| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name N,N,N-Trimethylglycinium | |
| Systematic IUPAC name N,N,N-Trimethyl-2-oxoethan-1-aminium | |
| Other names Betaine aldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
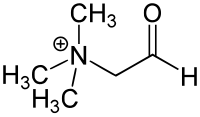
| Chemical formula | C5H12NO |
| Molar mass | 102.157 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Glycine betaine aldehyde, often simply called betaine aldehyde, is an intermediate in the metabolism of glycine, serine and threonine. The human aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.3) stimulates the transformation of betaine aldehyde to glycine betaine. Betaine aldehyde is a substrate for choline dehydrogenase (mitochondrial).
Chemical structure
Glycine betaine aldehyde is a short chain aldehyde and quaternary ammonium compound. It can be considered a derivative of the amino acid glycine. Its chemical formula is C5H12NO.
Biological function
Glycine betaine aldehyde is a component of glycine, serine and threonine metabolism. It also serves as an osmolyte.
It can be found in cytoplasm and mitochondria within the kidney, neurons, and stratum corneum.
References
- Betaine aldehyde Archived 2007-11-24 at the Wayback Machine, Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank
- Yilmaz JL, Bülow L. (December 2002). "Enhanced stress tolerance in Escherichia coli and Nicotiana tabacum expressing a betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase/choline dehydrogenase fusion protein". Biotechnol. Prog. 18 (6): 1176–82. doi:10.1021/bp020057k. PMID 12467448. S2CID 8054758.
- , Human Metabolome Database