| Eutardigrade Temporal range: Cretaceous–Recent PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|
| |
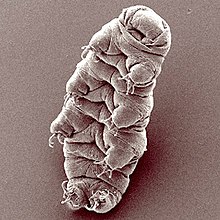
| Hypsibius dujardini | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Tardigrada |
| Class: | Eutardigrada Richters, 1926 |
| Orders, superfamilies and families | |
| |
Eutardigrada are a class of tardigrades (Tardigrada) without lateral appendages. Primarily freshwater bound, some species have secondarily gained the ability to live in marine environments (Halobiotus). By cryptobiosis many species are able to live temporarily in very dry environments. More than 700 species have been described.
The order Apochela consists of only one family, Milnesiidae, with two genera: Milnesium and Limmenius. Milnesium tardigradum can be found worldwide and is one of the biggest species among tardigrades (up to 1.4 mm); similar-looking species have been found in Cretaceous amber. The mouth of this predator has a wide opening, so the animal can eat rotifers and larger protists. Other eutardigrades belong to the order Parachela.
References
- ^ Budd, G. (2001). "Tardigrades as 'Stem-Group Arthropods': The Evidence from the Cambrian Fauna". Zoologischer Anzeiger. 240 (3–4): 265–279. Bibcode:2001ZooAn.240..265B. doi:10.1078/0044-5231-00034. ISSN 0044-5231.
- Zhang, Z.-Q. (2011). "Animal biodiversity: An introduction to higher-level classification and taxonomic richness" (PDF). Zootaxa. 3148: 7–12. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3148.1.3.
External links
 Data related to Eutardigrada at Wikispecies
Data related to Eutardigrada at Wikispecies- "Eutardigrada". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- Tardigrade taxa
- Pseudobiotus megalonyx
- Milnesium tardigradum (radiation experiments)
This tardigrade-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |