| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2,2,4,4,6,6-Hexafluoro-1,3,5,2λ,4λ,6λ-triazatriphosphinine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.019 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | (NPF2)3 |
| Molar mass | 248.933 g·mol |
| Appearance | White powder or lumps |
| Melting point | 27 °C (81 °F; 300 K) |
| Boiling point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) |
| Solubility in water | decomposes |
| Solubility | Toluene |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | Planar P3N3 ring |
| Dipole moment | 0 D |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338+P310, P363, P405, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Hexafluorophosphazene is an inorganic compound with the formula (NPF2)3. It takes the form of a white powder or lumps. It is sensitive to moisture and heat.
Structure
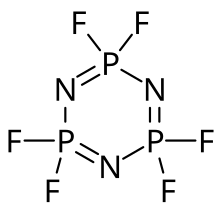
The molecule has a cyclic, unsaturated P3N3 backbone consisting of alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, and can be viewed as a trimer of the hypothetical compound N≡PF2 (phosphazyl difluoride). Its classification as a phosphazene highlights its relationship to benzene. Hexafluorophosphazene has a hexagonal P3N3 ring with six equivalent P–N bonds. Each phosphorus atom is additionally bonded to two fluorine atoms.
The molecule possesses D3h symmetry, and each phosphorus center is tetrahedral.
The P3N3 ring in hexachlorophosphazene deviates from planarity and is slightly ruffled (see chair conformation). By contrast, the P3N3 ring in hexafluorophosphazene is completely planar.
References
- ^ "Hexafluorocyclotriphosphazene 15599-91-4 | TCI AMERICA". www.tcichemicals.com.
- Allen, Christopher W. (1991-03-01). "Regio- and stereochemical control in substitution reactions of cyclophosphazenes". Chemical Reviews. 91 (2): 119–135. doi:10.1021/cr00002a002. ISSN 0009-2665.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |