| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Prince-Bishopric of HildesheimHochstift Hildesheim (German) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1235–1803 | |||||||||
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||
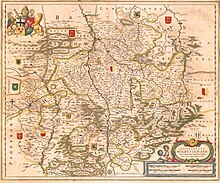
 The Hildesheim Abbey in 1789 within the boundaries that had been constant since 1643 The Hildesheim Abbey in 1789 within the boundaries that had been constant since 1643 | |||||||||
| Status | Prince-Bishopric | ||||||||
| Capital | Hildesheim | ||||||||
| Common languages | Eastphalian | ||||||||
| Government | Elective principality | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
| • Bishopric founded | 815 | ||||||||
| • Gained Imperial immediacy | 1235 | ||||||||
| • Joined Lower Saxon Circle | 1500 | ||||||||
| • Hildesheim Diocesan Feud | 1519–23 | ||||||||
| • Mediatised to Prussia | 1803 | ||||||||
| • To Hanover | 1815 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||

The Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim (German: Hochstift Hildesheim, Fürstbistum Hildesheim, Bistum Hildesheim) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the Middle Ages until its dissolution in 1803. The Prince-Bishopric must not be confused with the Diocese of Hildesheim, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the spiritual authority of an ordinary bishop.
History
After the Duchy of Saxony had been conquered by the Frankish Kingdom, Emperor Charlemagne in 800 founded a missionary diocese at his eastphalian court in Elze (Aula Caesaris), about 19 km (12 mi) west of Hildesheim. His son King Louis the Pious established the bishopric at Hildesheim in 815, dedicated to Virgin Mary.
According to legend delivered by the Brothers Grimm, the king was hunting in the wintery woods of Elze, when he realized that he had lost his pendant with the relic of Blessed Virgin Mary. Distraught he sent out his attendance who finally discovered a flowering rose bush with the relic in his branches, which it would not let go. Louis had a chapel built by the side of the rose, the later St. Mary's Cathedral. A rosa canina is still growing at the apse of the cathedral, called the Thousand-year Rose (Tausendjähriger Rosenstock).
His son King Louis the German appointed the former archbishop of Rheims, Ebbo, as bishop between 845 and 847. Ebbo's successor Altfrid began the construction of the cathedral. A close adviser to Louis the German, Altfrid founded Essen Abbey.

During the reign of the Saxon Ottonian dynasty Hildesheim, together with the neighbouring bishoprics of Halberstadt and Magdeburg, became the central ecclesiastical territory of the Holy Roman Empire. Bishop Bernward (993-1022) built up the cathedral district with a strong twelve-towered wall, built the Michaeliskirche, and commissioned bronze doors for the cathedral. During the tenure of his successor Gotthard (1022-1038), the cathedral school became a center for learning. Bernward and Gotthard added much to the architectonic and cultural tradition of the present-day World Heritage Site.

At the Reichstag at Mainz of August 15, 1235 Bishop Conrad II reached the official acknowledgement of Hildesheim as a Prince-bishopric (Hochstift) by Emperor Frederick II. As a negative consequence of this success, Hildesheim began to interfere with the neighbouring Welf duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg, culminating in the Hildesheim Diocesan Feud 1519-1523 with the warlike Brunswick duke Henry the Younger that led to a significant loss of territories.
In the 16th century, most of the diocese as well as most of the state of Hildesheim switched to Protestantism. But the Bishopric managed not only to retain its independence from the surrounding Protestant states of Brunswick-Lüneburg, but also to retrieve large parts of the lost estates, mostly because its bishops were members of the powerful House of Wittelsbach from 1573 until 1761, the last Clemens August of Bavaria from 1723, who also was archbishop and prince-elector of Cologne, prince-bishop of Münster, Osnabrück and Paderborn as well as Grand Master of the Teutonic Order.
-
Hildesheim Cathedral
-
 Former palace of the prince-bishops, today general vicariate of the diocese
Former palace of the prince-bishops, today general vicariate of the diocese
-
 Marienburg Castle (Hildesheim)
Marienburg Castle (Hildesheim)
-
 Steuerwald Castle
Steuerwald Castle
In the course of the German Mediatisation of 1803, Hildesheim was secularised and its territory was annexed to Prussia. Four years later, however, Prussia lost it to the newly established Kingdom of Westphalia. The Congress of Vienna of 1815 gave the territory of the former prince-bishopric to the Kingdom of Hanover.

Subdivisions (Ämter)
|
|
|
Wittelsbach prince-bishops
- Ernest (1573-1612)
- Ferdinand (1612-1650) (Administrator)
- Maximilian Henry (1650-1688)
- Joseph Clemens (1702-1723)
- Clemens August (1723-1761)
See also
Notes
- The map shows the diocese in its borders before the diocese feud. During the restitution in 1643, the offices of Aerzen, Grohnde, Coldingen-Lauenberg, Lutter am Barenberge, Westerhof and Lindau – all shown as Hildesheim in the map – remained with the principalities of Calenberg and Braunschweig-Wolfenbüttel. For more information, see Hildesheimer Stiftsfehde [de].
References
- "The History of the Hildesheim Cathedral", Mariendom Hildesheim
- Ott, Michael. "Ebbo." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 5. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1909
- Schäfer, Joachim. "Altfrid von Hildesheim", Ökumenischen Heiligenlexikon
- Giese, Martina. "Die Texfassungen der Lebensbeschreibung Bischof Bernwards von Hildesheim", Monumenta Germaniae Historica, Studien und Texte, 40. Hannover: Hahnsche Buchhandlung, 2006. p. xxviii. ISBN 3-7752-5700-4
External links
| Ecclesiastical |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Secular | ||
| Cities | ||
| until 1648. until 1701. from 1648. until 1731. until 1705. until 1596. from 1708. until 1773. until 1640. until 1695. from 1701. until 1734.
Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon Circles est. 1512: Austrian, Burgundian, Upper Saxon, Electoral Rhenish · Unencircled territories | ||
Categories: