| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Flexor digitorum brevis muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles of the sole of the foot. First layer. (Flexor digitorum brevis visible at center.) Muscles of the sole of the foot. First layer. (Flexor digitorum brevis visible at center.) | |
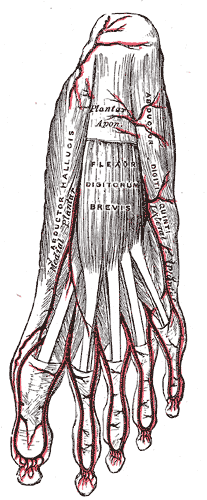 The plantar arteries. Superficial view. (Flexor digitorum brevis visible at center.) The plantar arteries. Superficial view. (Flexor digitorum brevis visible at center.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Calcaneus |
| Insertion | Middle phalanges of toe 2-5 |
| Artery | Medial and lateral plantar arteries and plantar arch, plantar metatarsal and plantar digital arteries |
| Nerve | Medial plantar nerve |
| Actions | Flexion of the lateral four digits |
| Antagonist | Extensor digitorum longus and extensor digitorum brevis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus flexor digitorum brevis |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.067 |
| TA2 | 2683 |
| FMA | 37450 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle[edit on Wikidata] | |
The flexor digitorum brevis or flexor digitorum communis brevis is a muscle which lies in the middle of the sole of the foot, immediately above the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, with which it is firmly united.
Its deep surface is separated from the lateral plantar vessels and nerves by a thin layer of fascia.
Structure
It arises by a narrow tendon, from the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, from the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, and from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles.
It passes forward, and divides into four tendons, one for each of the four lesser toes.
Opposite the bases of the first phalanges, each tendon divides into two slips, to allow of the passage of the corresponding tendon of the flexor digitorum longus; the two portions of the tendon then unite and form a grooved channel for the reception of the accompanying long Flexor tendon.
Finally, it divides a second time, and is inserted into the sides of the second phalanx about its middle. The mode of division of the tendons of the flexor digitorum brevis, and of their insertion into the phalanges, is analogous to that of the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis in the hand.
Innervation
Innervation is by the medial plantar nerve.
Variation
Slip to the little toe may occasionally be absent, where it may be replaced by a small fusiform muscle arising from the long flexor tendon or from the quadratus plantæ.
Additional images
-
 Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.
Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.
-
 Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints.
Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints.
-
 The bottom-most or first layer of muscles in the human foot include the flexor digitorum brevis.
The bottom-most or first layer of muscles in the human foot include the flexor digitorum brevis.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 491 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 491 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:16:st-0411 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Foot: Muscles"
- PTCentral
| Muscles of the hip and human leg | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iliac region | |||||||||||||||||
| Buttocks |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Thigh / compartments |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Leg/ compartments |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Foot |
| ||||||||||||||||