| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Indirect finance" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2021) |
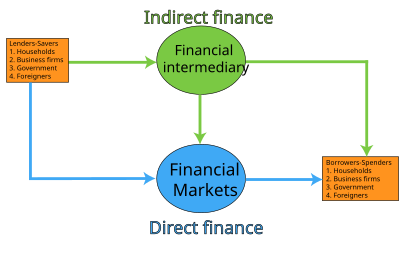
Indirect finance is where borrowers borrow funds from the financial market through indirect means, such as through a financial intermediary. This is different from direct financing where there is a direct connection to the financial markets as indicated by the borrower issuing securities directly on the market. Common methods for indirect financing include a financial auction (where price of the security is bid upon) or an initial public offering (where the security is sold for a set initial price). By allowing borrowers to obtain financing through a third party, indirect financing can improve risk management and liquidity.
Indirect financing (government)
This is where the government gives privilege, in the form of reduced tax burdens, as a means of supporting a particular interest rather than collecting and redistributing tax revenue (which would be considered as a direct financing method by the government). For example, a reduced tax burden on financiers provides focused monetary benefits and helps to effectively lower bond prices (provided that tax savings has a tangible effect on bond pricing and that the aforementioned would pass these tax savings to their respective clientele). This could be applied in a number of applications from infrastructural investment to education or military spending.
References
- Mishkin, Frederic (2012). The Economics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets (Global, Tenth ed.). Pearson Education Limited. p. 68. ISBN 978-0273765738.