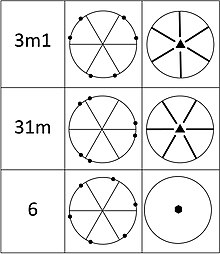
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann (who introduced it in 1928) and the French mineralogist Charles-Victor Mauguin (who modified it in 1931). This notation is sometimes called international notation, because it was adopted as standard by the International Tables For Crystallography since their first edition in 1935.
The Hermann–Mauguin notation, compared with the Schoenflies notation, is preferred in crystallography because it can easily be used to include translational symmetry elements, and it specifies the directions of the symmetry axes.
Point groups
Rotation axes are denoted by a number n – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, ... (angle of rotation φ = 360°/n). For improper rotations, Hermann–Mauguin symbols show rotoinversion axes, unlike Schoenflies and Shubnikov notations, that shows rotation-reflection axes. The rotoinversion axes are represented by the corresponding number with a macron, n – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, ... . 2 is equivalent to a mirror plane and usually notated as m. The direction of the mirror plane is defined as the direction perpendicular to it (the direction of the 2 axis).
Hermann–Mauguin symbols show non-equivalent axes and planes in a symmetrical fashion. The direction of a symmetry element corresponds to its position in the Hermann–Mauguin symbol. If a rotation axis n and a mirror plane m have the same direction, then they are denoted as a fraction n/m or n /m.
If two or more axes have the same direction, the axis with higher symmetry is shown. Higher symmetry means that the axis generates a pattern with more points. For example, rotation axes 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 generate 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, 8-point patterns, respectively. Improper rotation axes 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 generate 6-, 4-, 10-, 6-, 14-, 8-point patterns, respectively. If a rotation and a rotoinversion axis generate the same number of points, the rotation axis should be chosen. For example, the 3/m combination is equivalent to 6. Since 6 generates 6 points, and 3 generates only 3, 6 should be written instead of 3/m (not 6/m, because 6 already contains the mirror plane m). Analogously, in the case when both 3 and 3 axes are present, 3 should be written. However we write 4/m, not 4/m, because both 4 and 4 generate four points. In the case of the 6/m combination, where 2, 3, 6, 3, and 6 axes are present, axes 3, 6, and 6 all generate 6-point patterns, as we can see on the figure in the right, but the latter should be used because it is a rotation axis – the symbol will be 6/m.
Finally, the Hermann–Mauguin symbol depends on the type of the group.
Groups without higher-order axes (axes of order three or more)
These groups may contain only two-fold axes, mirror planes, and/or an inversion center. These are the crystallographic point groups 1 and 1 (triclinic crystal system), 2, m, and 2/m (monoclinic), and 222, 2/m2/m2/m, and mm2 (orthorhombic). (The short form of 2/m2/m2/m is mmm.) If the symbol contains three positions, then they denote symmetry elements in the x, y, z direction, respectively.
Groups with one higher-order axis
- First position – primary direction – z direction, assigned to the higher-order axis.
- Second position – symmetrically equivalent secondary directions, which are perpendicular to the z-axis. These can be 2, m, or 2/m.
- Third position – symmetrically equivalent tertiary directions, passing between secondary directions. These can be 2, m, or 2/m.
These are the crystallographic groups 3, 32, 3m, 3, and 32/m (trigonal crystal system), 4, 422, 4mm, 4, 42m, 4/m, and 4/m2/m2/m (tetragonal), and 6, 622, 6mm, 6, 6m2, 6/m, and 6/m2/m2/m (hexagonal). Analogously, symbols of non-crystallographic groups (with axes of order 5, 7, 8, 9, ...) can be constructed. These groups can be arranged in the following table
| Schoenflies | H–M symbol | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ... | ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cn | n | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ... | ∞ |
| Cnv | nm | 3m | 5m | 7m | 9m | 11m | ∞m | ||||||
| nmm | 4mm | 6mm | 8mm | 10mm | 12mm | ||||||||
| S2n | n | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | ∞/m | ||||||
| Sn | 4 | 8 | 12 | ||||||||||
| Cn/2h | 6 | 10 | |||||||||||
| Cnh | n/m | 4/m | 6/m | 8/m | 10/m | 12/m | |||||||
| Dn | n2 | 32 | 52 | 72 | 92 | (11)2 | ∞2 | ||||||
| n22 | 422 | 622 | 822 | (10)22 | (12)22 | ||||||||
| Dnd | n2/m | 32/m | 52/m | 72/m | 92/m | (11)2/m | ∞/mm | ||||||
| Dn/2d | n2m = nm2 | 42m | 82m | (12)2m | |||||||||
| Dn/2h | 6m2 | (10)m2 | |||||||||||
| Dnh | n/m2/m2/m | 4/m2/m2/m | 6/m2/m2/m | 8/m2/m2/m | 10/m2/m2/m | 12/m2/m2/m |
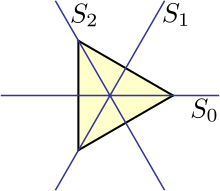
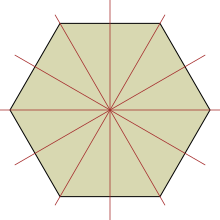
It can be noticed that in groups with odd-order axes n and n the third position in symbol is always absent, because all n directions, perpendicular to higher-order axis, are symmetrically equivalent. For example, in the picture of a triangle all three mirror planes (S0, S1, S2) are equivalent – all of them pass through one vertex and the center of the opposite side. For even-order axes n and n there are n/2 secondary directions and n/2 tertiary directions. For example, in the picture of a regular hexagon one can distinguish two sets of mirror planes – three planes go through two opposite vertexes, and three other planes go through the centers of opposite sides. In this case any of two sets can be chosen as secondary directions, the rest set will be tertiary directions. Hence groups 42m, 62m, 82m, ... can be written as 4m2, 6m2, 8m2, ... . For symbols of point groups this order usually doesn't matter; however, it will be important for Hermann–Mauguin symbols of corresponding space groups, where secondary directions are directions of symmetry elements along unit cell translations b and c, while the tertiary directions correspond to the direction between unit cell translations b and c. For example, symbols P6m2 and P62m denote two different space groups. This also applies to symbols of space groups with odd-order axes 3 and 3. The perpendicular symmetry elements can go along unit cell translations b and c or between them. Space groups P321 and P312 are examples of the former and the latter cases, respectively.
The symbol of point group 32/m may be confusing; the corresponding Schoenflies symbol is D3d, which means that the group consists of 3-fold axis, three perpendicular 2-fold axes, and 3 vertical diagonal planes passing between these 2-fold axes, so it seems that the group can be denoted as 32m or 3m2. However, one should remember that, unlike Schoenflies notation, the direction of a plane in a Hermann–Mauguin symbol is defined as the direction perpendicular to the plane, and in the D3d group all mirror planes are perpendicular to 2-fold axes, so they should be written in the same position as 2/m. Second, these 2/m complexes generate an inversion center, which combining with the 3-fold rotation axis generates a 3 rotoinversion axis.
Groups with n = ∞ are called limit groups or Curie groups.
Groups with several higher-order axes
These are the crystallographic groups of a cubic crystal system: 23, 432, 2/m3, 43m, and 4/m32/m. All of them contain four diagonal 3-fold axes. These axes are arranged as 3-fold axes in a cube, directed along its four space diagonals (the cube has 4/m32/m symmetry). These symbols are constructed the following way:
- First position – symmetrically equivalent directions of the coordinate axes x, y, and z. They are equivalent due to the presence of diagonal 3-fold axes.
- Second position – diagonal 3 or 3 axes.
- Third position – diagonal directions between any two of the three coordinate axes x, y, and z. These can be 2, m, or 2/m.
All Hermann–Mauguin symbols presented above are called full symbols. For many groups they can be simplified by omitting n-fold rotation axes in n/m positions. This can be done if the rotation axis can be unambiguously obtained from the combination of symmetry elements presented in the symbol. For example, the short symbol for 2/m2/m2/m is mmm, for 4/m2/m2/m is 4/mmm, and for 4/m32/m is m3m. In groups containing one higher-order axis, this higher-order axis cannot be omitted. For example, symbols 4/m2/m2/m and 6/m2/m2/m can be simplified to 4/mmm (or 4/mmm) and 6/mmm (or 6/mmm), but not to mmm; the short symbol for 32/m is 3m. The full and short symbols for all 32 crystallographic point groups are given in crystallographic point groups page.
Besides five cubic groups, there are two more non-crystallographic icosahedral groups (I and Ih in Schoenflies notation) and two limit groups (K and Kh in Schoenflies notation). The Hermann–Mauguin symbols were not designed for non-crystallographic groups, so their symbols are rather nominal and based on similarity to symbols of the crystallographic groups of a cubic crystal system. Group I can be denoted as 235, 25, 532, 53. The possible short symbols for Ih are m35, m5, m5m, 53m. The possible symbols for limit group K are ∞∞ or 2∞, and for Kh are ∞/m∞ or m∞ or ∞∞m.
Plane groups
Plane groups can be depicted using the Hermann–Mauguin system. The first letter is either lowercase p or c to represent primitive or centered unit cells. The next number is the rotational symmetry, as given above. The presence of mirror planes are denoted m, while glide reflections are only denoted g. Screw axes do not exist in two-dimensional spaces.
Space groups
Further information: List of space groups § listThe symbol of a space group is defined by combining the uppercase letter describing the lattice type with symbols specifying the symmetry elements. The symmetry elements are ordered the same way as in the symbol of corresponding point group (the group that is obtained if one removes all translational components from the space group). The symbols for symmetry elements are more diverse, because in addition to rotations axes and mirror planes, space group may contain more complex symmetry elements – screw axes (combination of rotation and translation) and glide planes (combination of mirror reflection and translation). As a result, many different space groups can correspond to the same point group. For example, choosing different lattice types and glide planes one can generate 28 different space groups from point group mmm, e.g. Pmmm, Pnnn, Pccm, Pban, Cmcm, Ibam, Fmmm, Fddd, and so on. In some cases, a space group is generated when translations are simply added to a point group. In other cases there is no point around which the point group applies. The notation is somewhat ambiguous, without a table giving more information. For example, space groups I23 and I213 (nos. 197 and 199) both contain two-fold rotational axes as well as two-fold screw axes. In the first, the two-fold axes intersect the three-fold axes, whereas in the second they do not.
Lattice types
These are the Bravais lattice types in three dimensions:
- P – Primitive
- I – Body centered (from the German "Innenzentriert")
- F – Face centered (from the German "Flächenzentriert")
- A – Base centered on A faces only
- B – Base centered on B faces only
- C – Base centered on C faces only
- R – Rhombohedral

|

|

|

|

|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primitive, P | Base centered, C | Face centered, F | Body centered, I | Rhombohedral in hexagonal setting, R |
Screw axes
The screw axis is noted by a number, n, where the angle of rotation is 360°/n. The degree of translation is then added as a subscript showing how far along the axis the translation is, as a portion of the parallel lattice vector. For example, 21 is a 180° (twofold) rotation followed by a translation of 1/2 of the lattice vector. 31 is a 120° (threefold) rotation followed by a translation of 1/3 of the lattice vector.
The possible screw axes are: 21, 31, 32, 41, 42, 43, 61, 62, 63, 64, and 65. There are 4 enantiomorphic pairs of axes: (31 – 32), (41 – 43), (61 – 65), and (62 – 64). This enantiomorphism results in 11 pairs of enantiomorphic space groups, namely
| Crystal system | Tetragonal | Trigonal | Hexagonal | Cubic | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First group Group Number |
P41 76 |
P4122 91 |
P41212 92 |
P31 144 |
P3112 152 |
P3121 151 |
P61 169 |
P62 171 |
P6122 178 |
P6222 180 |
P4132 213 |
| Second group Group Number |
P43 78 |
P4322 95 |
P43212 96 |
P32 145 |
P3212 154 |
P3221 153 |
P65 170 |
P64 172 |
P6522 179 |
P6422 181 |
P4332 212 |
Glide planes
The orientation of a glide plane is given by the position of the symbol in the Hermann–Mauguin designation, just as with mirror planes. They are noted by a, b, or c depending on which axis (direction) the glide is along. There is also the n glide, which is a glide along the half of a diagonal of a face, and the d glide, which is along a quarter of either a face or space diagonal of the unit cell. The d glide is often called the diamond glide plane as it features in the diamond structure. In cases where there are two possibilities among a, b, and c (such as a or b), the letter e is used. (In these cases, centering entails that both glides occur.) To summarize:
- a, b, or c glide translation along half the lattice vector of this face.
- n glide translation along half a face diagonal.
- d glide planes with translation along a quarter of a face diagonal or of a space diagonal.
- e two glides with the same glide plane and translation along two (different) half-lattice vectors.
References
- Sands, Donald E. (1993). "Crystal Systems and Geometry". Introduction to Crystallography. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications, Inc. p. 54. ISBN 0-486-67839-3.
- Hahn, Th.; Klapper, H. "Chapter 10.1. Crystallographic and noncrystallographic point groups". International Tables for Crystallography. Retrieved December 5, 2022.
- "(International Tables) Abstract". it.iucr.org. Archived from the original on 4 July 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- Zorky, Petr. "Семейства точечных групп". www.chem.msu.su. Archived from the original on 2012-04-15.
- Vainshtein, Boris K., Modern Crystallography 1: Fundamentals of Crystals. Symmetry, and Methods of Structural Crystallography, Springer. 1994, page 93.
- Point groups in three dimensions
- Shubnikov, A.V., Belov, N.V. & others, Colored Symmetry, Oxford: Pergamon Press. 1964, page 70.
- Donald Sands (1975). "Crystal Systems and Geometry". Introduction to Crystallography (PDF). Courier Corporation. p. 72. ISBN 0-486-67839-3.
- Compare the symmetry operations for space group 197 with those for space group 199.
External links
- Decoding the Hermann-Maguin Notation – An introduction into the Hermann-Maguin notation for beginners.
| Crystallography | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key concepts |
|  | ||||||||||
| Characterisation | ||||||||||||
| Algorithms | ||||||||||||
| Software | ||||||||||||
| Databases | ||||||||||||
| Journals | ||||||||||||
| Awards | ||||||||||||
| Organisation |
| |||||||||||