| GC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GC, DBP, DBP/GRD3, HEL-S-51, VDBG, VDBP, Gc-MAF, GcMAF, vitamin D binding protein, DBP-maf, VDB, GC vitamin D binding protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 139200; MGI: 95669; HomoloGene: 486; GeneCards: GC; OMA:GC - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin D-binding protein (DBP), also/originally known as gc-globulin (group-specific component), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GC gene. DBP is genetically the oldest member of the albuminoid family and appeared early in the evolution of vertebrates.
Structure
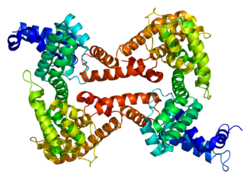
Human GC is a glycosylated alpha-globulin, ~58 kDa in size. Its 458 amino acids are coded for by 1690 nucleotides on chromosome 4 (4q11–q13). The primary structure contains 28 cysteine residues forming multiple disulfide bonds. GC contains 3 domains. Domain 1 is composed of 10 alpha helices, domain 2 of 9, and domain 3 of 4.
Function
Vitamin D-binding protein belongs to the albumin gene family, together with human serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein. It is a multifunctional protein found in plasma, ascitic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid and on the surface of many cell types.
It is able to bind the various forms of vitamin D including ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), the 25-hydroxylated forms (calcifediol), and the active hormonal product, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol). The major proportion of vitamin D in blood is bound to this protein. It transports vitamin D metabolites between skin, liver and kidney, and then on to the various target tissues.
As Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor it is a Macrophage Activating Factor (MAF) that has been tested for use as a cancer treatment that would activate macrophages against cancer cells.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.
[[File: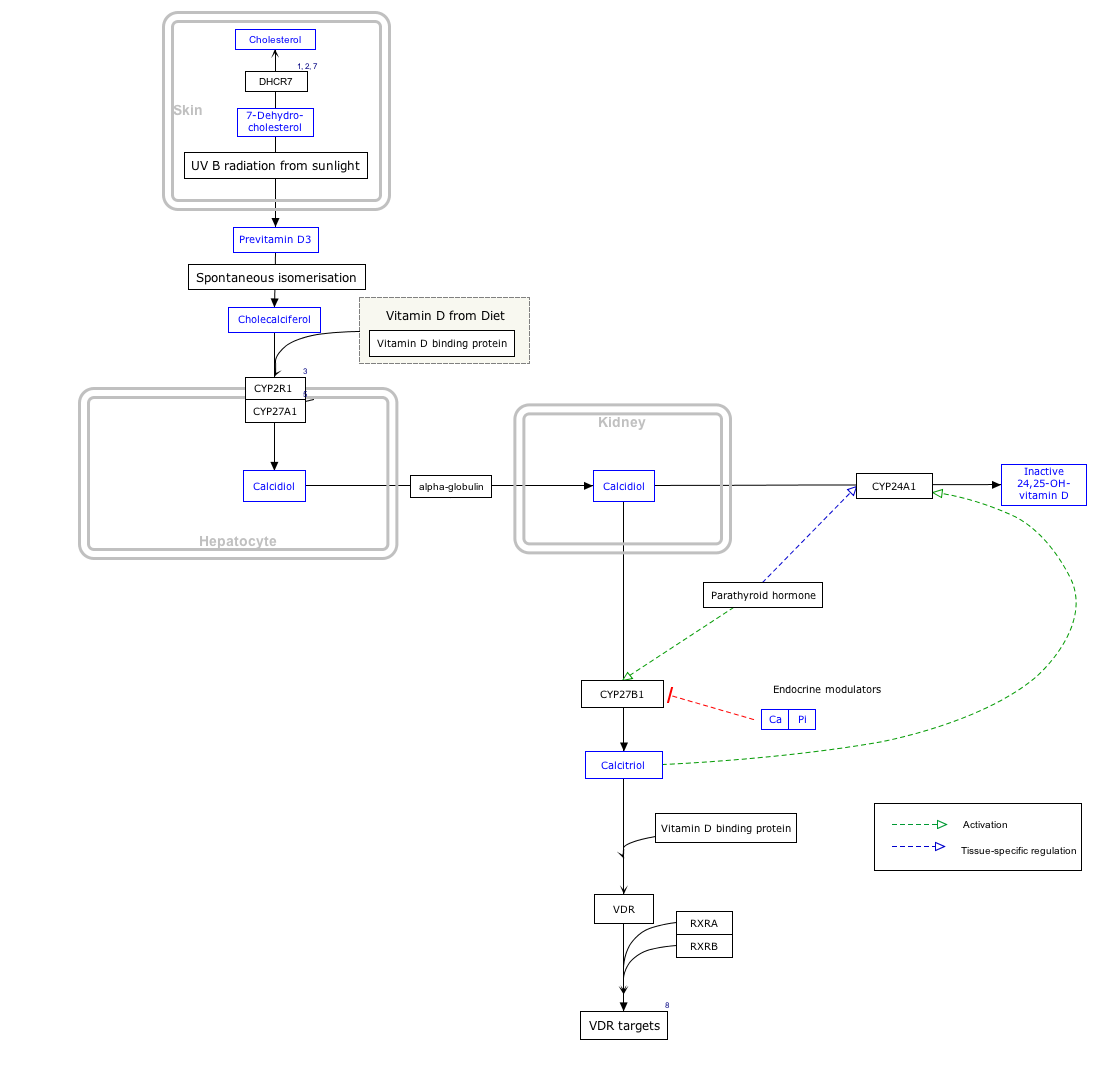

- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
Production
It is synthesized by hepatic parenchymal cells and secreted into the blood circulation.
Regulation
The transcription factors HFN1α is a positive regulator while HFN1β is a dominant negative regulator of DBP expression.
Variation
Many genetic variants of the GC gene are known. They produce 6 main haplotypes and 3 main protein variants (Gc1S, Gc1F and Gc2). The genetic variations are associated with differences in circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. They have been proposed to account for some of the differences in vitamin D status in different ethnic groups, and have been found to correlate with the response to vitamin D supplementation.
References
- ^ GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000145321 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000035540 – Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Mikkelsen M, Jacobsen P, Henningsen K (Jul 1977). "Possible localization of Gc-System on chromosome 4. Loss of long arm 4 material associated with father-child incompatibility within the Gc-System". Human Heredity. 27 (2): 105–7. doi:10.1159/000152857. PMID 558959.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: GC group-specific component (vitamin D binding protein)".
- Bouillon, R.; Schuit, F.; Antonio, L.; Rastinejad, F. (2020). "Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 10: 910. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00910. PMC 6965021. PMID 31998239.
- Verboven C, Rabijns A, De Maeyer M, Van Baelen H, Bouillon R, De Ranter C (February 2002). "A structural basis for the unique binding features of the human vitamin D-binding protein". Nature Structural Biology. 9 (2): 131–6. doi:10.1038/nsb754. PMID 11799400. S2CID 38990672.
- ^ Norman AW (August 2008). "From vitamin D to hormone D: fundamentals of the vitamin D endocrine system essential for good health". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 88 (2): 491S–499S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/88.2.491S. PMID 18689389.
- Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Yamamoto N (July 2008). "Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer with Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor, GcMAF" (). Translational Oncology. 1 (2): 65–72. doi:10.1593/tlo.08106. PMC 2510818. PMID 18633461.
- Bouillon R, Schuit F, Antonio L, Rastinejad F (2019). "Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 10: 910. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00910. PMC 6965021. PMID 31998239.
- ^ Malik S, Fu L, Juras DJ, Karmali M, Wong BY, Gozdzik A, Cole DE (January–February 2013). "Common variants of the vitamin D binding protein gene and adverse health outcomes". Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences. 50 (1): 1–22. doi:10.3109/10408363.2012.750262. PMC 3613945. PMID 23427793.
- McGrath JJ, Saha S, Burne TH, Eyles DW (July 2010). "A systematic review of the association between common single nucleotide polymorphisms and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 121 (1–2): 471–7. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.073. PMID 20363324. S2CID 20057294.
- Powe CE, Evans MK, Wenger J, Zonderman AB, Berg AH, Nalls M, Tamez H, Zhang D, Bhan I, Karumanchi SA, Powe NR, Thadhani R (November 2013). "Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D status of black Americans and white Americans". The New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (21): 1991–2000. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1306357. PMC 4030388. PMID 24256378.
Further reading
- Svasti J, Kurosky A, Bennett A, Bowman BH (April 1979). "Molecular basis for the three major forms of human serum vitamin D binding protein (group-specific component)". Biochemistry. 18 (8): 1611–7. doi:10.1021/bi00575a036. PMID 218624.
- Braun A, Bichlmaier R, Cleve H (June 1992). "Molecular analysis of the gene for the human vitamin-D-binding protein (group-specific component): allelic differences of the common genetic GC types". Human Genetics. 89 (4): 401–6. doi:10.1007/BF00194311. PMID 1352271. S2CID 1913655.
- Esteban C, Geuskens M, Ena JM, Mishal Z, Macho A, Torres JM, Uriel J (May 1992). "Receptor-mediated uptake and processing of vitamin D-binding protein in human B-lymphoid cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 267 (14): 10177–83. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)50216-2. PMID 1374401.
- Szpirer C, Riviere M, Cortese R, Nakamura T, Islam MQ, Levan G, Szpirer J (June 1992). "Chromosomal localization in man and rat of the genes encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors C/EBP, DBP, and HNF1/LFB-1 (CEBP, DBP, and transcription factor 1, TCF1, respectively) and of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor gene (HGF)". Genomics. 13 (2): 293–300. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90245-N. PMID 1535333.
- Dawson SJ, White LA (May 1992). "Treatment of Haemophilus aphrophilus endocarditis with ciprofloxacin". The Journal of Infection. 24 (3): 317–20. doi:10.1016/S0163-4453(05)80037-4. PMID 1602151.
- Yang F, Bergeron JM, Linehan LA, Lalley PA, Sakaguchi AY, Bowman BH (August 1990). "Mapping and conservation of the group-specific component gene in mouse". Genomics. 7 (4): 509–16. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90193-X. PMID 1696927.
- Yang F, Luna VJ, McAnelly RD, Naberhaus KH, Cupples RL, Bowman BH (November 1985). "Evolutionary and structural relationships among the group-specific component, albumin and alpha-fetoprotein". Nucleic Acids Research. 13 (22): 8007–17. doi:10.1093/nar/13.22.8007. PMC 322106. PMID 2415926.
- Yang F, Brune JL, Naylor SL, Cupples RL, Naberhaus KH, Bowman BH (December 1985). "Human group-specific component (Gc) is a member of the albumin family". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (23): 7994–8. Bibcode:1985PNAS...82.7994Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.23.7994. PMC 391428. PMID 2415977.
- Cooke NE, David EV (December 1985). "Serum vitamin D-binding protein is a third member of the albumin and alpha fetoprotein gene family". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 76 (6): 2420–4. doi:10.1172/JCI112256. PMC 424397. PMID 2416779.
- Schoentgen F, Metz-Boutigue MH, Jollès J, Constans J, Jollès P (June 1986). "Complete amino acid sequence of human vitamin D-binding protein (group-specific component): evidence of a three-fold internal homology as in serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology. 871 (2): 189–98. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(86)90173-1. PMID 2423133.
- McNearney TA, Odell C, Holers VM, Spear PG, Atkinson JP (November 1987). "Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gC-1 and gC-2 bind to the third component of complement and provide protection against complement-mediated neutralization of viral infectivity". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 166 (5): 1525–35. doi:10.1084/jem.166.5.1525. PMC 2189652. PMID 2824652.
- Yang F, Naberhaus KH, Adrian GS, Gardella JM, Brissenden JE, Bowman BH (1987). "The vitamin D-binding protein gene contains conserved nucleotide sequences that respond to heavy metal, adipocyte and mitotic signals". Gene. 54 (2–3): 285–90. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(87)90499-9. PMID 2958390.
- Cooke NE, Willard HF, David EV, George DL (July 1986). "Direct regional assignment of the gene for vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin) to human chromosome 4q11-q13 and identification of an associated DNA polymorphism". Human Genetics. 73 (3): 225–9. doi:10.1007/BF00401232. PMID 3015768. S2CID 38816588.
- Nestler JE, McLeod JF, Kowalski MA, Strauss JF, Haddad JG (May 1987). "Detection of vitamin D binding protein on the surface of cytotrophoblasts isolated from human placentae". Endocrinology. 120 (5): 1996–2002. doi:10.1210/endo-120-5-1996. PMID 3552627.
- Pierce EA, Dame MC, Bouillon R, Van Baelen H, DeLuca HF (December 1985). "Monoclonal antibodies to human vitamin D-binding protein". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (24): 8429–33. Bibcode:1985PNAS...82.8429P. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.24.8429. PMC 390929. PMID 3936035.
- Wooten MW, Nel AE, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Galbraith RM, Wrenn RW (October 1985). "Identification of a major endogenous substrate for phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent kinase in pancreatic acini as Gc (vitamin D-binding protein)". FEBS Letters. 191 (1): 97–101. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(85)81001-2. PMID 4054306. S2CID 29613843.
- Constans J, Oksman F, Viau M (August 1981). "Binding of the apo and holo forms of the serum vitamin D-binding protein to human lymphocyte cytoplasm and membrane by indirect immunofluorescence". Immunology Letters. 3 (3): 159–62. doi:10.1016/0165-2478(81)90120-6. PMID 7026425.
- Braun A, Kofler A, Morawietz S, Cleve H (December 1993). "Sequence and organization of the human vitamin D-binding protein gene". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1216 (3): 385–94. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(93)90005-x. PMID 7505619.
- Swamy N, Roy A, Chang R, Brisson M, Ray R (April 1995). "Affinity purification of human plasma vitamin D-binding protein". Protein Expression and Purification. 6 (2): 185–8. doi:10.1006/prep.1995.1023. PMID 7606167.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P02774 (Vitamin D-binding protein) at the PDBe-KB.