This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Outer ear | |
|---|---|
 A diagram of the anatomy of the human ear: Brown is outer ear.
Red is middle ear.
Purple is inner ear. A diagram of the anatomy of the human ear: Brown is outer ear.
Red is middle ear.
Purple is inner ear. | |
 The auricula. Lateral surface. The auricula. Lateral surface. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | auris externa |
| MeSH | D004431 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1705 |
| TA98 | A15.3.01.001 |
| TA2 | 6862 |
| FMA | 52781 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
 |
| This article is one of a series documenting the anatomy of the |
| Human ear |
|---|
| Outer ear |
| Middle ear |
| Inner ear |
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
Structure
Auricle
Main article: Auricle (anatomy)The visible part is called the auricle, also known as the pinna, especially in other animals. It is composed of a thin plate of yellow elastic cartilage, covered with integument, and connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles; and to the commencement of the ear canal by fibrous tissue. Many mammals can move the pinna (with the auriculares muscles) in order to focus their hearing in a certain direction in much the same way that they can turn their eyes. Most humans do not have this ability.
Ear canal
Main article: Ear canalFrom the pinna, the sound waves move into the ear canal (also known as the external acoustic meatus) a simple tube running through to the middle ear. This tube leads inward from the bottom of the auricula and conducts the vibrations to the tympanic cavity and amplifies frequencies in the range 2 kHz to 5 kHz.
Auricular muscles
Intrinsic muscles
| Intrinsic muscles of external ear | |
|---|---|
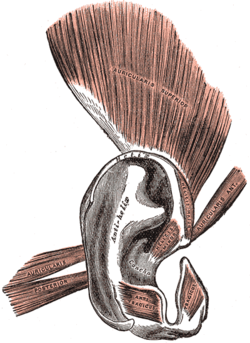 The muscles of the auricula The muscles of the auricula | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Facial nerve |
| Actions | Undeveloped in humans |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D004431 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1705 |
| TA98 | A15.3.01.001 |
| TA2 | 6862 |
| FMA | 52781 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle[edit on Wikidata] | |
The intrinsic auricular muscles are:
- The helicis major is a narrow vertical band situated upon the anterior margin of the helix. It arises below, from the spina helicis, and is inserted into the anterior border of the helix, just where it is about to curve backward.
- The helicis minor is an oblique fasciculus, covering the crus helicis.
- The tragicus is a short, flattened vertical band on the lateral surface of the tragus. Also known as the mini lobe.
- The antitragicus arises from the outer part of the antitragus, and is inserted into the cauda helicis and antihelix.
- The transverse muscle is placed on the cranial surface of the pinna. It consists of scattered fibers, partly tendinous and partly muscular, extending from the eminentia conchae to the prominence corresponding with the scapha.
- The oblique muscle also on the cranial surface, consists of a few fibers extending from the upper and back part of the concha to the convexity immediately above it.
The intrinsic muscles contribute to the topography of the auricle, while also function as a sphincter of the external auditory meatus. It has been suggested that during prenatal development in the womb, these muscles exert forces on the cartilage which in turn affects the shaping of the ear.
Extrinsic muscles
| Auricular muscles | |
|---|---|
 The muscles of the pinna The muscles of the pinna | |
 Auricular muscles in context with the other facial muscles Auricular muscles in context with the other facial muscles | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Galeal aponeurosis |
| Insertion | Front of the helix, cranial surface of the pinna |
| Artery | Posterior auricular artery |
| Nerve | Facial nerve |
| Actions | Subtle auricle movements (forwards, backwards and upwards) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculi auriculares |
| MeSH | D004431 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1705 |
| TA98 | A15.3.01.001 |
| TA2 | 6862 |
| FMA | 52781 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle[edit on Wikidata] | |
The extrinsic auricular muscles are the three muscles surrounding the auricula or outer ear:
The superior muscle is the largest of the three, followed by the posterior and the anterior.
In some mammals these muscles can adjust the direction of the pinna. In humans these muscles possess very little action. The auricularis anterior draws the auricula forward and upward, the auricularis superior slightly raises it, and the auricularis posterior draws it backward. The superior auricular muscle also acts as a stabilizer of the occipitofrontalis muscle and as a weak brow lifter. The presence of auriculomotor activity in the posterior auricular muscle causes the muscle to contract and cause the pinna to be pulled backwards and flatten when exposed to sudden, surprising sounds.
Function
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2013) |
One consequence of the configuration of the outer ear is selectively to boost the sound pressure 30- to 100-fold for frequencies around 3 kHz. This amplification makes humans most sensitive to frequencies in this range—and also explains why they are particularly prone to acoustical injury and hearing loss near this frequency. Most human speech sounds are also distributed in the bandwidth around 3 kHz.
