| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Diode modelling" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In electronics, diode modelling refers to the mathematical models used to approximate the actual behaviour of real diodes to enable calculations and circuit analysis. A diode's I-V curve is nonlinear.
A very accurate, but complicated, physical model composes the I-V curve from three exponentials with a slightly different steepness (i.e. ideality factor), which correspond to different recombination mechanisms in the device; at very large and very tiny currents the curve can be continued by linear segments (i.e. resistive behaviour).
In a relatively good approximation a diode is modelled by the single-exponential Shockley diode law. This nonlinearity still complicates calculations in circuits involving diodes so even simpler models are often used.
This article discusses the modelling of p-n junction diodes, but the techniques may be generalized to other solid state diodes.
Large-signal modelling
Shockley diode model
The Shockley diode equation relates the diode current of a p-n junction diode to the diode voltage . This relationship is the diode I-V characteristic:
- ,
where is the saturation current or scale current of the diode (the magnitude of the current that flows for negative in excess of a few , typically 10 A). The scale current is proportional to the cross-sectional area of the diode. Continuing with the symbols: is the thermal voltage (, about 26 mV at normal temperatures), and is known as the diode ideality factor (for silicon diodes is approximately 1 to 2).
When the formula can be simplified to:
- .
This expression is, however, only an approximation of a more complex I-V characteristic. Its applicability is particularly limited in case of ultra-shallow junctions, for which better analytical models exist.
Diode-resistor circuit example
To illustrate the complications in using this law, consider the problem of finding the voltage across the diode in Figure 1.

Because the current flowing through the diode is the same as the current throughout the entire circuit, we can lay down another equation. By Kirchhoff's laws, the current flowing in the circuit is
- .
These two equations determine the diode current and the diode voltage. To solve these two equations, we could substitute the current from the second equation into the first equation, and then try to rearrange the resulting equation to get in terms of . A difficulty with this method is that the diode law is nonlinear. Nonetheless, a formula expressing directly in terms of without involving can be obtained using the Lambert W-function, which is the inverse function of , that is, . This solution is discussed next.
Explicit solution
An explicit expression for the diode current can be obtained in terms of the Lambert W-function (also called the Omega function). A guide to these manipulations follows. A new variable is introduced as
- .
Following the substitutions :
and :
rearrangement of the diode law in terms of w becomes:
- ,
which using the Lambert -function becomes
- .
The final explicit solution being
- .
With the approximations (valid for the most common values of the parameters) and , this solution becomes
- .
Once the current is determined, the diode voltage can be found using either of the other equations.
For large x, can be approximated by . For common physical parameters and resistances, will be on the order of 10.
Iterative solution
The diode voltage can be found in terms of for any particular set of values by an iterative method using a calculator or computer. The diode law is rearranged by dividing by , and adding 1. The diode law becomes
- .
By taking natural logarithms of both sides the exponential is removed, and the equation becomes
- .
For any , this equation determines . However, also must satisfy the Kirchhoff's law equation, given above. This expression is substituted for to obtain
- ,
or
- .
The voltage of the source is a known given value, but is on both sides of the equation, which forces an iterative solution: a starting value for is guessed and put into the right side of the equation. Carrying out the various operations on the right side, we come up with a new value for . This new value now is substituted on the right side, and so forth. If this iteration converges the values of become closer and closer together as the process continues, and we can stop iteration when the accuracy is sufficient. Once is found, can be found from the Kirchhoff's law equation.
Sometimes an iterative procedure depends critically on the first guess. In this example, almost any first guess will do, say . Sometimes an iterative procedure does not converge at all: in this problem an iteration based on the exponential function does not converge, and that is why the equations were rearranged to use a logarithm. Finding a convergent iterative formulation is an art, and every problem is different.
Graphical solution

Graphical analysis is a simple way to derive a numerical solution to the transcendental equations describing the diode. As with most graphical methods, it has the advantage of easy visualization. By plotting the I-V curves, it is possible to obtain an approximate solution to any arbitrary degree of accuracy. This process is the graphical equivalent of the two previous approaches, which are more amenable to computer implementation.
This method plots the two current-voltage equations on a graph and the point of intersection of the two curves satisfies both equations, giving the value of the current flowing through the circuit and the voltage across the diode. The figure illustrates such method.
Piecewise linear model

In practice, the graphical method is complicated and impractical for complex circuits. Another method of modelling a diode is called piecewise linear (PWL) modelling. In mathematics, this means taking a function and breaking it down into several linear segments. This method is used to approximate the diode characteristic curve as a series of linear segments. The real diode is modelled as 3 components in series: an ideal diode, a voltage source and a resistor.
The figure shows a real diode I-V curve being approximated by a two-segment piecewise linear model. Typically the sloped line segment would be chosen tangent to the diode curve at the Q-point. Then the slope of this line is given by the reciprocal of the small-signal resistance of the diode at the Q-point.
Mathematically idealized diode

Firstly, consider a mathematically idealized diode. In such an ideal diode, if the diode is reverse biased, the current flowing through it is zero. This ideal diode starts conducting at 0 V and for any positive voltage an infinite current flows and the diode acts like a short circuit. The I-V characteristics of an ideal diode are shown below:
Ideal diode in series with voltage source
Now consider the case when we add a voltage source in series with the diode in the form shown below:
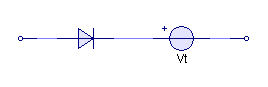
When forward biased, the ideal diode is simply a short circuit and when reverse biased, an open circuit.
If the anode of the diode is connected to 0 V, the voltage at the cathode will be at Vt and so the potential at the cathode will be greater than the potential at the anode and the diode will be reverse biased. In order to get the diode to conduct, the voltage at the anode will need to be taken to Vt. This circuit approximates the cut-in voltage present in real diodes. The combined I-V characteristic of this circuit is shown below:

The Shockley diode model can be used to predict the approximate value of .
Using and :
Typical values of the saturation current at room temperature are:
- for silicon diodes;
- for germanium diodes.
As the variation of goes with the logarithm of the ratio , its value varies very little for a big variation of the ratio. The use of base 10 logarithms makes it easier to think in orders of magnitude.
For a current of 1.0 mA:
- for silicon diodes (9 orders of magnitude);
- for germanium diodes (3 orders of magnitude).
For a current of 100 mA:
- for silicon diodes (11 orders of magnitude);
- for germanium diodes (5 orders of magnitude).
Values of 0.6 or 0.7 volts are commonly used for silicon diodes.
Diode with voltage source and current-limiting resistor
The last thing needed is a resistor to limit the current, as shown below:

The I-V characteristic of the final circuit looks like this:

The real diode now can be replaced with the combined ideal diode, voltage source and resistor and the circuit then is modelled using just linear elements. If the sloped-line segment is tangent to the real diode curve at the Q-point, this approximate circuit has the same small-signal circuit at the Q-point as the real diode.
Dual PWL-diodes or 3-Line PWL model

When more accuracy is desired in modelling the diode's turn-on characteristic, the model can be enhanced by doubling-up the standard PWL-model. This model uses two piecewise-linear diodes in parallel, as a way to model a single diode more accurately.


Small-signal modelling
Resistance
Using the Shockley equation, the small-signal diode resistance of the diode can be derived about some operating point (Q-point) where the DC bias current is and the Q-point applied voltage is . To begin, the diode small-signal conductance is found, that is, the change in current in the diode caused by a small change in voltage across the diode, divided by this voltage change, namely:
- .
The latter approximation assumes that the bias current is large enough so that the factor of 1 in the parentheses of the Shockley diode equation can be ignored. This approximation is accurate even at rather small voltages, because the thermal voltage at 300 K, so tends to be large, meaning that the exponential is very large.
Noting that the small-signal resistance is the reciprocal of the small-signal conductance just found, the diode resistance is independent of the ac current, but depends on the dc current, and is given as
- .
Capacitance
The charge in the diode carrying current is known to be
- ,
where is the forward transit time of charge carriers: The first term in the charge is the charge in transit across the diode when the current flows. The second term is the charge stored in the junction itself when it is viewed as a simple capacitor; that is, as a pair of electrodes with opposite charges on them. It is the charge stored on the diode by virtue of simply having a voltage across it, regardless of any current it conducts.
In a similar fashion as before, the diode capacitance is the change in diode charge with diode voltage:
- ,
where is the junction capacitance and the first term is called the diffusion capacitance, because it is related to the current diffusing through the junction.
Variation of forward voltage with temperature
The Shockley diode equation has an exponential of , which would lead one to expect that the forward-voltage increases with temperature. In fact, this is generally not the case: as temperature rises, the saturation current rises, and this effect dominates. So as the diode becomes hotter, the forward-voltage (for a given current) decreases.
Here is some detailed experimental data, which shows this for a 1N4005 silicon diode. In fact, some silicon diodes are used as temperature sensors; for example, the CY7 series from OMEGA has a forward voltage of 1.02 V in liquid nitrogen (77 K), 0.54 V at room temperature, and 0.29 V at 100 °C.
In addition, there is a small change of the material parameter bandgap with temperature. For LEDs, this bandgap change also shifts their colour: they move towards the blue end of the spectrum when cooled.
Since the diode forward-voltage drops as its temperature rises, this can lead to thermal runaway due to current hogging when paralleled in bipolar-transistor circuits (since the base-emitter junction of a BJT acts as a diode), where a reduction in the base-emitter forward voltage leads to an increase in collector power-dissipation, which in turn reduces the required base-emitter forward voltage even further.
See also
References
- B. Van Zeghbroeck (2011). "P-n junctions: I-V characteristics of real p-n diodes". Archived from the original on 2021-06-15. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
- . Popadic, Miloš; Lorito, Gianpaolo; Nanver, Lis K. (2009). "Analytical Model of I – V Characteristics of Arbitrarily Shallow p-n Junctions". IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices. 56 (1): 116–125. Bibcode:2009ITED...56..116P. doi:10.1109/TED.2008.2009028.
- Banwell, T.C.; Jayakumar, A. (2000). "Exact analytical solution for current flow through diode with series resistance". Electronics Letters. 36 (4): 291. Bibcode:2000ElL....36..291B. doi:10.1049/el:20000301.
- . A.S. Sedra and K.C. Smith (2004). Microelectronic Circuits (Fifth ed.). New York: Oxford. Example 3.4 p. 154. ISBN 978-0-19-514251-8.
- Kal, Santiram (2004). "Chapter 2". Basic Electronics: Devices, Circuits and IT Fundamentals (Section 2.5: Circuit Model of a P-N Junction Diode ed.). Prentice-Hall of India Pvt.Ltd. ISBN 978-81-203-1952-3.
- ^ R.C. Jaeger and T.N. Blalock (2004). Microelectronic Circuit Design (second ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-232099-2.
- "1n400x diode family forward voltage". www.cliftonlaboratories.com. Clifton Laboratories. Apr 14, 2009. Archived from the original on September 6, 2013. Retrieved 2019-02-10.
- http://www.omega.com/Temperature/pdf/CY7.pdf datasheet
 of a
of a  . This relationship is the diode I-V characteristic:
. This relationship is the diode I-V characteristic:
 ,
, is the saturation current or scale current of the diode (the magnitude of the current that flows for negative
is the saturation current or scale current of the diode (the magnitude of the current that flows for negative  , typically 10 A). The scale current is proportional to the cross-sectional area of the diode. Continuing with the symbols:
, typically 10 A). The scale current is proportional to the cross-sectional area of the diode. Continuing with the symbols:  , about 26 mV at normal temperatures), and
, about 26 mV at normal temperatures), and  is known as the diode ideality factor (for silicon diodes
is known as the diode ideality factor (for silicon diodes  the formula can be simplified to:
the formula can be simplified to:
 .
. .
. . A difficulty with this method is that the diode law is nonlinear. Nonetheless, a formula expressing
. A difficulty with this method is that the diode law is nonlinear. Nonetheless, a formula expressing  , that is,
, that is,  . This solution is discussed next.
. This solution is discussed next.
 is introduced as
is introduced as
 .
. :
:

 :
:

 ,
, -function becomes
-function becomes
 .
. .
. and
and  , this solution becomes
, this solution becomes
 .
. can be approximated by
can be approximated by  . For common physical parameters and resistances,
. For common physical parameters and resistances,  will be on the order of 10.
will be on the order of 10.
 .
. .
. ,
, .
. . Sometimes an iterative procedure does not converge at all: in this problem an iteration based on the exponential function does not converge, and that is why the equations were rearranged to use a logarithm. Finding a convergent iterative formulation is an art, and every problem is different.
. Sometimes an iterative procedure does not converge at all: in this problem an iteration based on the exponential function does not converge, and that is why the equations were rearranged to use a logarithm. Finding a convergent iterative formulation is an art, and every problem is different.
 .
.

 and
and  :
:

 for silicon diodes;
for silicon diodes; for germanium diodes.
for germanium diodes. , its value varies very little for a big variation of the ratio. The use of base 10 logarithms makes it easier to
think in orders of magnitude.
, its value varies very little for a big variation of the ratio. The use of base 10 logarithms makes it easier to
think in orders of magnitude.
 for silicon diodes (9 orders of magnitude);
for silicon diodes (9 orders of magnitude); for germanium diodes (3 orders of magnitude).
for germanium diodes (3 orders of magnitude). for silicon diodes (11 orders of magnitude);
for silicon diodes (11 orders of magnitude); for germanium diodes (5 orders of magnitude).
for germanium diodes (5 orders of magnitude). of the diode can be derived about some operating point (
of the diode can be derived about some operating point ( and the Q-point applied voltage is
and the Q-point applied voltage is  . To begin, the diode small-signal conductance
. To begin, the diode small-signal conductance  is found, that is, the change in current in the diode caused by a small change in voltage across the diode, divided by this voltage change, namely:
is found, that is, the change in current in the diode caused by a small change in voltage across the diode, divided by this voltage change, namely:
 .
. at 300 K, so
at 300 K, so  tends to be large, meaning that the exponential is very large.
tends to be large, meaning that the exponential is very large.
 .
. ,
, is the forward transit time of charge carriers: The first term in the charge is the charge in transit across the diode when the current
is the forward transit time of charge carriers: The first term in the charge is the charge in transit across the diode when the current  ,
, is the junction capacitance and the first term is called the
is the junction capacitance and the first term is called the  , which would lead one to expect that the forward-voltage increases with temperature. In fact, this is generally not the case: as temperature rises, the saturation current
, which would lead one to expect that the forward-voltage increases with temperature. In fact, this is generally not the case: as temperature rises, the saturation current