This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Probability density function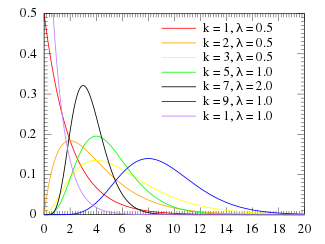 | |||
Cumulative distribution function | |||
| Parameters |
shape rate alt.: scale | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | No simple closed form | ||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Excess kurtosis | |||
| Entropy | |||
| MGF | for | ||
| CF | |||
The Erlang distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with support . The two parameters are:
- a positive integer the "shape", and
- a positive real number the "rate". The "scale", the reciprocal of the rate, is sometimes used instead.
The Erlang distribution is the distribution of a sum of independent exponential variables with mean each. Equivalently, it is the distribution of the time until the kth event of a Poisson process with a rate of . The Erlang and Poisson distributions are complementary, in that while the Poisson distribution counts the events that occur in a fixed amount of time, the Erlang distribution counts the amount of time until the occurrence of a fixed number of events. When , the distribution simplifies to the exponential distribution. The Erlang distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution in which the shape of the distribution is discretized.
The Erlang distribution was developed by A. K. Erlang to examine the number of telephone calls that might be made at the same time to the operators of the switching stations. This work on telephone traffic engineering has been expanded to consider waiting times in queueing systems in general. The distribution is also used in the field of stochastic processes.
Characterization
Probability density function
The probability density function of the Erlang distribution is
The parameter k is called the shape parameter, and the parameter is called the rate parameter.
An alternative, but equivalent, parametrization uses the scale parameter , which is the reciprocal of the rate parameter (i.e., ):
When the scale parameter equals 2, the distribution simplifies to the chi-squared distribution with 2k degrees of freedom. It can therefore be regarded as a generalized chi-squared distribution for even numbers of degrees of freedom.
Cumulative distribution function (CDF)
The cumulative distribution function of the Erlang distribution is
where is the lower incomplete gamma function and is the lower regularized gamma function. The CDF may also be expressed as
Erlang-k
The Erlang-k distribution (where k is a positive integer) is defined by setting k in the PDF of the Erlang distribution. For instance, the Erlang-2 distribution is , which is the same as .
Median
An asymptotic expansion is known for the median of an Erlang distribution, for which coefficients can be computed and bounds are known. An approximation is i.e. below the mean
Generating Erlang-distributed random variates
Erlang-distributed random variates can be generated from uniformly distributed random numbers () using the following formula:
Applications
Waiting times
Events that occur independently with some average rate are modeled with a Poisson process. The waiting times between k occurrences of the event are Erlang distributed. (The related question of the number of events in a given amount of time is described by the Poisson distribution.)
The Erlang distribution, which measures the time between incoming calls, can be used in conjunction with the expected duration of incoming calls to produce information about the traffic load measured in erlangs. This can be used to determine the probability of packet loss or delay, according to various assumptions made about whether blocked calls are aborted (Erlang B formula) or queued until served (Erlang C formula). The Erlang-B and C formulae are still in everyday use for traffic modeling for applications such as the design of call centers.
Other applications
The age distribution of cancer incidence often follows the Erlang distribution, whereas the shape and scale parameters predict, respectively, the number of driver events and the time interval between them. More generally, the Erlang distribution has been suggested as good approximation of cell cycle time distribution, as result of multi-stage models.
The kinesin is a molecular machine with two "feet" that "walks" along a filament. The waiting time between each step is exponentially distributed. When green fluorescent protein is attached to a foot of the kinesin, then the green dot visibly moves with Erlang distribution of k = 2.
It has also been used in marketing for describing interpurchase times.
Properties
- If then with
- If and then if are independent
Related distributions
- The Erlang distribution is the distribution of the sum of k independent and identically distributed random variables, each having an exponential distribution. The long-run rate at which events occur is the reciprocal of the expectation of that is, The (age specific event) rate of the Erlang distribution is, for monotonic in increasing from 0 at to as tends to infinity.
- That is: if then
- Because of the factorial function in the denominator of the PDF and CDF, the Erlang distribution is only defined when the parameter k is a positive integer. In fact, this distribution is sometimes called the Erlang-k distribution (e.g., an Erlang-2 distribution is an Erlang distribution with ). The gamma distribution generalizes the Erlang distribution by allowing k to be any positive real number, using the gamma function instead of the factorial function.
- That is: if k is an integer and then
- If and then
- The Erlang distribution is a special case of the Pearson type III distribution
- The Erlang distribution is related to the chi-squared distribution. If then
- The Erlang distribution is related to the Poisson distribution by the Poisson process: If such that then and Taking the differences over gives the Poisson distribution.
See also
- Coxian distribution
- Engset calculation
- Erlang B formula
- Erlang unit
- Phase-type distribution
- Traffic generation model
Notes
- "h1.pdf" (PDF).
- Choi, K. P. (1994). "On the medians of gamma distributions and an equation of Ramanujan". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 121: 245–251. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-1994-1195477-8. JSTOR 2160389.
- Adell, J. A.; Jodrá, P. (2010). "On a Ramanujan equation connected with the median of the gamma distribution". Transactions of the American Mathematical Society. 360 (7): 3631. doi:10.1090/S0002-9947-07-04411-X.
- Jodrá, P. (2012). "Computing the Asymptotic Expansion of the Median of the Erlang Distribution". Mathematical Modelling and Analysis. 17 (2): 281–292. doi:10.3846/13926292.2012.664571.
- Banneheka, BMSG; Ekanayake, GEMUPD (2009). "A new point estimator for the median of gamma distribution". Viyodaya J Science. 14: 95–103.
- Resa. "Statistical Distributions - Erlang Distribution - Random Number Generator". www.xycoon.com. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- Belikov, Aleksey V. (22 September 2017). "The number of key carcinogenic events can be predicted from cancer incidence". Scientific Reports. 7 (1). doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12448-7. PMC 5610194. PMID 28939880.
- Belikov, Aleksey V.; Vyatkin, Alexey; Leonov, Sergey V. (2021-08-06). "The Erlang distribution approximates the age distribution of incidence of childhood and young adulthood cancers". PeerJ. 9: e11976. doi:10.7717/peerj.11976. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 8351573. PMID 34434669.
- Yates, Christian A. (21 April 2017). "A Multi-stage Representation of Cell Proliferation as a Markov Process". Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 79 (1): 2905–2928. doi:10.1007/s11538-017-0356-4. PMC 5709504.
- Gavagnin, Enrico (21 November 2019). "The invasion speed of cell migration models with realistic cell cycle time distributions". Journal of Theoretical Biology. 481: 91–99. arXiv:1806.03140. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.09.010.
- Yildiz, Ahmet; Forkey, Joseph N.; McKinney, Sean A.; Ha, Taekjip; Goldman, Yale E.; Selvin, Paul R. (2003-06-27). "Myosin V Walks Hand-Over-Hand: Single Fluorophore Imaging with 1.5-nm Localization". Science. 300 (5628): 2061–2065. doi:10.1126/science.1084398. ISSN 0036-8075.
- Chatfield, C.; Goodhardt, G.J. (December 1973). "A Consumer Purchasing Model with Erlang Interpurchase Times". Journal of the American Statistical Association. 68: 828–835. doi:10.1080/01621459.1973.10481432.
- Cox, D.R. (1967) Renewal Theory, p20, Methuen.
References
- Ian Angus "An Introduction to Erlang B and Erlang C", Telemanagement #187 (PDF Document - Has terms and formulae plus short biography)
- Stuart Harris "Erlang Calculations vs. Simulation"

