Health in Iraq refers to the country's public healthcare system and the overall health of the country's population. Iraq belongs to WHO health region Eastern Mediterranean and classified as upper middle according to World Bank income classification 2013. The state of health in Iraq has fluctuated during its turbulent recent history and specially during the last 4 decade. The country had one of the highest medical standards in the region during the period of 1980s and up until 1991, the annual total health budget was about $450 million in average. The 1991 Gulf War incurred Iraq's major infrastructures a huge damage. This includes health care system, sanitation, transport, water and electricity supplies. UN economic sanctions aggravated the process of deterioration. The annual total health budget for the country, a decade after the sanctions had fallen to $22 million which is barely 5% of what it was in 1980s. During its last decade, the regime of Saddam Hussein cut public health funding by 90 percent, contributing to a substantial deterioration in health care. During that period, maternal mortality increased nearly threefold, and the salaries of medical personnel decreased drastically. Medical facilities, which in 1980 were among the best in the Middle East, deteriorated. Conditions were especially serious in the south, where malnutrition and water-borne diseases became common in the 1990s. Health indicators deteriorated during the 1990s. In the late 1990s, Iraq's infant mortality rates more than doubled. Because treatment and diagnosis of cancer and diabetes decreased in the 1990s, complications and deaths resulting from those diseases increased drastically in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
The Iraq War in 2003 destroyed an estimated 12% of hospitals and Iraq's two main public health laboratories. The collapse of sanitation infrastructure in 2003 led to an increased incidence of cholera, dysentery, and typhoid fever. Malnutrition and childhood diseases, which had increased significantly in the late 1990s, continued to spread. In 2005 the incidence of typhoid, cholera, malaria, and tuberculosis was higher in Iraq than in comparable countries. In 2006 some 73 percent of cases of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) in Iraq originated with blood transfusions and 16 percent from sexual transmission. The AIDS Research Centre in Baghdad, where most cases have been diagnosed, provides free treatment, and testing is mandatory for foreigners entering Iraq. Between October 2005 and January 2006, some 26 new cases were identified, bringing the official total to 261 since 1986. The 2003 invasion and its aftermath of considerable insecurity and instability combined with battered infrastructure make that the progress in health indicator had not been that good as they should be compared with many countries in the region. In 2010, the life expectancy 58 years, down from 65 years 30 years prior. By 2011, tuberculosis had reached levels 6 times higher than in Syria and 30 times higher than in Jordan. Between 2000 and 2011, the child immunization rates dropped by 20%. Iraq have not achieved its Millennium development goals number 4 and 5 by 2015.
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that Iraq is fulfilling 75.0% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. When looking at the right to health with respect to children, Iraq achieves 93.1% of what is expected based on its current income. In regards to the right to health amongst the adult population, the country achieves only 86.4% of what is expected based on the nation's level of income. Iraq falls into the "very bad" category when evaluating the right to reproductive health because the nation is fulfilling only 45.4% of what the nation is expected to achieve based on the resources (income) it has available.
History
Before Gulf War
Iraq used the income from oil resources, which accounted for the major part of its GDP to build a modern and solid health care system. Health services were free and available for the majority of the population. The country had a good sanitary infrastructure and safe water supply to almost all people in urban areas and the majority in rural areas.
| Indicator | 1960 | 1970 | 1990 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude death rate | 17.5 | 11.7 | 6.9 |
| Crude birth rate | 42.1 | 45.6 | 37.7 |
| Life expectancy at birth | 48.0 | 58.2 | 68.3 |
| Infant mortality rates | 131.7 | 81.5 | 42.3 |
| Under-five mortality rate | 195.7 | 115 | 54.1 |
After Gulf War
After the Gulf War, the country had been almost left in ruins and most of its infrastructure broke down. The majority of the population had no safe water supply and electricity. The sanitary infrastructure was damaged. Distribution of food and medical supplies was prevented because transport capabilities were reduced to critical levels. This resulted in both malnutrition an outbreak of many infectious diseases like cholera, malaria, typhoid and gastroenteritis. Iraqis who died because of health effects of the Gulf War have been estimated at 100 000. After the war in 1991 and in eight months from January to August, infant and child mortality had increased by threefold. The UN economic sanctions against Iraq declared in August 1990 after invasion of Kuwait made it difficult for Iraq to rebuild and rehabilitate the country's infrastructure. The economic sanctions had also resulted in a shortage in medical supplies and equipment such that health services to population were badly affected including the immunization services which put millions of children at risk of infection. In the 1990s many Iraqis, therefore, died from diseases which were treatable or preventable before the sanctions and the war. Iraq's Government agreed to UN terms in 1996 and this resulted in oil for food programme which allowed the country to import humanitarian supplies and equipment. The programme resulted in a modest recover in water and electricity supply, sanitation and health services.