Clinical significance
Malformations of the external ear can be a consequence of hereditary disease, or exposure to environmental factors such as radiation, infection. Such defects include:
- A preauricular fistula, which is a long narrow tube, usually near the tragus. This can be inherited as an autosomal recessive fashion and may suffer from chronic infection in later life.
- Cosmetic defects, such as very large ears, small ears.
- Malformation that may lead to functional impairment, such as atresia of the external auditory meatus or aplasia of the pinna,
- Genetic syndromes, which include:
- Konigsmark syndrome, characterised by small ears and atresia of the external auditory canal, causing conductive hearing loss and inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
- Goldenhar syndrome, a combination of developmental abnormalities affecting the ears, eyes, bones of the skull, and vertebrae, inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
- Treacher Collins syndrome, characterised by dysplasia of the auricle, atresia of the bony part of the auditory canal, hypoplasia of the auditory ossicles and tympanic cavity, and 'mixed' deafness (both sensorineural and conductive), inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
- Crouzon syndrome, characterised by bilateral atresia of the external auditory canal, inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Surgery
Usually, malformations are treated with surgery, although artificial prostheses are also sometimes used.
- Preauricular fistulas are generally not treated unless chronically inflamed.
- Cosmetic defects without functional impairment are generally repaired after ages 6–7.
If malformations are accompanied by hearing loss amenable to correction, then the early use of hearing aids may prevent complete hearing loss.
Additional images
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1033 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1033 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- nyu.edu/classes/bello/FMT_files/2_hearing.pdf "Hearing" by Juan P Bello
- "Why Can Some People Wiggle Their Ears?". Live Science. 30 March 2012.
- "Acoustics Chapter One: The ear". cmtext.indiana.edu. Retrieved 2024-10-21.
- Liugan, Mikee; Zhang, Ming; Cakmak, Yusuf Ozgur (2018). "Neuroprosthetics for Auricular Muscles: Neural Networks and Clinical Aspects". Frontiers in Neurology. 8: 752. doi:10.3389/fneur.2017.00752. ISSN 1664-2295. PMC 5775970. PMID 29387041.
- Chon, Brian H.; Blandford, Alex D.; Hwang, Catherine J.; Petkovsek, Daniel; Zheng, Andrew; Zhao, Carrie; Cao, Jessica; Grissom, Nick; Perry, Julian D. (February 2021). "Dimensions, Function and Applications of the Auricular Muscle in Facial Plastic Surgery". Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 45 (1): 309–314. doi:10.1007/s00266-020-02045-x. ISSN 1432-5241. PMID 33258010. S2CID 227236615.
- Strauss, Daniel J; Corona-Strauss, Farah I; Schroeer, Andreas; Flotho, Philipp; Hannemann, Ronny; Hackley, Steven A (2020-07-03). Groh, Jennifer M; Shinn-Cunningham, Barbara G; Verhulst, Sarah; Shera, Christopher; Corneil, Brian D (eds.). "Vestigial auriculomotor activity indicates the direction of auditory attention in humans". eLife. 9: e54536. doi:10.7554/eLife.54536. ISSN 2050-084X. PMC 7334025. PMID 32618268.
- Purves, Dale, George J. Augustine, David Fitzpatrick, William C. Hall, Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, James O. McNamara, and Leonard E. White (2008). "Chapter 13". Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sinauer Associates. p. 317. ISBN 978-0-87893-697-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Богомильский, Чистякова 2002, pp. 68–69. sfn error: no target: CITEREFБогомильский,_Чистякова2002 (help)
- Богомильский, Чистякова 2002, pp. 65–66. sfn error: no target: CITEREFБогомильский,_Чистякова2002 (help)
- ^ Пальчун, Крюков 2001, p. 489. sfn error: no target: CITEREFПальчун,_Крюков2001 (help)
- СЭС 1986, p. 89. sfn error: no target: CITEREFСЭС1986 (help)
- СЭС 1986, p. 68. sfn error: no target: CITEREFСЭС1986 (help)
- Богомильский, Чистякова 2002, pp. 66–67. sfn error: no target: CITEREFБогомильский,_Чистякова2002 (help)
- Богомильский, Чистякова 2002, p. 67. sfn error: no target: CITEREFБогомильский,_Чистякова2002 (help)
- Богомильский, Чистякова 2002, pp. 67–68. sfn error: no target: CITEREFБогомильский,_Чистякова2002 (help)
- Асанов и др. 2003, pp. 198–199. sfn error: no target: CITEREFАсанов_и_др.2003 (help)
- Асанов и др. 2003, p. 198. sfn error: no target: CITEREFАсанов_и_др.2003 (help)
- ^ Богомильский, Чистякова 2002, p. 65. sfn error: no target: CITEREFБогомильский,_Чистякова2002 (help)
External links
![]() Media related to Outer ear at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Outer ear at Wikimedia Commons
| Anatomy of hearing and balance | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer ear | |||||||||||||||
| Middle ear |
| ||||||||||||||
| Inner ear |
| ||||||||||||||