 rate
rate 









 for
for 

 the "shape", and
the "shape", and the "rate". The "scale",
the "rate". The "scale",  the reciprocal of the rate, is sometimes used instead.
the reciprocal of the rate, is sometimes used instead.
 each. Equivalently, it is the distribution of the time until the kth event of a
each. Equivalently, it is the distribution of the time until the kth event of a  . The Erlang and Poisson distributions are complementary, in that while the Poisson distribution counts the events that occur in a fixed amount of time, the Erlang distribution counts the amount of time until the occurrence of a fixed number of events. When
. The Erlang and Poisson distributions are complementary, in that while the Poisson distribution counts the events that occur in a fixed amount of time, the Erlang distribution counts the amount of time until the occurrence of a fixed number of events. When  , the distribution simplifies to the
, the distribution simplifies to the 
 , which is the reciprocal of the rate parameter (i.e.,
, which is the reciprocal of the rate parameter (i.e.,  ):
):


 is the lower
is the lower  is the
is the 
 is defined by setting k in the PDF of the Erlang distribution. For instance, the Erlang-2 distribution is
is defined by setting k in the PDF of the Erlang distribution. For instance, the Erlang-2 distribution is  , which is the same as
, which is the same as  .
.
 i.e. below the mean
i.e. below the mean 
 ) using the following formula:
) using the following formula:

 then
then  with
with 
 and
and  then
then  if
if  are independent
are independent that is,
that is,  The (age specific event) rate of the Erlang distribution is, for
The (age specific event) rate of the Erlang distribution is, for  monotonic in
monotonic in  increasing from 0 at
increasing from 0 at  to
to  tends to infinity.
tends to infinity.
 then
then 
 ). The
). The  then
then  and
and  then
then 
 then
then 
 such that
such that  and
and  Taking the differences over
Taking the differences over  gives the Poisson distribution.
gives the Poisson distribution.