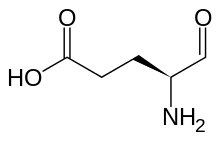
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (4S)-4-Amino-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | glutamate-1-semialdehyde |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H9NO3 |
| Molar mass | 131.131 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde is a molecule formed from by the reduction of tRNA bound glutamate, catalyzed by glutamyl-tRNA reductase. It is isomerized by glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase to give aminolevulinic acid in the biosynthesis of porphyrins, including heme and chlorophyll.
See also
References
- Beale SI (August 1990). "Biosynthesis of the Tetrapyrrole Pigment Precursor, delta-Aminolevulinic Acid, from Glutamate". Plant Physiol. 93 (4): 1273–9. doi:10.1104/pp.93.4.1273. PMC 1062668. PMID 16667613.
- Willows, R.D. (2004). "Chlorophylls". In Goodman, Robert M. (ed.). Encyclopaedia of Plant and Crop Science. Marcel Dekker. pp. 258–262. ISBN 0-8247-4268-0.
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |