 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | September 28, 1986 |
| Dissipated | October 2, 1986 |
| Category 2 hurricane | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 100 mph (155 km/h) |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 10 |
| Damage | $350 million |
| Areas affected | Mexico, inland United States |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1986 Pacific hurricane season | |
Hurricane Paine was the sixteenth tropical storm and eighth hurricane of the fairly active 1986 Pacific hurricane season; moisture from the system contributed to one of the most significant flooding events in Oklahoma history. Paine formed on September 28 off the southeast coast of Mexico. It moved around a ridge, later turning to the north and brushing the Baja California Peninsula. By that time, Paine had attained peak winds of 100 mph (160 km/h), but it weakened slightly before hitting the Mexican state of Sonora. The remnant moisture combined with a cold front to produce heavy rainfall in the South Central United States.
In Mexico, Paine produced rainfall along much of the coastline, with maxima in inland Oaxaca, Jalisco, and Sonora where it moved ashore. Prior to the arrival of the remnants of Paine in the United States, there was an extended period of heavy rainfall, which caused at least 10 deaths, forced thousands of people from their homes, and resulted in heavy flooding damage. The moisture from Paine produced the highest daily rainfall for any station in Oklahoma. Severe river flooding occurred along the Osage and Arkansas Rivers. The overall flooding event caused $350 million in damage, of which half came from crop losses.
Meteorological history

Map key Saffir–Simpson scale Tropical depression (≤38 mph, ≤62 km/h)
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown Storm type
 Tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone  Subtropical cyclone
Subtropical cyclone  Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression
Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression The origins of Hurricane Paine were from a system that entered the eastern Pacific Ocean through Central America on September 27. By the next day, it organized into Tropical Depression Twenty-Three while located about 185 miles (298 km) southwest of the coast of Guatemala. With a high pressure system to its north, the depression moved generally westward at first, although an approaching upper-level trough influenced a more northerly track. The depression slowly organized while paralleling the Mexican coastline, and it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Paine on September 30, while the storm was about 350 miles (560 km) west-southwest of Acapulco.
Tropical Storm Paine quickly intensified after it was first upgraded to a tropical storm. Late on September 30, a NOAA reconnaissance plane flew into the storm, one of two cyclones in the basin that warranted aircraft data, the other being Hurricane Newton. The plane observed sustained winds of 82 mph (132 km/h), and as a result, Paine was upgraded to hurricane status. As it neared the Baja California Peninsula, the hurricane turned more northward, and late on October 1 reached peak winds of 100 mph (160 km/h), while located just offshore of the southern tip of Baja California. Hurricane Paine did not intensify further due to the presence of mid-level wind shear, as well as insufficient moisture in the air; nevertheless, it was located over an area of 82.9 °F (28.3 °C) water temperatures. The outer eyewall moved across Cabo San Lucas, and the resultant land interaction was believed to have slightly weakened the inner core of the hurricane.

After reaching its peak intensity, the hurricane turned north-northeastward, making landfall near San José, Sonora with winds of 90 mph (140 km/h). Paine rapidly dissipated over land, although the remnants continued northeastward across Mexico into Texas and the south-central United States. Moisture from the system combined with an advancing cold front, producing heavy rainfall over Oklahoma and southeastern Kansas.
Impact
As a tropical cyclone, Paine brought rainfall to most of Mexico, including heavier amounts along the coastline and interior northern Oaxaca. The highest total in the country was 12.01 inches (305 mm) in Apazulco, Jalisco. Light precipitation fell in the southern portion of the Baja California Peninsula, and where Paine moved ashore, upwards of 7 inches (180 mm) fell across its path. In the area around where it made landfall, strong winds knocked down trees and caused disruptions to city services.
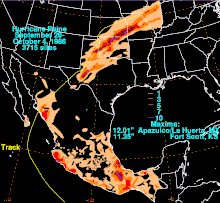
In the south-central United States, the remnants of Paine dropped moderate to heavy rainfall in regions that already received above normal rainfall. Isolated locations in Texas, northern Oklahoma, and southeastern Kansas received over 10 inches (250 mm) of precipitation, and the highest total in the United States was 11.35 inches (288 mm) at Fort Scott, Kansas. Moderate rainfall extended northeastward through Missouri and Illinois. In Barnsdall, Oklahoma, a station recorded 10.42 inches (265 mm) on September 29, which was the highest daily precipitation for any station in the state. In combination with previous storms, some locations received over 20 inches of rainfall in an 8-day period, which produced severe river flooding along the Osage and Arkansas Rivers. The flooding resulted in record discharge rates along many streams and creeks, while many reservoirs were nearly filled to capacity. The Mississippi River in St. Louis reached the fifth highest flood stage on record.
Prior to its arrival, flooding across the central United States killed six people, forced thousands of people from their homes, and left at least $76 million in damage (1986 USD). Additional flooding from Paine exacerbated the situation; the flooding affected 52 of the 77 counties in Oklahoma, which resulted in a total of $350 million in damage, half of which from agriculture. The remnants of Paine brought about the end of the extended period of rainfall, which overall had forced 55,000 people from their homes, including 1,200 in East Saint Louis, Illinois where a floodgate broke. It was described as one of the worst floods in Oklahoma history.
See also
References
- ^ E.B. Gunther; R.L. Cross; Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center (1987). "Eastern North Pacific Tropical Cyclones of 1986". Monthly Weather Review. 115 (10). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 2507. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<2507:ENPTCO>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1520-0493. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- Sean K. Daida and Gary M. Barnes, University of Hawaii (2002). "Hurricane Paine (1986) Grazes the High Terrain of the Baja California Peninsula". Weather and Forecasting. 18 (5). American Meteorological Society: 981. doi:10.1175/1520-0434(2003)018<0981:HPGTHT>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1520-0434. S2CID 122628497. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ C.A. Perry; B.N. Aldridge; H.C. Ross (2000). "Summary of Significant Floods in the United States, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands, 1986". United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on 2006-09-25. Retrieved 2010-02-08.
- ^ David M. Roth (2007). "Hurricane Paine — September 26-October 4, 1986". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- Staff Writer (1986-10-03). "Hurricane Paine Sweeps Into Mexico". Akron Beach Journal. Retrieved 2010-10-14.
- ^ Howard Johnson (2003). "Oklahoma Weather History, Part 9 (September)". Oklahoma Climatological Survey. Archived from the original on April 16, 2009. Retrieved 2010-02-10.
- Milwaukee Sentinel (1986). "Hurricane Paine Drenches Oklahoma". Retrieved 2010-02-10.
- Oklahoma Mesonet. "Weather Time Line: Oklahoma 1900-2000" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-08-21. Retrieved 2010-02-11.
- "Flooding victims left homeless". Associated Press. 1986. Retrieved 2010-02-11.
- United Press International (1986). "Floods Hit Tulsa Area". Retrieved 2010-02-11.
| Tropical cyclones of the 1986 Pacific hurricane season | ||
|---|---|---|
 | 1Agatha TDTwo-E TSBlas 1Celia TSDarby 4Estelle TDSeven-E TDEight-E 1Frank TDTen-E TDOne-C TSGeorgette TDTwelve-E TSHoward TSIsis 4Javier TSKay TDSeventeen-E TSLester TSMadeline 1Newton TDTwenty-One-E 1Orlene 2Paine 4Roslyn TDTwenty-Five-E | |
Categories: