
Israel Jordan
Jordan Kuwait
Kuwait Lebanon
Lebanon Libya
Libya Morocco
Morocco Somalia
Somalia Oman
Oman Palestine
Palestine Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Sudan
Sudan Syria
Syria Tunisia
Tunisia United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates Yemen
Yemen
Sub-Saharan Africa
Eastern Africa
Central Africa
 Cameroon
Cameroon Central African Republic
Central African Republic Chad
Chad Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Gabon
Gabon São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe
Southern Africa
 Angola
Angola Botswana
Botswana Comoros
Comoros Eswatini
Eswatini Lesotho
Lesotho Madagascar
Madagascar Malawi
Malawi Mauritius
Mauritius Mozambique
Mozambique Namibia
Namibia Seychelles
Seychelles South Africa
South Africa Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Western Africa
 Benin
Benin Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Cape Verde
Cape Verde Gambia
Gambia Ghana
Ghana Guinea
Guinea Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast Liberia
Liberia Mali
Mali Mauritania
Mauritania Niger
Niger Nigeria
Nigeria Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Senegal
Senegal Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Togo
Togo
See also
References
- Kenton, Will. "Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA)". Investopedia. Retrieved 26 September 2019.
- "Sekiro Sales Dethrone The Division 2 in Global Charts". PlayStation LifeStyle. 30 March 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ Tucker, Ernest, 1961–. The Middle East in modern world history (Second ed.). New York, NY. ISBN 978-1-351-03170-7. OCLC 1055566281.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Fletcher, Max E. (1 December 1958). "The Suez Canal and World Shipping, 1869–1914". The Journal of Economic History. 18 (4): 556–573. doi:10.1017/S0022050700107740. ISSN 0022-0507. S2CID 153427820.
- Crouzet, François (1999). "Outside the walls of Europe – the pax britannica". European Review. 7 (4): 447–453. doi:10.1017/S1062798700004373. ISSN 1062-7987. S2CID 144363475.
- "CEMEA - Definition by AcronymFinder". www.acronymfinder.com.
- "Company Overview - About IDC - IDC CEMA". idc-cema.com.
| Countries and dependencies of Asia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
| ||||||
| States with limited recognition | |||||||
| Dependent territories |
| ||||||
| Special administrative regions of China | |||||||
| |||||||
| Countries and territories of Africa | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
| ||||||||||
| States with limited recognition | |||||||||||
| Dependent territories |
| ||||||||||
| African territories fully part of non-African states |
| ||||||||||
| Regions of Europe | |
|---|---|
| North | |
| East |
|
| Central | |
| West | |
| South | |
| Related | |
| Regions of Asia | |
|---|---|
| Central (The 'stans) |
|
| East (Northeast) |
|
| North (Siberia) | |
| Southeast (East Indies) | |
| South (Indian Subcontinent) |
|
| West (Middle East and South Caucasus) |
|
| Regions of Africa | |
|---|---|
| Central | |
| East | |
| North | |
| South | |
| West | |
| Macro-regions |
|
| Earth's primary regions and subregions | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worlds | |||||||||||||||
| Hemispheres | |||||||||||||||
| Landmasses | |||||||||||||||
| Continents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Islands |
| ||||||||||||||
| Oceans | |||||||||||||||
| Other waterbodies | |||||||||||||||
| Rim | |||||||||||||||
| Polar | |||||||||||||||
| Global | |||||||||||||||
| Continents of Earth | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||