| Indicator | 1991 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude death rate | 6.6 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.1 |
| Crude birth rate | 37.5 | 35.6 | 35.5 | 34.2 |
| Life expectancy at birth | 66.8 | 69.1 | 68.4 | 69.5 |
| Infant mortality rates | 41.6 | 35.2 | 30.0 | 26.5 |
| Under-five mortality rate | 53 | 44.7 | 36.6 | 32 |
| Maternal mortality ratio | -- | 290 | 60 | 35 |
Health statistics and health indicators
Basic statistics
| Indicators | Statistics | year |
|---|---|---|
| population (thousands) | 41190 | 2021 |
| Population aged under 15 (%) | 40 | 2013 |
| Population aged over 60 (%) | 5 | 2013 |
| Median age | 20 | 2013 |
| Population living in urban areas (%) | 69 | 2013 |
| Total fertility rate (per woman) | 4.0 | 2013 |
| Number of live births (thousands) | 1052.2 | 2013 |
| Number of deaths (thousands) | 162.7 | 2013 |
| Birth registration coverage (%) | 99 | 2011 |
| Cause-of-death registration coverage (%) | 65 | 2008 |
| Gross national income per capita (PPP int $) | 15220 | 2013 |
| WHO region | Eastern Mediterranean | 2013 |
| World Bank income classification | Upper middle | 2013 |
Life expectancy at birth
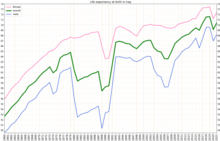
In 2015 the life expectancy at birth, total was 69.59 years. Iraq was ranked as country number 125 in the world which is lower than all the neighbor countries. For females it was 71.85 years ranked as country number 127 higher than that for males which was 67,44 years but ranked as country number 115. Life expectancy at birth for both sexes decreased by one year over the period of 2000–2012; the WHO region average increased by 3 year(s)in the same period. In 2012, healthy life expectancy at birth in both sexes was 9 years lower than overall life expectancy at birth. This lost healthy life expectancy represents 9 equivalent years of full health lost throw years lived with morbidity and disability.
Millennium Development Goals (Md Gs)
| Indicators | Baseline statistics at 1990 for the first 2 and at 2000 for the last 3 | Latest statistics 2013 for the first 3 & 2012 for the last 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) | 53 | 34 |
| Maternal mortality ratio(per 100 000 live births | 110 | 67 |
| Deaths due to HIV/AIDS (per 100 000 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Deaths due to malaria (per 100 000 population | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Deaths due to tuberculosis among HIV-negative people (per 100 000) | 3.8 | 2.3 |
In the 1960s, Iraq was "one of the best countries in which to be a child" according to the UNICEF statistics. At the same time in 1981, Iraq had the 2nd lowest Infant Mortality Rate worldwide. In the late 1990s, Iraq's under-five mortality rates have dropped by approximately 50% - from 44.8 deaths per 1000 live births in 2000 to 34.4 in 2012.
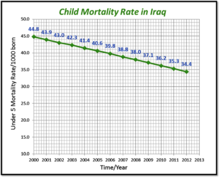
Thus mortality rates are gradually decreasing since the late 1990s. On the other hand, if Iraq had progressed at the same average rate as the other countries, by 2011. Iraq would have achieved the 2⁄3 reduction in child mortality rate in the period between 1990 and 2015, which is the target of Millennium Development Goal number four. Iraq's health services are struggling to regain lost momentum after decades of war, sanctions, and occupation. Although there is renewed progress across all sectors of child development, substantial work is still needed to achieve national targets and global goals.
according to WHO, Iraq: Quality of Care 2018 Analysis, infection measure control increased 14-15%
See also
References
- Aziz, C. Struggling to rebuild Iraq's Health-care System. The Lancet 2003;362(9392):1288-1289.
- ^ Iraq country profile Archived 2010-12-04 at the Wayback Machine. Library of Congress Federal Research Division (August 2006). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Webster, Paul C (2011). Iraq's Health System yet to Heal from Ravages of War. The Lancet 378(9794): 863-866
- "Human Rights Measurement Initiative – The first global initiative to track the human rights performance of countries". humanrightsmeasurement.org. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- ^ "Iraq - HRMI Rights Tracker". rightstracker.org. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- Frankish, Helen. Health of the Iraqi people hangs in the balance; The Lancent 2003 Feb 22; 361
- ^ "Mortality rate, under-5 (Per 1,000 live births) - Country Comparison".
- Frankish, Helen. Health of the Iraqi people hangs in the balance. The Lancet 2003;361
- "المؤشرات الديمغرافية والسكانية - الجهاز المركزي للاحصاء". cosit.gov.iq. Retrieved 2021-05-08.
- "Iraq Country Overview | World Health Organization".
- "Under-fine Mortaliy Rates". gapminder.org.
- "Under-five Mortality Rates". UNICEF.
- Alsamarai, Abdulghani Alsamarai; Bashir, Alaa (2018-04-20). "Quality improvement of health care in Iraq". International Journal of Medical Sciences. 1 (1): 1–5. doi:10.32441/ijms.v1i1.29. ISSN 2522-7386.
| Health in Asia | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other territories | |