| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (October 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Novorossiya GovernorateНовороссийская губерния | |
|---|---|
| Governorate of the Russian Empire | |
| 1764–1783 1796–1802 | |
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
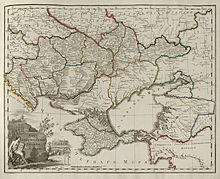 General-Governorate of New Russia in 1800 | |
| Capital | St Elizabeth Fort (1764) Kremenchug (1765–1776) Yekaterinoslav (Novorossiysk) (1776–1783) |
| Demonym | New Russian |
| History | |
| • Established | 22 March 1764 |
| • First disestablishment | 1783 |
| • Reestablished | December 1796 |
| • Disestablished | 1802 |
| Political subdivisions | provinces, uyezds |
| Today part of | |



Novorossiya Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1764–1783 and again in 1796–1802. It was created and governed according to the "Plan for the Colonization of New Russia Governorate" issued by the Russian Senate. It became the first region in Russia where Catherine the Great allowed foreign Jews to settle.
Most of its territories belonged to the Zaporozhian Sich as well as the Poltava Regiment and Myrhorod Regiment of the Cossack Hetmanate. Its establishment was strategically successful and advantageous for Russia, and after the conclusion of the Russian war against Turkey in 1774 it gave a way for Russia to access the Black Sea and establish an area that became known as Novorossiya ("New Russia"). It was created based on the Military Frontier of the Austrian Empire against the Ottoman Empire and involved many military units from the region that were resettled in Ukraine. The military units included mounted cossacks (or hussars) and mounted pikers (or lancers).
In 1796, the governorate was reestablished, but with the centre not in Kremenchug but in Yekaterinoslav, and in 1802 was split into three governorates: the Yekaterinoslav Governorate, the Taurida Governorate, the Nikolayev Governorate (known as the Kherson Governorate from 1803).
History
It was created on 2 April [O.S. 22 March] 1764 as a military district for the protection of the southern border of the empire and in preparation for the major military campaign of the Russo-Turkish War. The governorate united the territories of New Serbia, Slavo-Serbia, and the Slobidskyi regiment (today in Kirovohrad Oblast) which were the northern regions of Buhohard Palatinate (Zaporizhian Sich). The governorate, centered in the fortress of Saint Elizabeth, initially was divided into three territories (polki) assigned to each regiment in the area: Elizabeth City Pikers Regiment, Black Hussars Regiment, and Yellow Hussars Regiment.
As of 22 June [O.S. 11 June] 1764 the governorate also included the so-called Ukrainian Line, a line of Russian built fortresses between Dnieper and Donets) that was administrated by the Dnieper and Donets Pikers regiments (based on the Habsburg's Pandurs, the cossacks of Poltava, the Myrhorod regiments), the Slavo-Serbia with Luhansk Pikers Regiment, and the Raiko Preradovic and Ivan Sevic Hussars regiments (soon the later two were united into the Bakhmut Hussars Regiment) as well as the Samara Hussar Regiment (originally the Moldavian Hussars Regiment based in Kiev).
The first capital of the governorate was the city of Kremenchug (1765) with the fortress of Saint Elizabeth (today Kropyvnytskyi) serving that administrative function previously (1764).
Pikers unrest
In 1769–70 during the 1768–74 Russian-Ottoman War there was an uprising among the Dnieper and Donets Pikers regiments. The unrest started on territory of today's Poltava Oblast and eventually spread across the lands of the Zaporizhian Host. It was mercilessly put down by Russian Imperial forces and its instigators were punished by knout or sent to katorga. The Donets Pikers Regiment eventually was forcefully sent to the war where it played a key role in forcing Syvash, taken of Perekop, Caffa (Feodosiya).
Destruction of Zaporizhian Sich
In June 1775 the Russian Imperial Army razed the capital of the Zaporizhian Sich, after which all its lands were annexed to the Novorossiysk Governorate. The following year, Bakhmut Province and Yekaterinoslav Province were transferred to the newly established Azov Governorate.
Subdivisions
The governorate was subdivided into 12 provinces (circuluses) and further into uyezdes (counties). The city of Yekaterinoslav (today – Novomoskovsk) was located in Azov Governorate. The city of Yekaterinoslav (today – Dnipro) was located in Novorossiya Governorate.
List of provinces (circuluses):
- Territories before partitioning of the Sich
- Olviopolsk – Olviopol (today Pervomaisk)
- Elizabethgrad – Elizabethgrad (today Kropyvnytskyi)
- Krukov – Krukov (today the city district of Kremenchuk)
- Kremenchuk – Kremenchuk (the administrative center of the governorate)
- Poltava – Poltava
- Novo-Senzhar – Novo-Senzhar (today Novi Sanzhary)
- Added territories after partitioning
- Kherson – Kherson (newly built settlement with fortress and the main Black Sea Admiralty)
- Novopavlovsk – Novopavlovsk (today Voznesensk)
- Ingulsk – Ingulsk (today village of Inhulo-Kamianka in Kropyvnytskyi Raion)
- Slavensk – Slavensk (today Nikopol)
- Kisikermen – Kisikermen (today Beryslav)
- Saksagan – Saksagan (today village of Saksahan in Kamianske Raion, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast)
Second establishment
In December 1796, Paul I reestablished the Novorossiya Governorate, mostly with land from the former Yekaterinoslav Viceroyalty. In 1802, this province was divided into the Nikolayev Governorate (known as the Kherson Governorate from 1803), the Yekaterinoslav Governorate, and the Taurida Oblast.
A Decree of 12 December 1796 set up a serf system on the territory of South Ukraine and Caucasus by attaching peasants to the land.
Novorossiysk-Bessarabia General Governorate
The Novorossiysk and Bessarabian General Governorate was formed on May 23, 1822, with the center in Odessa. It consisted of the Kherson, Yekaterinoslav and Tauride provinces, as well as the Odessa, Taganrog, Feodosiya and Kerch-Yenikalsky city administrations. Nevertheless, Duke Richelieu, who was appointed to this position in 1805, was still considered the governor of the Novorossiysk Territory.
The Governate was abolished in 1874.
Subdivisions
- Bakhmut Province (1764–1775) transferred to the Azov Governorate
- The city of provincial significance Kremenchuk
- Yekaterinoslav Province
- Elizabethgrad Province [uk]
Governors

General Governors
- 1764–65 Aleksei Melgunov [ru]
- 1765–66 Yakov Brandt [ru]
- 1766–74 Fyodor Voeikov [ru]
- 1774–91 Grigory Potemkin
- 1791–96 Platon Zubov
- 1796–97 Nikolai Berdiayev [ru]
- 1805–14 Duc de Richelieu
- 1815–22 Alexandre de Langeron
- 1822–23 Ivan Inzov
- 1822–54 Mikhail Vorontsov
- 1830–32 Friedrich von der Pahlen
- 1854–55 Nicholas Annenkov
- 1855–64 Alexander Stroganov
- 1864–73 Paul Demetrius von Kotzebue
Viceroys (namestnik)
- 1779–83 Timofei Tutolmin [ru]
- 1783–88 Ivan Sinelnikov [ru]
- 1788–94 Vasiliy Kakhovsky
- 1794–96 Iosif Khorvat
- 1797–1800 Ivan Seletsky
- 1800–01 Ivan Nikolayev
- 1801–02 Mikhail Miklashevsky
See also
References
- ^ New Russia Governorate at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- ^ 1769–70 Pikers Uprising. Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia.
External links
- Yekaterinoslav Guberniya – Historical coat of arms
- New Russia Governorate at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- Katerinoslav Governorate – Article in the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
| Historical regions in present-day Ukraine | |
|---|---|
| Geographical regions | |
| States and tribes of classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages | |
| Principalities of Kyivan Rus' | |
| Post-Mongol era regions | |
| Polish–Lithuanian regions | |
| Ottoman provinces | |
| Cossack regions | |
| Imperial Russian regions |
|
| Austro-Hungarian provinces | |
| 20th-century regions and states |
|
| Ethno-Ukrainian regions abroad | |
| Subdivisions of the Russian Empire | |
|---|---|
| Governorates (List) |
|
| Oblasts | |
| Oblasts of Stepnoy Krai | |
| Oblasts of Turkestan Krai | |
| Caucasus Viceroyalty | |
| Baltic Governorates³ | |
| Governorates of Finland | |
| Governorates of Poland | |
| Governorates of Galicia and Bukovina | |
| Dependencies | |
| ¹ Italics indicates renamed or abolished governorates, oblasts, etc on 1 January 1914. ² An asterisk (+) indicates governorates formed or created with renaming after 1 January 1914. ³ Ostsee or Baltic general-governorship was abolished in 1876. | |
N 48.43649 E 35.04639 48°24′N 35°00′E / 48.4°N 35.0°E / 48.4; 35.0Categories:
- States and territories established in 1764
- States and territories disestablished in 1802
- Novorossiya Governorate
- Novorossiya
- Governorates of the Russian Empire
- Governorates of Ukraine
- 1764 establishments in the Russian Empire
- 1802 disestablishments in the Russian Empire
- 18th century in the Zaporozhian Host
- Zaporizhian Sich